Lecture - MSK (Axilla, Arm and Elbow) Flashcards
(21 cards)
- What is the axilla?
- What’s on the four walls and the base? What about apex?
3.


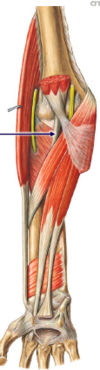
After the pectoralis minor and major, what vein do you get? Label this


This is the lateral aspect of axilla - label the three stickies

Pec major, minor and axillary vein respectively
Looking at this, what can you tell me about the axillary artery?
Axillary artery runs through the axillary region and it is a direct continuation of subclavian artery and becomes brachial artery after it leaves the axillary region. If you bleed from this, you can die
Brachial vessels:
- Subclavian artery brahches off what on the left and right side?
- What does the subclavian artery become once it passes the first rib?
- When does the axillary artery become the brachial artery?
- Upper limb is drained by what?

What three parts does the axillary artery have?

What is the name and contents of each space?

Sticky #1: Quad because 4 borders =
Through this opening, the anxillary nerve and post circum art comes through
If break humerus at cullum then this artery can become disrupted so loss of sensory and motor function
Axillary nerve provides motor fibres to delatoid muscle and can identify this
Sticky #2: This art perforates through
Sticky #3: All extensors of arm (radial nerve) and profunda = deep
Brachial plexus - nerve supply of the upper limb (provides nerve supply to entire upper extremity
- Roots formed by what rami of spinal nerves? What are the spinal nerves in brachial plexus?
- What do the roots combine to make?
- What do the trunks divide into? (3)
- What do the divisions dividde and combine into?
- What do the cords divide and combine into? (5 of them)
- Even at level of trunks, or divisions or cords, you already have certain nerves branching off to supply what?
- What is the axillary artery like?
- Supply motor and sensory in shoulder region
- Like a guiding rod for the brachial plexus to develop





Elbow joint:
- What sort of joint is it? What are the two joints in the elbow joint?
- What two movements can those two joints do?
- What three joints does the joint capsule contain?

Elbow joint ctnd:
- Little finger - is it medial or lateral? What about thumb? So if you follow them up the the arm, you’ll find the medial and lateral side
- Label this
- Where is the annular ligament?
- Where does the coronoid process sit?

- Neck - pink circle
- In the fossa. The trochlea fruther extends into the coronoid fossa

Label this
What can you say about the radial collateral and annular ligament?

Radial collateral:
Lateral collateral ligameets
And ulanr collateral ligamnets - offer more alog with capsule for stabllility
Annular ligament:
Wraps around neck of radius

What is the heuter trinagle and what does it look like in elbow flexion and extension?
Triangle becomes flat at extension of elbow

What are the 5 flexors and 1 extensor at the elbow joint?
- Biceps is a key supinator too
- brachillis is under biceps - these two are at arm
- the bottom three flexors are in the forearm so weak flexing motion but they exist

Label


Label

Triceps brachii
Anoceneus also provides some extension but rather weak at elbow

Lable this
- So the two are strongly connected by the annular ligament but also the dorsal and radial radioulnar ligament
- what is the oblique cord?
- what’s the interosseous membrane?

Oblique cord:
A dense reinforcment of interorsseous - dense fibre running opposite way of key fibres of interosseous membrane
Usually fibres run from radius distally and medially towards ulanr - the oblique cord is running opposite way
Prevents overpronation or oversupination of radio-ulnar joint so it’s a bit of a stabaliser
Interosseous membrane:
of forearm
Also have this in leg -
In both regions, reinforces stability bw both bones and helps agaisnt dislocation
Also imp for musclualr attachments - some muscles originate from this memebrane

What are the movements you can do at radioulnar jonts?
That red line is the axis that runs connects the head of the radius to the head of the ulna and it runs through interosseous membrane

Label these supinators and pronators of the radio ulnar joint #1:

Supinator is actually a muslce - it wraps around the radius

Last one - label this strongest supinator in the elbow joint