Anatomy 3 Flashcards
which mengingeal layer is shown on the right?

arachnoid (& pia mater below)
the falxi cerebri lies where in the brain? [1]
which meningeal layer is the falxi cerebri formed from? [1]
the falxi cerebri lies where in the brain? [1]
longitudinal fissue
which meningeal layer is the falxi cerebri formed from? [1]
dura matter (meningeal)
which is the largest dural fold (septa)?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
which is the largest dural fold (septa)?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli

which of the following is a gap through which the brainstem and blood vessels pass to enter the middle cranial fossa?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
which of the following is a gap through which the brainstem and blood vessels pass to enter the middle cranial fossa?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum

which of the following covers the posterior fossa structures (hindbrain) and supports the temporal and occipital lobes.
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
which of the following covers the posterior fossa structures (hindbrain) and supports the temporal and occipital lobes.
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum

which of the following separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobe of the cortex?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
which of the following separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobe of the cortex?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum

which of the following separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobe of the cortex?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
which of the following separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobe of the cortex?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
tumours in which space raise intercranial pressure and may cause herniation of the temporal lobe, especially the uncus?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
tumours in which space raise intercranial pressure and may cause herniation of the temporal lobe (uncus)?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
the uncus is an postieorly located lobe located in which part of the brain?
temporal
parietal
cerebellum
occipital
temporal
the uncus is an postieorly located lobe located in which part of the brain?
temporal
parietal
cerebellum
occipital
temporal
what is A?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum

what is A?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
infundibulum
what are the blue arrows point at? [1]
what is the yellow arrow pointing at? [1]
blue arrows: straight sinus
yellow aroow: tranverse sinus

what is A?
infundibulum
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli

what is A?
infundibulum
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli

what is B?
infundibulum
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli

what is B?
infundibulum
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli
what is C?
corpus callosum
lateral ventricles
third ventricle
thalamus
hypothalamus

what is C?
corpus callosum
lateral ventricles
third ventricle
thalamus
hypothalamus
what is D?
carotid canal
optic tract
olfactory tract
optic chiasm
superior sagital sinus

what is D?
carotid canal
optic tract
olfactory tract
optic chiasm
superior sagital sinus
What is E?
oculomotor nerve
optic nerve
olfactory nerve
trochlear nerve
optic tract

What is E?
oculomotor nerve
optic nerve
olfactory nerve
trochlear nerve
optic tract
Label A-D


what is highlighted here?

superior saggital sinus
which sinus is this?
Superior sagital sinus
Inferior sagital sinus
Straight sinus
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse sinuses
Sigmoid sinuses

which sinus is this?
Superior sagital sinus
Inferior sagital sinus
Straight sinus
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse sinuses (right)
Sigmoid sinuses

which sinus is this?
Superior sagital sinus
Inferior sagital sinus
Straight sinus
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse sinuses
Sigmoid sinuses

which sinus is this?
Superior sagital sinus
Inferior sagital sinus
Straight sinus
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse sinuses
Sigmoid sinuses
which sinus is this?
Superior sagital sinus
Inferior sagital sinus
Straight sinus
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse sinuses
Sigmoid sinuses

which sinus is this?
Superior sagital sinus
Inferior sagital sinus
Straight sinus
Confluence of sinuses
Transverse sinuses
Sigmoid sinuses
which of the following is arachnoid mater?
A
B
C
D
E
F
G

which of the following is arachnoid mater?
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
which of the following is pia mater?
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
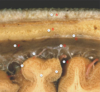
which of the following is pia mater?
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
which of the following is dura mater
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
which of the following is dura mater
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
which cranial fold seperates the cerebellum from the cerebrum ? [1]
Tentorium cerebelli (it tents up in the middle to meet the falx cerebri )

what is highlighted here? [1]
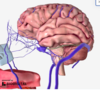
superior petrosal sinus

