Anatomy of the neck Flashcards
what makes up the posterior triangle of neck?
- posterior border? [1]
- anterior border? [1]
- other border? lol [1]
what important structures run through it? [4]
what makes up the posterior triangle of neck? [3]
- posterior border: sternocloidomastoid
- anterior border: trapezius
- other border: middle 1/3 clavicle
what important structures run through it? [4]
- *- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)** comes out of it and **innervates the trapezius
- external jugular vein
- brachail plexus (in inferior section)
- part of subclavian**

what is the difference in the prominance of EJV
- for normal venous pressure? [1]
- raised venous pressure? [1]
what is the difference in the prominance of EJV
- for normal venous pressure? [1]
- *visible above clavicle for less that 4cm**
- raised venous pressure? [1]
- *prominent throughout course**

what is A?
what is B?

what is A: EJV
what is B: sternocleidomastoid
spinal accessory nerve:
- come from which spinal levels?
- describe the route:
a) enters brain?
b) exits brain? - type of innervation?
spinal accessory nerve:
- come from which spinal levels: C1-5
- describe the route:
a) enters brain: foramen magnum
b) exits brain: jugular foramen - type of innervation: motor

why is there a difference in spinal accessory nerve injury affecting traps and sternocloidomastal? [1]
which is more likely to be injured? [1]
why is there a difference in spinal accessory nerve injury affecting traps and sternocloidomastal? [1]
different sub cut pathway: comes off first and more protected e.g. from lymph node surgery
trapezius more likely to be damaged
if have spinal accessory CN XI damage - what movement of arm would u see impaired? [1]
if have spinal accessory CN XI damage - what movement of arm would u see impaired? [1]
difficulty abducting arm above 90 degrees

what is the ansa cervicalis?
where is it found? [1]
which spinal cord nerve rootlets make it? [3]
what does it provide motor innervation to? [1]
what is the ansa cervicalis?
where is it found? [1]
cervical plexus
which spinal cord nerve rootlets make it? [3]
C1, C2, C3
what does it provide motor innervation to? [1]
infrahyoid muscles
which of the following is submental division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is submental division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D
which of the following is carotid division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is carotid division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D
which of the following is submandibular / digastric division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is submandibular / digastric division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D
which of the following is the muscular division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is the muscular division of anterior triangle?
A
B
C
D
what is each section?
purple:
green:
red
yellow?

what is each section?
purple: digastric
green: submental
red: carotid
yellow: muscular
label the borders of the carotid triangle xx
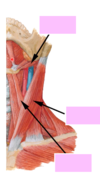

why is the carotid triangle clinically relevent?
- what vasculature goes through it? [2]
- which nerves? [6]
why is the carotid triangle clinically relevent?
- what vasculature goes through it? [2]
common carotid artery (In & Ex)
internal jugular vein
- which nerves? [6]
- *- glossopharyngeal**
- **vagus
- spinal accessory
- hypoglossal**
- *- cervical symp trunk
- ansa cervicalis**
where do u find the carotid body? [1]
what type of receptors do u find in the carotid body? [1]
whre do u find carotid sinus?
what type of receptors do u find in the carotid sinus? [1]
where do u find the carotid body? [1]
bifurcation of carotid artery (into internal CA & external CA)
what type of receptors do u find in the carotid body? [1]
chemorecptors
whre do u find carotid sinus?
bifurcation of carotid artery (into internal CA & external CA)
what type of receptors do u find in the carotid sinus? [1]
baroreceptors

which structures are always in the carotid sheath? xx [3]
which structures escape the carotid sheath? [4]
which structures are just outside? [2]
which structures are always in the carotid sheath? xx [3]
common and internal carotid arteries
internal jugular vein
vagus nerve
which structures escape the carotid sheath? 4]
CNIX
Superior laryngeal nerve
spinal root of CN XI
CN XII
which structures are just outside? [2]
ansa cervicalis
sympathetic trunk

describe path of symp. innervation to head
what are the three sympathetic trunk ganglia that innervate the head & neck? [3]
what are the three sympathetic trunk ganglia that innervate the head & neck? [3]superior, middle & inferior cervical ganglia
sympathetic innervation:
- *- presynaptic fibres via superior thoracic nerves –>** **synapse in ganglia (superior, middle & inferior cervical ganglia)
- post ganglionic sympathetic fibres go to neck / head. BUT need to hold onto strucutres to go up (like scaffolding)
i) wrap around the cartoid sheath to go up**
what is the name for the symptoms created when get sympathetic neck trunk damage ? [1]
- what are the characteristics of this? [4]
horners syndrome:
- contraction of pupils: miosis
- drooping of superior eyelid: paralysis of levator palpebrae superioris smooth muscle
- sinking of eye: enopthalmos
- vasodilation and abscence of sweating:
in which three conditions does internal jugular vein pulse rise? [3]
in which three conditions does internal jugular vein pulse rise? [3]
mitral valve disease
increased pulmonary circ pressure
right side of heart failure
what is the overall role of the suprahyoid muslces ? [1]
what is the overall role of the infrahyoid muscles? [1]
combined, what do these guys do? [1]
what is the overall role of the suprahyoid muslces ? [1]
elevate the hyoid and larynx
what is the overall role of the infrahyoid muscles? [1]
depress hyoid and larynx during swallowin and speaking
combined, what do these guys do? [1]
move larynx as a whole xx

which of the following is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve?
thyroartyenoid
cricoartyenoid
cricothyroid
transverse arytenoid
olbique arytenoid
what are the others innervated by?
which of the following is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve?
thyroartyenoid
cricoartyenoid
cricothyroid
transverse arytenoid
olbique arytenoid
others = recurrent laryngeal nerve
what happens to the rima glottidis during:
- normal resp
- deep resp
- phonation
- whispering
what happens to the rima glottidis during:
- normal resp: narrow slit (laryngeal muscles relax)
- deep resp: open wide (vocal ligaments abducted by contraction of posterior cricoarytenoids(
- phonation: air if forced between vocal ligaments to create sound
- whispering: vocal ligaments strongly adducted by relaxed arytenoids

describe the pathway for innervation to the laryngeal muscles
what does each do specifically?
vagus –> superior laryngeal nerve
- -> internal laryngeal (larynx above vocal cords)
- -> external laryngeal (motor to cricothyroid)
–> recurrent laryngeal nerve: motor to all intrinsic muslces of the layrnx and sensory to all below vocal folds
injury to superior laryngeal nerve causes? [1]
injury to recurrent laryngeal nerve causes? [1]
injury to superior laryngeal nerve causes? [1]
paralysed cricothyroid - cant ary length & tension = monotone voice
injury to recurrent laryngeal nerve causes? [1]
paralysed vocal folds: horseness (cant abduct the vocal folds)







