Upper Extremity: Rotator Cuff Flashcards
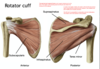
rotator cuff muscles
The rotator cuff muscles include the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
Rotator cuff tears can occur at any age but are most common in the older patient and usually involve the ___ tendon. Degenerative changes and chronic inflammation from repetitive use (baseball pitchers are a good example) can cause the tendon to fray and rupture.
Rotator cuff tears can occur at any age but are most common in the older patient and usually involve the supraspinatus tendon. Degenerative changes and chronic inflammation from repetitive use (baseball pitchers are a good example) can cause the tendon to fray and rupture.
supportive muscles to the rotator cuff
- biceps brachii. The tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii passes through the intertubercular groove of the humerus and enters the joint cavity, where it is ensheathed by the synovial layer of the capsule. It prevents dislocation of the humerus during abduction and flexion.
- coracobrachialis: assisnt in flexion of the arm
- long head of the triceps brachii crosses the joint posteriorly and assists in adduction and extension
Outline muscles that help with these movements at the GH joint


O/I/F of supraspinatous
O: supraspinous fossa of scapula
I: greater tubercle of humerus
Stabilization of glenohumeral joint
Abduction at glenohumeral joint
O/I/F of infraspinatous
I; infraspinous fossa of scapula,
I: greater tubecler of humerus
F: stabilization of GH joint, lateral rotation of glenohumeral joint.
O/I/F of of terest minor
O: lateral aspect of posterior side of scapular
I: greater tuberlcle of humerus
F: stabilization of GH joint.
- lateral rotation of GH joint.
O/I/F of subscapularis
O; subscapular fossa of scapula (anterior side)
I: lesser tubercle of humerus
F: stabilization of the GH joint
- medial rotation at the GH joint.



outline the process of how abducting engages which muscles of the shoulder at whcih time.
DELTOIDS DONT DO ALL THE WORK WHEN YOU”RE DOING LATERAL RAISES AT THE GYM.
- the supraspinatus muscle first abducts the first 15 degrees
- then the deltoids can flex (what youre normally trying to work on at the gym) from 15-110 degrees- this is the ROM that you should attempt to achive
- after 110, the RC cuff muscles collectively work to abduct and rotate the GH joint. honestly it’s pointless to go above 110 degrees when you lateral raise a heavy weight, you’re more likely to injure yourself.


