Skull anatomy Flashcards
how can the bones of the brain be divided? [2] desribe basic roles of each
neurocranim: cranial vault: protect brain
visecerocranium: facial skeleton: cavities for sense organs, secure teeth, framework of face
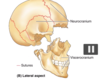
how are flat bones of brain formed? [1]
how are flat bones of brain formed? [1]
Intramembranous ossification: the replacement of sheet-like connective tissue membranes with bony tissue.


what are the
red
yellow
light green
purple
blue
bones?
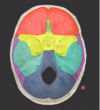
what are the
red: tempora
yellow: sphenoid
light green: temporal bone
purple: parietal bone
blue: occipital
bones?



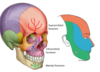
what is A?
why is it clinically significant? [1]

Pterion
clinically significant: junction of bones so is a weak spot. behind it closely runs the middle meningial artery. trauma here can damage artery easily
what are fontanelles? [1]
what is their function [2]?
what are fontanelles? [1]
wide sutures in new born covered by membrane
function
- allow bone to expand with growth of brain
- allow pressure on skull during birth
which fontanelle do you examine when looking at increase in cranial pressure / dehydation of baby? [1]
anterior fontanelle

which bone houses the middle and internal ear?
parietal
temporal
sphenoidal
lacrimal
ethmoid
which bone houses the middle and internal ear?
parietal
temporal
sphenoidal
lacrimal
ethmoid
which part of the temporal bone contains the organs of hearing?
squamous
external acoustic meatus
petrous part
mastoid process
styloid process
which part of the temporal bone contains the organs of hearing?
squamous
external acoustic meatus
petrous part
mastoid process
styloid process

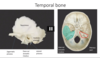
which bone is this?
temporal
ethmoid
mandible
maxilla
sphenoid

which bone is this?
temporal
ethmoid
mandible
maxilla
sphenoid


which part of the sphenoid does pituitary gland sit it?
anterior clinoid process
greater wing
superior orbital fissure
sella turcicia
posterior clinoid process
which part of the sphenoid does pituitary gland sit it?
anterior clinoid process
greater wing
superior orbital fissure
sella turcicia
posterior clinoid process
what is the green bit? what find in it?
what do you find at the anteiror and posterior ends?

sella tucicia - pituitary gland!
anterior clinoid process
posterior clinoid process


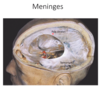
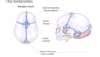
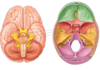
which of the following is the tentorial notch?
A
B
C
D
E
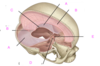
which of the following is the tentorial notch?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is the falx cerebri
A
B
C
D
E
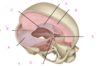
which of the following is the falx cerebri
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is the tentorium cerebellum?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the tentorium cerebellum?
A
B
C
D
E
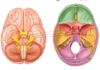
what are dural venous sinuses? [1]
what are dural venous sinuses? [1]
between periosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater is a network of endothlial lined spaces filled wtih venois blood




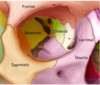
label A-E

A: temporal
B: sphenoid
C: ethmoid
D: occipital bone
E: temporal bone
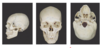

what is

ethmoid bone - purple
sphenoid bone - red
zygomatic bone - yellow


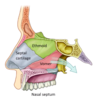
which bone is cribiform plate in?
sphenoid
temporal
vomer
ethmoid
palatine
which bone is cribiform plate in?
sphenoid
temporal
vomer
ethmoid
palatine
maxillary sinus drains into:
- superior meatus
- middle meatus
- inferior meatus
- ethmoid sinus
- inferior cochae
maxillary sinus drains into:
- superior meatus
- *- middle meatus**
- inferior meatus
- ethmoid sinus
- inferior cochae
what are A & B?

