Blood Supply to the Brain Flashcards
- what is ~ avergae brain blood flow? [1]
- does this fluctuate much (e.g. with hyper /hypotension)? [1]
- what changes in O2 [1] & CO2 [1] cause an increase in blood flow to brain?
- what is ~ avergae brain blood flow? [1] ~ 50 ml per 100g of brain tissue per minute
- does this fluctuate much (e.g. with hyper /hypotension)? [1]
- *no: flow regulated by auto-regulation**
- what changes in O2 [1] & CO2 [1] cause an increase in blood flow to brain?
decrease in o2
increase in co2 = both increase flow to brain
what is different about cerebral arteries compared to other arteries? [3]
what is different about cerebral veins compared to other veins? [3]
arteries
- thin walled
- easily blocked
- easily distorted & ruptured
veins:
- no valves
- thin walled
- gravity helps flow back
- found in dural sinuses
which arteries provide 80% of total cerebral blood flow to anterior 2/3 cerebral cortex?
which arteries provide 20% of total cerebral blood flow to posterior 1/3 cerebral cortex?
which arteries provide 80% of total cerebral blood flow to anterior 2/3 cerebral cortex?
internal carotid arteries
which arteries provide 20% of total cerebral blood flow to posterior 1/3 cerebral cortex?
vertebral arteries

ICA: branch into: anterior cerebral artery (goes anterior & 2 are connected by anterior communicating artery) & middle cerebral artery
posterior blood supply:
- vertebral arteries come in & merge to form basilar artery. at midbrain, basilar artery –> posterior cerebral artery
which of the following is formed from basilar artery:
anterior spinal artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior cerebral artery
posterior inferior cerebellar artery
anterior cerebral artery
which of the following is formed from basilar artery:
anterior spinal artery
middle cerebral artery
posterior cerebral artery
posterior inferior cerebellar artery
anterior cerebral artery
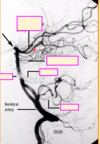
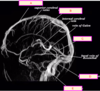
what is D?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery

what is C?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery
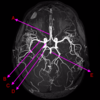
what is A?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery
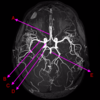
what is A?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery
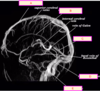
what is E?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery
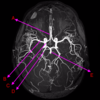
what is E?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery
what is C?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery

what is C?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery

what is B?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery
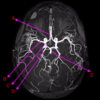
what is B?
middle cerebral artery
basilar artery
posterior cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
internal carotid artery
draw the circle of willis xxx
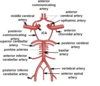
Label A-C

A: anterior cerebral artery
B: middle cererbral artery
C: internal carotid artery
under normal circumstances, what are the anterior and posterior communicating arteries like?
closed !!
classic circle of willis is seen in ~1/3rd pop
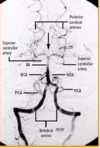
label A-D [4]

A: vertebral artery
B: superior cerebellar artery
C: posterior cerebral artery
D: basilar artery

when does collateral circulation open? [1]
collateral circulation should only open when there is a pressure difference (increased pressure can open anterior / posterior communicating arteries)
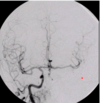
what is most normal variant in cerebral arterial circle? [1]
what is most normal variant in cerebral arterial circle? [1]
one / both posterior communicating arteries are missing (e & f)

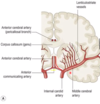
what are the main branches of the internal carotid artery? [4]
- opthalmic artery: orbit & retina. connects to external carotid artery
- posterior communicating: connext with carotid & vertebral artery system
- middle cerebral artery: connects to basal ganglia and lateral 2/3rds of cortex
- anterior cerebral artery: connects with medial side frontal & parietal lobes, anastamoses with MCA
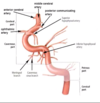
which artery is a branch of the ICA that occurs in the cavernous sinus?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which artery is a branch of the ICA that occurs in the cavernous sinus?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following supplies the basal ganglia & lateral 2/3rd of the cortex?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following supplies the basal ganglia & lateral 2/3rd of the cortex?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following supplies the medial side of frontal and parietal lobes?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following supplies the medial side of frontal and parietal lobes?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following anastamoses with the MCA?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following anastamoses with the MCA?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following connects to the external carotid artery?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following connects to the external carotid artery?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following supplies the corpus callosum?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following supplies the corpus callosum?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
what is A?

cavernous sinus