CV/Resp Part 5 Flashcards
(36 cards)
major functions of the pleural cavity and serous fluid
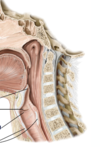
The pleural cavity is a potential space between the parietal and visceral pleura. It contains a small volume of serous fluid, which has two major functions. It lubricates the surfaces of the pleurae, allowing them to slide over each other. The serous fluid also produces a surface tension, pulling the parietal and visceral pleura together. This ensures that when the thorax expands, the lung also expands, filling with air.
The parietal pleura is sensitive to pressure, pain, and temperature. It produces a well localised pain, and is innervated by the __ and __ nerves.
• Referred pain from __ stimulation will occur in the dermatomes of the thoracic wall.
• Referred pain from __ nerve stimulation will occur in the dermatomes of C__-__, on the
shoulder and at the base of the neck.
The blood supply is derived from the __ arteries.
The parietal pleura is sensitive to pressure, pain, and temperature. It produces a well localised pain, and is innervated by the phrenic and intercostal nerves.
• Referred pain from intercostal stimulation will occur in the dermatomes of the thoracic wall.
• Referred pain from phrenic nerve stimulation will occur in the dermatomes of C3-5, on the
shoulder and at the base of the neck.
The blood supply is derived from the intercostal arteries.
note: the parietal pleura is innervated by the intercostal and the phrenic nerve, but the visceral pleura is not sensitive to pain, temperature or tough. its sensory fibers only detect __
stretch.
The bronchial tree is a series of passages that supplies air to the alveoli of the lungs. It begins with the __, which divides into a left and right __.
Each bronchus enters the root of the lung, passing through the hilum. Inside the lung, they divide to form __ __ – one supplying each lobe.
Each lobar bronchus then further divides into several tertiary __ bronchi. Each segmental bronchus provides air to a __ __ – these are the functional units of the lungs. The segmental bronchi give rise to many __ bronchioles, which eventually lead into __ bronchioles. Each __ bronchiole gives off __ bronchioles, which feature thin walled outpocketings that extend from their lumens. These are the __
The bronchial tree is a series of passages that supplies air to the alveoli of the lungs. It begins with the trachea, which divides into a left and right bronchus.
Each bronchus enters the root of the lung, passing through the hilum. Inside the lung, they divide to form lobar bronchi – one supplying each lobe.
Each lobar bronchus then further divides into several tertiary segmental bronchi. Each segmental bronchus provides air to a bronchopulmonary segment – these are the functional units of the lungs. The segmental bronchi give rise to many conducting bronchioles, which eventually lead into terminal bronchioles. Each terminal bronchiole gives off respiratory bronchioles, which feature thin walled outpocketings that extend from their lumens. These are the alveoli
At the bifurcation of the primary bronchi, a ridge of cartilage called the __ runs anteroposteriorly between the openings of the two bronchi.
This is the most sensitive area of the trachea for triggering the __ reflex, and can be seen on bronchoscopy.
At the bifurcation of the primary bronchi, a ridge of cartilage called the carina runs anteroposteriorly between the openings of the two bronchi. This is the most sensitive area of the trachea for triggering the cough reflex, and can be seen on bronchoscopy.
The trachea receives sensory innervation from the __ __ nerve. Arterial supply comes from the tra__cheal branches of the __ __ artery, while venous drainage is via the __, __ and __ __ veins.
The trachea receives sensory innervation from the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Arterial supply comes from the tracheal branches of the inferior thyroid artery, while venous drainage is via the brachiocephalic, azygos and accessory hemiazygos veins.
The peanut is likely to be lodged in the __ main bronchus.
The peanut is likely to be lodged in the right main bronchus. The right main bronchus is more vertically oriented and wider than the left main bronchus, and thus foreign bodies are more likely to lodge on the right side.

The bronchi derive innervation from pulmonary branches of the __ nerve (CN X). Blood supply to the bronchi is from branches of the __ __, while venous drainage is into the __ __.
The bronchi derive innervation from pulmonary branches of the vagus nerve (CN X). Blood supply to the bronchi is from branches of the bronchial arteries, while venous drainage is into the bronchial veins.
The __ sinuses are air-filled extensions of the nasal cavity. There are four paired sinuses –
The paranasal sinuses are air-filled extensions of the nasal cavity. There are four paired sinuses – named according to the bone in which they are located – maxillary, frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid. Each sinus is lined by a ciliated pseudostratified epithelium, interspersed with mucus-secreting goblet cells. The sinuses increase surface area for exchange of heat and moisture

label the paranasal sinuses



The __ nerve supplies both the maxillary sinus and maxillary teeth, and so inflammation of that sinus can present with toothache.
The maxillary nerve supplies both the maxillary sinus and maxillary teeth, and so inflammation of that sinus can present with toothache.
Projecting out of the lateral walls of the nasal cavity are curved shelves of bone. They are called conchae (or turbinates). The are three conchae – inferior, middle and superior. They project into the nasal cavity, creating four pathways for the air to flow. These pathways are called meatuses:
Inferior meatus – between the inferior concha and floor of the nasal cavity.
• Middle meatus – between the inferior and middle concha.
• Superior meatus – between the middle and superior concha.
• Spheno-ethmoidal recess – superiorly and posteriorly to the superior concha.
outline the concha and the meatus


outline the concha and the meatus


Auditory (Eustachian) tube – opens into the nasopharynx at the level of the __ __.
It allows the middle ear to equalise with the atmospheric air pressure.
Auditory (Eustachian) tube – opens into the nasopharynx at the level of the inferior meatus.
It allows the middle ear to equalise with the atmospheric air pressure.


voice box
larynx
4 functions of larynx
couh reflex
protection of lower resp tract via epiglottis
- glottis voice
- pronation
There are nine cartilages located within the larynx;__ unpaired, and __ paired. They form the laryngeal __, which provides rigidity and stability.
There are nine cartilages located within the larynx; three unpaired, and six paired. They form the laryngeal skeleton, which provides rigidity and stability.
3 unpaired cartilagres of the larynx
The three unpaired cartilages are the epiglottis, thyroid and cricoid cartilages.
The __ cartilage is a large, prominent structure which is easily visible in adult males. It is composed of two sheets (laminae), which join anteriorly to form the laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple).
The thyroid cartilage is a large, prominent structure which is easily visible in adult males. It is composed of two sheets (laminae), which join anteriorly to form the laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple).
The __ cartilage is a complete ring of hyaline cartilage, consisting of a broad sheet posteriorly and a much narrower arch anteriorly (said to resemble a signet ring in shape). The cartilage completely encircles the airway
The cricoid cartilage is a complete ring of hyaline cartilage, consisting of a broad sheet posteriorly and a much narrower arch anteriorly (said to resemble a signet ring in shape). The cartilage completely encircles the airway.
-The cricoid is the only complete circle of cartilage in the larynx or trachea. This is of clinical relevance during emergency intubation – as pressure can be applied to the cricoid to occlude the oesophagus, and thus prevent regurgitation of gastric contents (known as cricoid pressure or Sellick’s manoeuvre).
The __ folds (false vocal cords) lie superiorly to the true vocal cords. They consist of the vestibular ligament (free lower edge of the quadrangular membrane) covered by a mucous membrane, and are pink in colour. They are fixed folds, which act to provide protection to the larynx.
The vestibular folds (false vocal cords) lie superiorly to the true vocal cords. They consist of the vestibular ligament (free lower edge of the quadrangular membrane) covered by a mucous membrane, and are pink in colour. They are fixed folds, which act to provide protection to the larynx.