The visualised ventricles are enlarged - this is known as hydrocephalus (or ventriculomegaly).
what is function of CSF? [4]
- Buoyancy - the CSF that surrounds the brain acts to reduce the weight of the brain. This can also enable to to work as a shock absorber.
- Physical buffer - the CSF can acts as a physical buffer for the brain. If the pressure within the cranium increases, CSF can be displaced first to help to prevent ischaemia.
- Homeostasis - acting as a chemical buffer as well, CSF can help to regulate various substances around the brain.
- Excretion of waste - metabolites excreted by the brain into the CSF can be recirculated into the bloodstream to be excreted via bodily mechanisms.
CSF is made by which type of cells in the choroid plexi? [1]
ependymal cells - in the chorionic villi
how does CSF get from lateral ventricles into the third ventricle? [1]
how does CSF get from third ventricle into the 4th ventricle? [1]
how can CSF leave the 4th ventricle? [2]
how does CSF get from lateral ventricles into the third ventricle? [1]
via the interventricular foramina
how does CSF get from third ventricle into the 4th ventricle? [1]
via the cerebral aquaduct
how can CSF leave the 4th ventricle? [2]
via:
- central canal
- median / lateral apertures
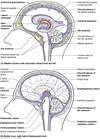
what is A? [1]

pineal gland / body

what is the role of arachnoid granulations? [1]
resorption of CSF

In the image, we can see that the lateral ventricles and the third ventricle are enlarged. This would suggest that the obstruction is distal to that, and therefore the most likely answer is the cerebral aqueduct.
which of the following is for language production
a) brocas area
b) wernickes area
which of the following is for language production
- *a) brocas area**
b) wernickes area
which of the following is for language comprehension
a) brocas area
b) wernickes area
which of the following is for language comprehension
a) brocas area
* *b) wernickes area**
which of the following is the area responsible for language production?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the area responsible for language production?
A
B
C: Brocas area
D
E

which of the following is the primary auditory area?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the primary auditory area?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is the precentral gyrus?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the precentral gyrus?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is the postcentral gyrus?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the postcentral gyrus?
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is an area involved in planning movements
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is an area involved in planning movements
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is an area involved in planning movements
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is an area involved in planning movements
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is responsible for further processing of visual information from the primary visual cortex
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is responsible for further processing of visual information from the primary visual cortex
A: Visual association cortex
B
C
D
E
which of the following is responsible for further processing processing of auditory information
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is responsible for further processing processing of auditory information
A
B
C: Secondary auditory cortex
D
E
which of the following is typically associated with ‘executive function’, including planning and decision making, as well as behaviour and personality
A
B
C
D
E
which of the following is typically associated with ‘executive function’, including planning and decision making, as well as behaviour and personality
A
B
C
D: prefrontal cortex
E
which of the following is final destination of the optic pathway
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is final destination of the optic pathway
A
B
C
D
E

It is relatively straightforward to exclude the prefrontal cortex (which lies at the frontal pole) and the visual cortex (which lies at the occipital pole), leaving the auditory and primary motor cortices as possibilities. This cannot be the auditory cortex, however, as we know this is in the temporal lobe, which is at the same transverse level as the eyes and ears, which cannot be seen here. We are, therefore slightly higher, approximately at the midpoint of the right primary motor cortex.
The blood supply to the brain can be divided into its anterior and posterior circulation which are joined by a network of vessels known as the circle of Willis.
the anterior portion is derived from which arteries? [1]
the posterior portion is derived from which arteries? [1]
The blood supply to the brain can be divided into its anterior and posterior circulation which are joined by a network of vessels known as the circle of Willis.
the anterior portion is derived from which arteries? [1]
internal carotid arteries (ICA)
the posterior portion is derived from which arteries? [1]
vertebral

how does the ica branch? [3]
internal carotid A –> anterior cerebral artery & middle cerebral artery
connected by the anterior communicating artery

how does vertebral artery branch?
vert. a –> basilar artery –> posterior cerebral arteries
Two communicating vessels exist between the two posterior cerebral arteries and the internal carotid arteries called the posterior communicating arteries (PComm)
As well as providing blood supply to the posterior aspect of the cerebral cortex, the posterior circulation also supplies the brainstem and cerebellum via several branches; the superior cerebellar arteries, the anterior inferior cerebellar arteries, the posterior inferior cerebellar arteries and the pontine arteries.



