Cervico-Occipital Junction Flashcards


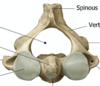
C2


C2 side view

C1 articulates articulates with the occipital bone of the skull at the __ __ __. this allows for a yes/nodding movement.
C1 is distinctive because it does not have a _ body.
the vertebral artery enters the _ _ of the skull through the groove for vertebral artery.
the smooth surface of the interior-anterior side on the anterior tubercle which acts as a _ _ for C2, and is labelled as a _ _ _ _.
C1 articulates articulates with the occipital bone of the skull at the supeiror articular facets. this allows for a yes/nodding movement.
C1 is distinctive because it does not have a vertebral body. is also has a distinc transver process and foramen.
the vertebral artery enters the formaen magnum of the skull through the groove for vertebral artery.
the smooth surface of the interior-anterior side on the anterior tubercle which acts hinge point for C2, and is labelled as a facet for the dens.

the dens is located on ___, acting as a hinge point for the first two cervical vertebrae.
allows left and right rotation of the head.
C1 rotates on C2, carrying the skull.
the __ __ __ of C2 articulates with the ___ ___ of C1 is is horizontally oriented, allowing C1 to slide relative to C2.
the dens is located on C2, acting as a hinge point for the first two cervical vertebrae.
allows left and right rotation of the head.
C1 rotates on C2, carrying the ksull.
the superior articular facet of C2 that articulates with the inferior articulation of C1 is horixontally oriented, allowing C1 to slide relative to C2.
inferior articular process of C1 is not pictured


this is C1 and C2 attached

c1 and c2 are articulated. the ____ of C2 connects with the ___ of the ___ is C1 and acts as a hinge point.
the vertebral artery goes through the ___ ____ and turns into the groove to make it’s way into the ___ __.
c1 and c2 are articulated. the dens of C2 connects with the facet of the dens is C1 and acts as a hinge point.
the vertebral artery goes through the transver foramena and turns into the groove to make it’s way into the foramen magnum.
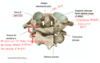


each synovial joint is surrounded by a joint capsule. the ___-___ joint capsule and the capsule between _ and _ are important for maintaining structural integrity in the connection between head and neck
the ligament from tip of dens to anterior foramen magnum called the _ ligament of the dens contributes very little to the stability of the joints
two ligaements run obliquely form the side of the dens to the left and right inner margein of the foramen magnum. the _ ligaments limit rotation of the head.

each synovial joint is surrounded by a joint capsule. the antlanto-occipital joint capsule and the capsule between C1 and C2 are important for maintaining structural integrity in the connection between head and neck
the ligament from tip of dens to anterior foramen magnum called the apical ligament of the dens contributes very little to the stability of the joints
two ligaements run obliquely form the side of the dens to the left and right inner margein of the foramen magnum. the alar ligaments limit rotation of the head.


ligaments of the medial atalantoaxial joint, superior view

the ___ ligament of the atlas forms a band that runs behind the dens. the ligaments holds the dens on the anterior portion of the C1 and protects the spinal cord.
the ___ ligaemnts are behind the transverse ligament. the transverse ligament is helad in place by superior and intferior __ ___. they are sometimes referred to as the cruciate ligament of the atlas.
the apical ligament is deep to the __ __ __.

the transnverse ligament of the atlas forms a band that runs behind the dens. the ligaments holds the dens on the anterior portion of the C1 and protects the spinal cord.
the alar ligaemnts are behind the transverse ligament. the transverse ligament is helad in place by superior and intferior longitudianl fasciles. they are sometimes referred to as the cruciate ligament of the atlas.
the apical ligament is deep to the superior longiturdinal fascles.



the posteiror ligament transitions to the __ ligament at the skull.

the posteiror ligament transitions to the tectoral ligament at the skull.




uncovertebral joints are specific to the last 5 cervical vertebrae. they appear with age. the uncovertebral joint forms where a lip forms of the superior surface of the vertebrae body. often associated with degredataion with age.



