CV/Rep Part 4: Innervation Flashcards
(26 cards)
The heart is innervated by __ and __ fibers. The right vagus nerve primarily innervates the __ node, whereas the left vagus innervates the __ node; however, there can be significant overlap in the anatomical distribution.
The heart is innervated by vagal and sympathetic fibers. The right vagus nerve primarily innervates the SA node, whereas the left vagus innervates the AV node; however, there can be significant overlap in the anatomical distribution.
The heart receives visceral innervation from the __ __ which includes __ and parasympathetic motor fibers, and __ __ sensory fibers.
Sympathetic innervation derives from __ __ nerves arising from the __ and __ thoracic portion of the sympathetic chain, which terminate at the SA and AV nodes, and along coronary arteries (T__-T__: increased heart rate, impulse conduction, force of contraction, coronary flow).
Parasympathetic innervation derives from the __ nerve (CN __), with cell bodies located near the___ and __ nodes and along ___ arteries (decreased heart rate, force of contraction, coronary flow).
The heart receives visceral innervation from the cardiac plexus which includes sympathetic and parasympathetic motor fibers, and visceral afferent sensory fibers.
Sympathetic innervation derives from cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves arising from the cervical and superior thoracic portion of the sympathetic chain, which terminate at the SA and AV nodes, and along coronary arteries (T1-T5: increased heart rate, impulse conduction, force of contraction, coronary flow).
Parasympathetic innervation derives from the vagus nerve (CN X), with cell bodies located near the SA and AV nodes and along coronary arteries (decreased heart rate, force of contraction, coronary flow).


label the sympathetic components of the heart innervation

- innervated by sympathetic outflow T1-T5 cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves

outline the effects of sympathetic stimulation on the heart, and parasympathethic motor stimulation of the heart

label the conduction system


The __ (__) node is the pacemaker of the heart. It initiates and regulates impulses for contraction, which are transmitted via myogenic conduction through the walls of the right atrium.
The sinoatrial (SA) node is the pacemaker of the heart. It initiates and regulates impulses for contraction, which are transmitted via myogenic conduction through the walls of the right atrium.
- *The rate at which the SA node generates impulses is influenced by the autonomic nervous system:**
- *• Sympathetic nervous system –** increases firing rate of the SA node, and thus increases heart rate.
• Parasympathetic nervous system – decreases firing rate of the SA node, and thus decreases heart rate.
The fibrous skeleton insulates the atria and ventricles so that they contract independently. The __ bundle is the only place where electrical signals can cross the skeleton of the heart!
The fibrous skeleton insulates the atria and ventricles so that they contract independently. The AV bundle is the only place where electrical signals can cross the skeleton of the heart!
purkinje fibers are located in the ___ surface of the ventricular walls, and are able to rapidly transmit cardiac action potentials from the AV bundle to the myocardium of the ventricles
PFs are located on the subenocardial surface
F E T A L C I R C U L A T O R Y S H U N T S
The lungs are bypassed by two separate shunts, firstly the __ __ between the two atria, which is responsible for bypassing the majority of the circulation.
Any blood that does not pass through the first strucutre enters the pulmonary trunk, which is linked to the distal arch of aorta by the __ __.
These two separate shunts allow the circulation to bypass the lungs.
The oxygenated blood entering the fetus also needs to bypass the primitive liver, this ensures that enough oxygen reaches the developing brain. This is achieved by passage through the __ __ , which is estimated to shunt around 30% of umbilical blood directly to the __ __ __.
The lungs are bypassed by two separate shunts, firstly the foramen ovale between the two atria, which is responsible for bypassing the majority of the circulation.
Any blood that does not pass through the first strucutre enters the pulmonary trunk, which is linked to the distal arch of aorta by the ductus arteriosus.
These two separate shunts allow the circulation to bypass the lungs.
The oxygenated blood entering the fetus also needs to bypass the primitive liver, this ensures that enough oxygen reaches the developing brain. This is achieved by passage through the ductus venosus , which is estimated to shunt around 30% of umbilical blood directly to the inferior vena cava.

outline the remanents of the fetal shunts in this table


label these fetal shunts/fetal circulation componenets


The right lung has three lobes; superior, middle and inferior. The lobes are divided from each other by two fissures:
The left lung contains superior and inferior lobes, which are separated by a similar __ fissure.
- oblique
- horizontal
The left lung contains superior and inferior lobes, which are separated by a similar oblique fissure.