which arerty is labelled?
right anterior cerebral A
righ middle cerebral A
left anterior cerebral A
left middle cerebral A

which arerty is labelled?
right anterior cerebral A
righ middle cerebral A
left anterior cerebral A
left middle cerebral A
what is highlighted?
vertebral A
basilar A
ICA
Posterior cerebral
anterior cerebral

what is highlighted?
vertebral A
basilar A
ICA
Posterior cerebral a
which artery provides
purple
green
yellow?

which artery provides
purple : middle cerebral artery (MCA)
green : anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
yellow poster cerebral artery (PCA)
Through which foramen do the internal carotid arteries (ICA) enter the skull?
Foramen lacerum
Carotid canal
Foramen rotundum
foramen magnum
jugular foramen
Through which foramen do the internal carotid arteries (ICA) enter the skull?
Foramen lacerum
Carotid canal
Foramen rotundum
foramen magnum
jugular foramen
Through which foramen do the vertebral arteries enter the skull?
Foramen lacerum
Carotid canal
Foramen rotundum
foramen magnum
jugular foramen
Through which foramen do the vertebral arteries enter the skull?
Foramen lacerum
Carotid canal
Foramen rotundum
foramen magnum
jugular foramen
Marie has a thrombus in her right middle cerebral artery, which functional areas would you expect to be affected?
Facial sensation
Facial movements
Leg movements
Leg sensation
Speech production
Speech comprehension
The MCA provides blood supply for the somatosensory and motor cortices, but only the regions dedicated to the face and upper limb. The lower limb is supplied by the ACA. Broca and Wernicke’s regions are usually located in the left cortex, and so are unlikely to be affected in this case.
Marie has a thrombus in her right middle cerebral artery, which functional areas would you expect to be affected?
Facial sensation
Facial movements
Leg movements
Leg sensation
Speech production
Speech comprehension
The MCA provides blood supply for the somatosensory and motor cortices, but only the regions dedicated to the face and upper limb. The lower limb is supplied by the ACA. Broca and Wernicke’s regions are usually located in the left cortex, and so are unlikely to be affected in this case.
the lower limb somatosensory and motor cortices are provided by which artery?
ICA
MCA
ACA
Basilar A
PCA
the lower limb somatosensory and motor cortices are provided by which artery?
ICA
MCA
ACA
Basilar A
PCA
the upper limb & face somatosensory and motor cortices are provided by which artery?
ICA
MCA
ACA
Basilar A
PCA
the upper limb & face somatosensory and motor cortices are provided by which artery?
ICA
MCA
ACA
Basilar A
PCA
which artery is highlighted in green?
anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior communicating arteries
anterior communicating arteries
basilar artery
which two arteries does it connect? [1]

which artery is highlighted in green?
anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior communicating arteries
anterior communicating arteries
basilar artery
which two arteries does it connect? [1]
anterior cerebal arteries
which artery is labeled A?
anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior communicating arteries
anterior communicating arteries
basilar artery

which artery is labeled A?
anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior communicating arteries
anterior communicating arteries
basilar artery
which artery is labeled D?
anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior communicating arteries
anterior communicating arteries
basilar artery

which artery is labeled D?
anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior communicating arteries
anterior communicating arteries
basilar artery
Label B [1] & C [1]

B: corpus callosum
C: pineal body
which structures in the brain form the diencephalon ? [3]
diencaphalon:
thalamus
epithalamus
hypothalamus
what is highlighted?
vertebral A
basilar A
ICA
Posterior cerebral
anterior cerebral

what is highlighted?
vertebral A
basilar A
ICA
Posterior cerebral
anterior cerebral
what is A?
vertebral A
basilar A
ICA
Posterior cerebral
anterior cerebral

what is A?
vertebral A
basilar A
ICA
Posterior cerebral
anterior cerebral