A: ethmoid sinus
B: sphenoid sinus
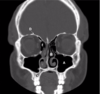
A: maxillary sinus
B: middle conchae
C: maxilla
D: frontal bone
E: ethmoid sinus


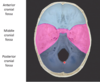
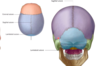
which bones make up the anterior cranial fossa? [3]
which lobe of brain lies in the anterior cranial fossa? [1]
which bones make up the middle cranial fossa? [3]
which lobe of brain lies in the middle cranial fossa? [2]
which bones make up the posterior cranial fossa? [4]
which lobe of brain lies in the posterior cranial fossa? [1]
which bones make up the anterior cranial fossa? [3]
frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid
which lobe of brain lies in the anterior cranial fossa? [1]
frontal lobe
which bones make up the middle cranial fossa? [3]
sphenoid, temporal and parietal
which lobe of brain lies in the middle cranial fossa? [1]
temporal lobes & pituitaury gland
which bones make up the posterior cranial fossa? [4]
sphenoid, parietal, temporal and occipital
which lobe of brain lies in the posterior cranial fossa? [1]
cerebellum
which is the smallest foramen in the brain?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
damage to the middle meningeal artery at the pterion results in what? [1]
damage to the middle meningeal artery at the pterion results in what? [1]
extradural haemotoma
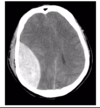
which foramen do the dural venous sinuses drain out of and into the internal jugular vein?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
which foramen do the dural venous sinuses drain out of and into the internal jugular vein?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
which foramen does the internal carotid artery enter brain?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
which foramen does the internal carotid artery enter brain?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
label A-C x


label the different parts of the internal carotid artery

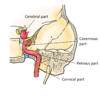
which foramen does the internal carotid artery pass over the top of?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
which foramen does the internal carotid artery pass over the top of?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
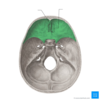

which CN is this?
which strucutre does it enter the skull through? which bone does this lie in?

which CN is this? olfactory nerve
which strucutre does it enter the skull through?
through cribiform plate
which bone does this lie in?
ethmoid bone

which nerves are these? [3] (going down)
which structure do they innervate?
which opening do they all pass through?

which nerves are these? [3] (going down)
oculomotor III
trochlea IV
abducens VI
which structure do they innervate?
muscles that surround eye
which opening do they all pass through?
superior orbital fissure
which is the largest cranial nerve?
opthamalic
VN
trigeminal
optic
glosspharnyngeal
which is the largest cranial nerve?
opthamalic
VN
trigeminal
optic
glosspharnyngeal
which nerve is this?
what are three divisions?
what is function? [1]
trigeminal nerve
- opthamalic (V1)
- maxillary (V2)
- mandibular (V3)
go on to provide sensory innervation to face
which foramen do the followng leave brain the inside of cranium from?
trigeminal nerve
- opthamalic (V1)
- maxillary (V2)
- mandibular (V3)
which foramen do the followng leave from?
trigeminal nerve
- opthamalic (V1): superior orbtial fissure
- maxillary (V2): foramen rotundum
- mandibular (V3): foramen ovale
the
which foramen do the followng leave the skull from?
trigeminal nerve
- opthamalic (V1)
- maxillary (V2)
- mandibular (V3)
which foramen do the followng leave the skull from?
trigeminal nerve
- opthamalic (V1): supraorbital foramen
- maxillary (V2): infraoribal foramen
- mandibular (V3): mental foramen
which foramen does the facial nerve exit the skull via? [1]
what does the facial nerve innervate? [1]
which foramen does the facial nerve exit the skull via? [1]
stylomastoid foramen
what does the facial nerve innervate? [1]
motor muscles of facial expression
glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve leave the skull via which foramen?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve leave the skull via which foramen?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
spinal accessory nerves leave the skull via which foramen?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
spinal accessory nerves leave the skull via which foramen?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
which muscles does the spinal accessory provide innervation to? [2]
which muscles does the spinal accessory provide innervation to? [2]
sternocloidalmastoid
trapezius