The lung root is a collection of structures that suspends the lung from the mediastinum. Each root contains a bronchus, pulmonary artery, :
The lung root is a collection of structures that suspends the lung from the mediastinum. Each root contains a bronchus, pulmonary artery, two pulmonary veins, bronchial vessels, pulmonary plexus of nerves and lymphatic vessels.
The lungs receive most of their blood supply through the __ __ and are drained by the pulmonary veins, except for the structures around the __ of the lungs.
The pulmonary arteries arise from the pulmonary trunk at the __ __.
The lungs receive most of their blood supply through the pulmonary arteries and are drained by the pulmonary veins, except for the structures around the root of the lungs.
The pulmonary arteries arise from the pulmonary trunk at the sternal angle.
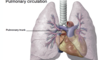
The lungs are supplied with deoxygenated blood by the paired __ __. The pulmonary arteries give rise to __ arteries, which in turn give rise to __ arteries, which run parallel to the bronchi. Each alveolus is surrounded by a __ __.
The lungs are supplied with deoxygenated blood by the paired pulmonary arteries. The pulmonary arteries give rise to lobar arteries, which in turn give rise to segmental arteries, which run parallel to the bronchi. Each alveolus is surrounded by a capillary plexus.
The bronchi, lung roots, visceral pleura and supporting lung tissues require an extra nutritive blood supply. (not just the deoxy functional blood supply) This is delivered by the __ arteries, which arise from the __ aorta. The roots of the lungs are supplied by the two left and single right __ arteries.
The bronchi, lung roots, visceral pleura and supporting lung tissues require an extra nutritive blood supply. (not just the deoxy functional blood supply) This is delivered by the bronchial arteries, which arise from the descending aorta. The roots of the lungs are supplied by the two left and single right bronchial arteries.
Functional blood supply: Once the blood has received oxygenation, it leaves the lungs via __ pulmonary __ (__ for each lung). The superior and inferior __ __ drain the __ and __ veins, and return oxygenated blood to the heart.
The __ veins provide venous drainage. The right __ vein drains into the __ vein, whilst the left drains into the accessory __ vein.
Functional blood supply: Once the blood has received oxygenation, it leaves the lungs via four pulmonary veins (two for each lung). The superior and inferior pulmonary veins drain the lobar and segmental veins, and return oxygenated blood to the heart.
The bronchial veins provide venous drainage. The right bronchial vein drains into the azygos vein, whilst the left drains into the accessory hemiazygos vein.
Three venous structures entering the right atrium:
Three venous structures entering the right atrium: IVC, SVC, coronary sinus
Venous blood from the legs has to be actively pumped by the leg muscles so that it will be able to return the blood up to the level of the heart. The largest veins in the legs are the deep veins which are completely surrounded by the muscle compartments in the calf and thigh. The deep vein at the top of the calf is called the __ __ and it drains all the venous blood from the calf muscles.
Venous blood from the legs has to be actively pumped by the leg muscles so that it will be able to return the blood up to the level of the heart. The largest veins in the legs are the deep veins which are completely surrounded by the muscle compartments in the calf and thigh. The deep vein at the top of the calf is called the Popliteal Vein and it drains all the venous blood from the calf muscles.
INNERVATION OF LUNGS:
The nerves of the lungs are derived from the __ __. They feature sympathetic, parasympathetic and visceral afferent fibres:
• Parasympathetic – derived from the __ nerve (CN __). They stimulate secretion from the
bronchial glands, contraction of the bronchial smooth muscle, and vasodilation of the pulmonary vessels. bronchoconstriction, vasodilation, secretomotor).
• Sympathetic – derived from the sympathetic trunks (T__-__). They stimulate relaxation of the
bronchial smooth muscle, and vasoconstriction of the pulmonary vessels. (bronchodilation, vasoconstriction, secretory inhibition).
• Visceral afferent – also carried by the __ nerve (CN __). Conduct __ to the sensory ganglion of the vagus nerve.
The nerves of the lungs are derived from the pulmonary plexuses. They feature sympathetic, parasympathetic and visceral afferent fibres:
• Parasympathetic – derived from the vagus nerve (CN X). They stimulate secretion from the
bronchial glands, contraction of the bronchial smooth muscle, and vasodilation of the pulmonary vessels. bronchoconstriction, vasodilation, secretomotor).
• Sympathetic – derived from the sympathetic trunks (T1-4). They stimulate relaxation of the
bronchial smooth muscle, and vasoconstriction of the pulmonary vessels. (bronchodilation, vasoconstriction, secretory inhibition).
• Visceral afferent – also carried by the vagus nerve (CN X). Conduct pain impulses to the sensory ganglion of the vagus nerve.




