:C Flashcards
(62 cards)
which nuclei in the hypothalamus do u need to know? [2]
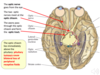
paraventricular nucleus
supraoptic nucleus
what is the difference in anterior and posterior pituitary development? [1]
what is the difference in anterior and posterior pituitary development? [1]
- *posterior pit** = direct outgrowth of brain (specifically the hypothalamus)
- *anterior pit** = indirect growth: develops from ectoderm in roof of mouth & migrates up
which part of the pituitary gland do the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei project into? [1]
what occurs here? [1]
where do the other hypothalamic nuclei release their peptides? [1]
which part of the pituitary gland do the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei project into? [1]
project into the posterior lobe
what occurs here? [1]
release peptides into the capillaries in the posterior pit
where do the other hypothalamic nuclei release their peptides? [1]
capillary plexus in the neck of the pit. stalk
- where do you find thermoreceptors? [2]
- where do you find thermoreceptors? [2]
- *i) cutaneous thermoreceptors
ii) anterior nucleus of hypothalamus: blood temp**
how does the hypothalamus regulate water balance?
- where do you find osmoreceptors? [1]
- which hypothalamic nuclei are stimulated to increase water in ur body ? how do they work?
- where do you find osmoreceptors? [1]
- *subfornical organ (wall of third ventricle): detects osmolarity**
- subforrnical organ activates cells in the:
- *i) medial preoptic nucleus**
- this nucleus connects to the limbic system: regulates concious sense of thirst
- *ii) paraventricular nucleus & supraoptic nucleus**
- secrete ADH (makes more aquaporins in CD)
- oxytocin
what are three mechanisms of ADH reducing water loss? [3]
- Increase aquaporins in CD
- increases perm. of CD to urea (water follows)
- stimulates sodium reab in thick loop of henle: Na/K/2Cl
describe the mechanism of HPA axis (hypothalamus-pit-adrenal axis)
describe the mechanism of HPA axis (hypothalamus-pit-adrenal axis):
- Cells in hypothalamus release CRH (Corticotropin releasing hormone)
- CRH acts on anterior pit to releease ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
- ACTH acts on adrenal cortex to release cortisol
- *BUT: negative feedback system:**
- cortisol inhbits release of above

how is baby sucking on a breast an example of creating a neuro-hormonal reflex? [2]
how does oxytocin promote maternal bonding? [2]
baby sucking on a teat:
- sucking action is transmitted to the hypothalamus via spinothalamic tract (neuro)
- releases oyxtocin from posterior pit. (hormonal)
- activates the milk down reflex
how does oxytocin promote maternal bonding? [2]
- suckiling - causes oxytocin release in mothers brain
- this is associated with reward - limbic system
why are anterior pituitary hormones released in ‘two hormone’ mechanism?
- double negative feedback means hormones are released in cyclic fashion (diurnal system or montly cycles)
WORK IN CYCLES !!
MESS:
- how do supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei release peptides in circulation? [1]
- how does hypothalamic cell bodies from anterior lobe release peptides into circulation? [1]
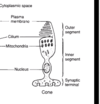
•Posterior lobe: Hypothalamic cell bodies in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei have axons that project down the pituitary stalk to the posterior lobe of the pituitary. They release peptides into the capillaries in the posterior pituitary which circulate in the blood to other organs
•Anterior lobe: Hypothalamic cell bodies have shorter axons that release peptides on to the capillary plexus in the neck of the pituitary stalk

what is growth hormone (GH) inhibited by? [1]
•Is inhibited by growth hormone inhibiting hormone = somatostatin.
which anterior pituitary hormone is inhibited by its hypothalamic releasing hormone?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which anterior pituitary hormone is inhibited by its hypothalamic releasing hormone?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL): inhibited by prolactin inhbiting factor (e.g. dopamine)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which of the following stimulates production of sex hormones by gonads?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which of the following stimulates production of sex hormones by gonads?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which of the following stimulates production of spem and eggs
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which of the following stimulates production of spem and eggs
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which of the following regulates metabolism
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which of the following regulates metabolism
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
which of the following induces targers to produce insulin-like growth factors?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following induces targers to produce insulin-like growth factors?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following regulates metabolism and the stress response?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following regulates metabolism and the stress response?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is released by gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH)
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is released by gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH)
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is inhibited by prolactin inhbiting factor?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is inhibited by prolactin inhbiting factor?
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is released by Corticotrophin Releasing Hormone (CRH)
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is released by Corticotrophin Releasing Hormone (CRH)
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is released gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) [2]
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
which of the following is released gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) [2]
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PL)
Lutenising hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone (GH)