Lower Limb Part 1 Flashcards
(29 cards)
spondylolysis
stress fracture throuhg parts interarticularis of the lumbar vertebrae

spondylolithesis
Spondylolisthesis occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the vertebra below it.

Intervertebral joints form between intervertebral (IV) disks and the articular surfaces of vertebral bodies. There are no IV disks between ___ and __.
Intervertebral joints form between intervertebral (IV) disks and the articular surfaces of vertebral bodies. There are no IV disks between C1 and C2.
The IV discs act as shock absorbers and are composed of an outer fibrous ring, the __ __,
and a gelatinous core, the __ __

The IV discs act as shock absorbers and are composed of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus,
and a gelatinous core, the nucleus pulposus

Herniation of an intervertebral disc occurs when the __ __ ruptures, breaking through the annulus fibrosus. The rupture usually occurs in a __-__ direction
Herniation of an intervertebral disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus ruptures, breaking through the annulus fibrosus. The rupture usually occurs in a posterior-lateral direction, after which the nucleus pulposis can irritate nearby spinal nerves – resulting in a variety of neurological and muscular symptoms.
The most common sites of nerve root compressed are at levels of L__–__ and L__–S__. . L__nerve root is the most common one that could be compressed.
The most common sites of nerve root compressed are at levels of L4–5 and L5–S1. The compressing factors can be at lateral recess and/or foramina; they are at different adjacent lumbar levels for one nerve root. L5 nerve root is the most common one that could be compressed.
The most common sites of nerve root compressed are at levels of L4–5 and L5–S1.Posterolateral IV disc herniations are most common because:
Posterolateral IV disc herniations are most common because:
Annulus fibrosus is thinner in this region
Lacking structural support from the anterior longitudinal ligament in this region
Lacking structural support from the posterior longitudinal ligament in this region
is there is a disk herniation in the L4/L5 reggion, the __ is affeced. If it’s an L5-S1 herniation, the __ is mostly affected

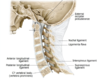
Two ligaments strengthen the vertebral body joints:
: the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments, which run the full length of the vertebral column.

The posterior longitudinal ligament is weaker and prevents hyperflexion.
• Superior to the foramen magnum, fans out and attaches within cranial cavity as __ __.
The posterior longitudinal ligament is weaker and prevents hyperflexion.
• Superior to the foramen magnum, fans out and attaches within cranial cavity as tectorial membrane.
• Located between the vertebral body and the dura matte
The joints between the articular facets, called facet joints, allow for some gliding motions between the vertebrae. They are strengthened by several ligaments:


The __ __ ligament is most susceptible to stretching or tearing during a whiplash injury.
The anterior longitudinal ligament is most susceptible to stretching or tearing during a whiplash injury.
__-__ joints consist of an articulation between the spine and the cranium. They permit motion in multiple planes stabilized by anterior and posterior atlanto-occipital membranes.
atlanto-occipital joints consist of an articulation between the spine and the cranium. They permit motion in multiple planes stabilized by anterior and posterior atlanto-occipital membranes.
The atlanto-axial joints are stabilized by ligaments:
- __ ligaments of the atlas (with longitudinal fascicles = cruciate ligaments of the atlas)
- • __ ligaments
- __ membrane (posterior longitudinal l.)
- __ ligament (supraspinous l.)
The atlanto-axial joints are stabilized by ligaments:
- transverse ligaments of the atlas (with longitudinal fascicles = cruciate ligaments of the atlas)
- • alar ligaments
- tectorial membrane (posterior longitudinal l.)
- nuchal ligament (supraspinous l.)




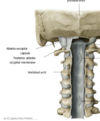

Each spinal cord segment has four roots: an anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) root on both right and left sides.
- the anterior/ventral root contains efferent nerve fibres, which carry stimuli away
from the CNStowards their target structures (motor) - The posterior/dorsal root contains afferent nerve fibres, which return sensory
information from the trunk and limbs to the CNS.
The anterior and posterior roots join to form the spinal nerve proper, containing a
mixture of sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers.
Each spinal cord segment has four roots: an anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) root on both right and left sides.
- the anterior/ventral root contains __ nerve fibres, which carry stimuli __
- *from the __** towards their target structures (motor)
- The posterior/dorsal root contains __ nerve fibres, which return sensory
information from the trunk and limbs to the CNS.
The anterior and posterior roots join to form the __ __ proper, containing a
mixture of sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers.

Having exited the vertebral canal, the spinal nerve divides into two branches (this is not the same as the original anterior motor and posterior sensory roots on the spinal cord) : a larger anterior or
ventral ramus, and a smaller posterior orposterior/dorsal ramus.
-Anterior/ventral ramus innervates the skin and muscle on the anterior aspect of the trunk (
innervate the hypaxial musculature, including the limb musculature that sits on the trunk)
- Posterior/dorsal ramus innervates the post-vertebral muscles and the skin of the back. (
innervate the epaxial musculature)
-Anterior/ventral ramus innervates the skin and muscle on the __ aspect of the trunk (
innervate the __ musculature, including the __ musculature that sits on the trunk)
- Posterior/dorsal ramus innervates the __-__ muscles and the skin of the back. (
innervate the __ musculature)
Note- the anterior and posterior muscles of the trunk are innervated by spinal nerves, with one
exception: the Accessory nerve- Cranial Nerve XI (1 out of 12 paired nerves that originate directly from
the brain) innervates the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
Note- the anterior and posterior muscles of the trunk are innervated by spinal nerves, with one
exception: the __ nerve- Cranial Nerve XI (1 out of 12 paired nerves that originate directly from
the brain) innervates the trapezius and __ muscles
. The spinal nerves that arise from the end of the spinal cord are bundled together, forming a structure known as the __ __.
. The spinal nerves that arise from the end of the spinal cord are bundled together, forming a structure known as the cauda equina.

Two swellings occur in the regions of the spinal cord that innervate the limbs:
The cervical enlargement is located proximally, at the __-T__ level. It represents the origin of the __ plexus. Between T-__and L_ is the lumbar enlargement, representing the origin of the _ and _ plexi.
The cervical enlargement is located proximally, at the C4-T1 level. It represents the origin of the brachial plexus. Between T11 and L1 is the lumbar enlargement, representing the origin of the lumbar and sacral plexi.




