Vertebral Column Flashcards
(26 cards)
the vertebral column is composed of a series of articulating vertebrae
there are ___ cerbical, ____ thoracic, _____ lumba and ____ sacrum vertebrae
the vertebral column has 4 natural curvatures: the cervical vertebrae is curved rearwards into a ____, and the thoracic is curved forward into a ___. the lumbosacral region is also ___ and the sacrum bone itself is curved forward into a ____
the vertebral column is composed of a series of articulating vertebrae
there are 7 cerbical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumba and 1 sacrum vertebrae, but the sacrum itself is composed of the fusion of 5 vertebrae
the vertebral column has 4 natural curvatures: the cervical vertebrae is curved rearwards into a lordosis, and the thoracic is curved forward into a kyphosis. the lumbosacral region is also lordosis and the sacrum bone itself is curved forward into a kyphosis

function of the vertebal column is to provide an axis of support for the body and to house and protect the spinal cord.
there are 7 cervical vertebrae but 8 cerival spinal nerves.
the C1 spinal nerve exits ___ the C__ vertebra
the C8 spinal nerve exits ___ the C___ vertebra.
there are two enlargements of the spinal cord; a ___ enlargemnet and a ___ enlargement, serving the lower extremity. the spinal cord proper ends at the L1 level at the __ __.
below this level, the anterior and posterior nerve roots continue to the segment they exit, this forms a structure called the ___ __ with the nerve roots flowing within the ___ in the ____ sac.
among the nerve roots is a non nerve continuation of the ___ mater called the ___ ___
the C1 spinal nerve exits above the C1 vertebra
the C8 spinal nerve exits below the C7 vertebra
the termination of the spinal cord in the lumbar region is known as the conus medullaris.
there are two enlargements of the spinal cord; a CERVICAL enlargemnet and a LUMBAR enlargement, serving the lower extremity. the spinal cord proper ends at the L1 level at the conus medullaris.
below this level, the anterior and posterior nerve roots continue to the segment they exit, this forms a structure called the caudate equina with the nerve roots flowing within the CSF in the dural sac.
among the nerve roots is a non nerve continuation o fthe pIA mater called the termianl phylum

what layer makes up the terminal phylum of nerve roots
pia mater
the sacrum is formed from the fusion of adjacent vertebrae. note the ____ ___ ____ that will allow the exit of the posterior rami (the holes)

the sacrum is formed from the fusion of adjacent vertebrae. note the posterior sacral foramina that will allow the exit of the posterior rami (the holes)
nerve roots come out of the sacral canal and the posterior ramus exits aronund the foramen. the anterior ramus enters through the anterior sacral foamen.

spinal cord and it’s meningeal layers


the CNS is covered by three membranes: externally is a tough fibrous membranes called the ___ mater. underneath is the ____ mater, a delicate membrane. CSF circulates underneath the ___ mater and the CSF is slightly pressurized to push the ___ up against the ___. forming the external surface of the cord is the __ mater.
The pia mater can be seen in the ___ ____. the surface of the cord comes out in a little membrane that attaches to the arachnoid to the dura and basically pins the spinal cord within the dura.
the CNS is covered by three membranes: externally is a tough fibrous membranes called the DURA mater. underneath is the arachnoid mater, a delicate membrane. CSF circulates underneath the arachnoid mater and the CSF is slightly pressurized to push the arachnoid up against the dura. forming the external surface is the pia mater.
The pia mater can be seen in the denticulate ligaments. the surface of the cord comes out in a little membrane that attaches to the arachnoid to the dura and basically pins the spinal cord within the dura.

denticulate ligaments are transverse extensions of the pia mater, which attach to the dura mater and suspend the spinal cord within the dural sac.
the filum terminale, a thin cord of pia mater, extends from the conus medullaris to the apex of the dural sac. there ir is surrounded by spinal dura mater and extends to the end of the vertebral column, where it anchors both membranes to the coccyx.
3 spaces separate the layers of the meninges
- the ___ spaces lies between the bony wall fo the vertebral canal and the dura mater. it contains fat and the ____ ___ plexus.
2.
- the ____ space is between the dura and arachnoid layers, containing ___ fluid
- the subarachnoid space contains ___. the ____ ___ is an enlargement in this space within the dural sac inferior to the __ __.
the epidural spaces lies between the bony wall fo the vertebral canal and the dura mater. it contains fat and the vertebral venous plexus.
- the subdural space is between the dura and arachnoid layers, containing lubricating fluid
- the subarachnoid space contains CSF. the lumbar cistern is an enlargement in this space within the dural sac inferior to the conus medullaris.


