CV/Resp Part 2 Flashcards
3 branches of the aortic arch that supplies the head, neck, and upper limbs.
- brachiocephalic trunk
- left common carotid artery
- left subclavian artery.


The pulmonary __ receive deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle and deliver it to the lungs for gas exchange to take place.
At around the level of __-__, the pulmonary trunk splits into the right and left pulmonary __.
The pulmonary arteries receive deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle and deliver it to the lungs for gas exchange to take place.
At around the level of T5-T6, the pulmonary trunk splits into the right and left pulmonary arteries.


The pulmonary __ receive oxygenated blood from the lungs, delivering it to the left side of the heart to be pumped back around the body.
The pulmonary veins receive oxygenated blood from the lungs, delivering it to the left side of the heart to be pumped back around the body.
The superior vena cava receives ___ blood from the upper body (superior to the diaphragm, excluding the lungs and heart), delivering it to the right atrium.
- It is formed by merging of the __ veins, travelling inferiorly through the thoracic region until draining into the superior portion of the right atrium at the level of the 3rd rib.
The superior vena cava receives DEOXYGENATED blood from the upper body (superior to the diaphragm, excluding the lungs and heart), delivering it to the right atrium.
- It is formed by merging of the BRACHIOCEPHALIC veins, travelling inferiorly through the thoracic region until draining into the superior portion of the right atrium at the level of the 3rd rib.
The inferior vena cava receives __ blood from the lower body (all structures inferior to the diaphragm), delivering it back to the heart.
It is initially formed in the pelvis by the _ _ veins joining together. It travels through the abdomen, collecting blood from the _, _, gonadal, _ and _ veins.
It drains into the _ portion of the right atrium.
The inferior vena cava receives deoxygenated blood from the lower body (all structures inferior to the diaphragm), delivering it back to the heart.
It is initially formed in the pelvis by the common iliac veins joining together. It travels through the abdomen, collecting blood from the hepatic, lumbar, gonadal, renal and phrenic veins.
It drains into the inferior portion of the right atrium.
the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the __ and __ vena cavae, and from the __
veins. It pumps this blood through the right atrioventricular orifice (guarded by the tricuspid valve) into the right ventricle.
the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cavae, and from the coronary
veins. It pumps this blood through the right atrioventricular orifice (guarded by the tricuspid valve) into the right ventricle.
-The coronary sinus receives blood from the coronary veins. It opens into the right atrium between the inferior vena cava orifice and the right atrioventricular orifice.




The septal wall in the right atrium is marked by a small oval-shaped depression called the __ __. This is the remnant of the __ __ in the fetal heart, which allows right to left shunting of blood to bypass the __. It closes once the newborn takes its first breath.
The septal wall in the right atrium is marked by a small oval-shaped depression called the fossa ovalis. This is the remnant of the foramen ovale in the fetal heart, which allows right to left shunting of blood to bypass the lungs. It closes once the newborn takes its first breath.

note: atrial septal defects often occur because of a malformed fossa ovalis/foramen ovale still open

The right ventricle receives __ blood from the right atrium, and pumps it through the pulmonary __ (guarded by the pulmonary valve), into the pulmonary artery. Pumps blood to the pulmonary circulation. Blood exits through pulmonary __ valve and pulmonary trunk.
The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium, and pumps it through the pulmonary orifice (guarded by the pulmonary valve), into the pulmonary artery. Pumps blood to the pulmonary circulation. Blood exits through pulmonary semilunar valve and pulmonary trunk.



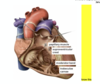
The interior of the inflow part of the right ventricle is covered by a series of irregular muscular elevations, called trabeculae carnae.
A type of TC are pillars, aka __ muscles, which are anchored by their base to the ventricles.
Their apices are attached to fibrous cords (__ __), which are in turn attached to the three __ __ cusps. By contracting, the __ muscles ‘pull’ on the __ __ to prevent prolapse of the valve leaflets during ventricular systole.
The interior of the inflow part of the right ventricle is covered by a series of irregular muscular elevations, called trabeculae carnae.
A type of TC are pillars, aka papillary muscles, which are anchored by their base to the ventricles.
Their apices are attached to fibrous cords (chordae tendineae), which are in turn attached to the three tricuspid valve cusps. By contracting, the papillary muscles ‘pull’ on the chordae tendineae to prevent prolapse of the valve leaflets during ventricular systole.




all valves are tricuspid except
bicsurpid mitral valve.


The mitral and tricuspid valves are supported by the attachment of fibrous cords (__ __) to the free edges of the valve cusps. The __ __ are, in turn, attached to __ __ , located on the interior surface of the ventricle
The mitral and tricuspid valves are supported by the attachment of fibrous cords (chordae tendineae) to the free edges of the valve cusps. The chordae tendineae are, in turn, attached to papillary muscles , located on the interior surface of the ventricle
There are five papillary muscles in total. Three are located in
There are five papillary muscles in total. Three are located in the right ventricle, and support the tricuspid valve. The remaining two are located within the left ventricle, and act on the mitral valve.