the ___ ____ runs vertically within the lower lumbar vertebrae. there’s no nerve cord in the lumbar vertebrae, just the roots.
the caudate equina runs vertically within the lower lumbar vertebrae. there’s no nerve cord in the lumbar vertebrae, just the roots.
image 2.25

note: the caudate equina runs vertically in order to find the intervertebral formaina in which they exit from. it’s imporant because it changes the relationship between the lumbar nerve roots to the discs that are adjacent to them

the caudate equina runs vertically in order to find the intervertebral formaina in which they exit from. it’s imporant because it changes the relationship between the lumbar nerve roots to the discs that are adjacent to them
outline the components of the vertebrae. which ones are missing certain elements

with the exception of atlas (C1) and axis (c2), all vertebrae consist of the same structural elements

components of the vertebra:
the large supporting portion of the vetebra is the ___/___ ____
on the posteior aspect of the centrum is two pedacles; the base of the arch one covering the spinal cord. the pedacle is continued as the ___,a sheet of bone that joins the ___ of the other side to complete the arch.
attached to the arch are __ and __ __processes.
there are also __ and __ processes laterally and posteriorly. these are bondy projections that provide anchor points for __ and _–. the transver process indicates the division between __ (served by __ ramus innervation) and ___ musculature (served by __ ramus innervation)
the large supporting portion of the vetebra is the centrum/verterbral body
on the posteior aspect of the centrum is two pedacles; the base of the arch one covering the spinal cord. the pedacle is continued as the lamina,a sheet of bone that joins the lamina of the other side to complete the arch.
attached to the arch are superior and inferior articular processes.
there are also transverse and spinous processes laterally and posteriorly. these are bony projections that provide anchor points for muscles and ligaments. the transver process indicates the division between hypoaxial (served by anterior ramus innervation) and epaxial musculature (served by posterior ramus innervation)
the ___ ___ facet , the cartilaginous joint surface sits on the __ ___ process. the arch forms a canal referred to as the __ __, which houses the spinal cord.
the segmental nerves exit bilaterally through the __ __ formed by the __ __ notch and the inferior vertebral notch of the adjacent vertebra.
NOTE: pars interarticularis is indicated in this picture. clinically relevant site– it is the bone connecting the superior and inferior processes within the vertebra, so is a poriton of the lamina and because the superior and inferior processes are bearing a fair amount of load, that piece of bone in between them can fracture.

the lumbar vertebrae
the official name of the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae are costal processes. not really used tho.
the superior articualr facet , the cartilaginous joint surface sits on the superior articular process. the arch forms a canal referred to as the vertebral formamen, which houses the spinal cord.
the segmental nerves exit bilaterally through the intervertebral foramen formed by the superior vertebral notch and the inferior vertebral notch of the adjacent vertebra.
NOTE: pars interarticularis is indicated in this picture. clinically relevant site– it is the bone connecting the superior and inferior processes within the vertebra, so is a poriton of the lamina and because the superior and inferior processes are bearing a fair amount of load, that piece of bone in between them can fracture.


fracture of the pars interarticularis causes spondylolysis, which is a fracture of the PI. if there is displacement of the PI, then it is considered spondylolisthesis.

name characteristics that define the cervical vertebrae from L, T or S regions
( you need to know C1 and C2 individualluy)
- cervial vertebrae tend to be smaller cause they don’t support the smae load as a lumbar vertebrae for example.
- the transverse processes of Cercial vertebrae are small, and within them there is the transverse forament which is not present in either the lumbar or thoracic vertebrae.
- the vertebral artery and vein run throguh the transverse forament. the vertebral foramen is also large relateive to the vertebrae body
- is also has a bifid spinous process and the superior articular process is large and flat.

name characteristics that define a typical thoracic vertebrae
- heart shaped centrum.
- transverse processes have the facets for the attachments for the ribs.

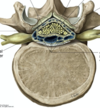
what level of vertebrae? label


what level of vertebrae? label

thoracic vertebrae have a heart shaped centrum and the transverse process has facets for rib attachments

many ribs articulate with adjacent vertebrae.
the head of the rib connect with an inferior ___ facet on the ___ vertebrae, and the __ __ facet on the inferior __.
there’s alsmost always a connection to the transverse process as well. the connection of the ribs to the __ __ is complex and allows elevation and depression of the ribs as an important compoent of the breathing cycle.
the __ and __ verebral __ combine to form the __ foramen, in whcih the segmental nerves exit the __ foramen.
many ribs articulate with adjacent vertebrae.
the head of the rib connect with an inferior costal facet on the superior vertebrae, and the superior costal facet on the inferior centrum.
there’s alsmost always a connection to the transverse process as well. the connection of the ribs to the thoracic vertebrae is complex and allows elevation and depression of the ribs as an important compoent of the breathing cycle.
the inferior and superior verebral notches combine to form the intervertebral foramen, in whcih the segmental nerves exit the vertebral foramen.



the costal facets of the thoracic vertebrae are on the ___ ___
on the transverse processes

this is the complex attachment of the rib where we can see the head of the rib attaching to the centrum, then another component of the rib attaching to the transverse process of the vertebrae.




