Retinal Physiology Flashcards
which three layers make the eye tissue? [3]
- outer layer: [2] (front and back?)
- middle layer: [1]
- inner laye: [1]
which three layers make the eye tissue? [3]
- outer layer: sclera (back); cornea (front)
- middle layer: uvea
- inner laye: retina

which of the following is the iris?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the iris?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the uvea?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the uvea?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the choroid?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the choroid?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the ciliary body?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the ciliary body?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the retina?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the retina?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which of the following is the cornea?
A
B
C
D
E
F
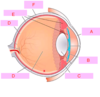
which of the following is the cornea?
A
B
C
D
E
F
which part of the eye is the light sensing organ?
choroid
uvea
retina
sclera
iris
which part of the eye is the light sensing organ?
choroid
uvea
retina
sclera
iris
what is the name for the clear bulging surface in front of the eye? [1]
where does it recieve its nutrition from? [1]
whats the nerve supply like? [1]
what is the name for the clear bulging surface in front of the eye? [1]
cornea
where does it recieve its nutrition from? [1]
aqueous humour diffusion (its avasucular) BUT: richly supplied with nerve fibres
function? [2]
the main focussing surface of the eye: where the refractive index of the medium changes from air to transparent tissue !
what keeps the cornea’s shape? [1]
what keeps the cornea’s shape? [1]
intraocular pressure
what is the name for the white of the eye? [1]
what is the name for the pigmented bit of eye? [1]
what is the name for the white of the eye? [1]
sclera (although interior: brown & grooved)
what is the name for the pigmented bit of eye? [1]
iris

what is the conjunctiva? [1]
what type of cells make up the conjuctiva? [1]
function? [1]
what is the conjunctiva? [1]
layer
what type of cells make up the conjuctiva? [1]
stratified columnar epithelium; goblet cells
function? [2]
mucous secreted: mixes with tears to make more viscous
covers sclera & inside of eyelids

which part of the eye contrains pigment epithelial cells which prevent light scattering and reflection & sits inbetween the sclera and the retina?
iris
choroid
cornea
ciliary body
lens
which part of the eye contrains pigment epithelial cells which prevent light scattering and reflection & sits inbetween the sclera and the retina?
iris
choroid
cornea
ciliary body
lens
which part of the eye contains smooth muscle bundles which shapes the lens?
iris
choroid
cornea
ciliary body
lens
which part of the eye contains smooth muscle bundles which shapes the lens?
iris
choroid
cornea
ciliary body
lens

what is the role of the lens? [1]
how is the shape of the lens changed? [1]
what shape is the lens for:
a) close images?
b) distant images?
what is the role of the lens? [1]
- allows eye to focus on objects at various distances
how is the shape of the lens changed? [1]
- ciliary muscles contract / relax
a) close images: bulges
b) distant images: flat
where are the interneurons and ganglion cells which make up the optic nerve found in the eye? [1]
where are the interneurons and ganglion cells which make up the optic nerve found in the eye? [1]
retina
what is the fovea? [1]
what is the fovea? [1]
centre of the retina: where visual acuity (sensitivty) is highest

what is the blind spot? [1]
blind spot: place where visual axons leave the eye to form the optic nerve, so there are no photoreceptors here

what are the two types of photoreceptors? [2]
which of ^ do you only find in the fovea? [1]
which of ^ are more active in dark? [1]
what are the two types of photoreceptors? [2]
rods & cones (red, blue, green)
which of ^ do you only find in the fovea? [1]
cones
which of ^ are more active in dark? [1]
rods
describe the structre of rods & cones
outer segment: **photoreceptive part
i) rods contain photopigment called rhodopsin
ii) cones contain photopigment called cone opsins**
* *occur in stacked plates**
inner segment: cell body (& mito)

why are rods & cones have stacked free floating discs? [1]
why do eyes require high amounts of oxygen? [1]
why are rods & cones have stacked free floating discs? [1]
maximises the chance of a photon interacting with a molecule of photopigment
why do eyes require high amounts of oxygen? [1]
one of most metabolically active cells in the body
what happens to photoreceptors in the dark? [2]
what happens to photoreceptors in the light? [1]
what happens to photoreceptors in the dark? [1]
constant inward leak of sodium in outerpart of the receptor: keeps the cell depolarised. causes the release of glutamate from its synaptic ending
what happens to photoreceptors in the light? [1]
light hyperpolarises the tonic glutamate release

how does photorecption in rods occur? [3]
- absorbtion of light causes a confirmational change in shape of rhodopsin
- changed rhodopsin then acts via a G-protein to reduced the level of cyclic GMP in the rod
- reduced cyclin GMP: closes sodium channel, cell can repolarise & stop release of glutamate
how does photoreception in cones occur? VIA WHAT?
- contain opsins that absorb light at different wavelengths
- classes of opsins react to different ranges of light frequency: give **colour perception
signal transduction pathway v similar in rods & cones
BOTH DARK DETECTORS**
after photoreception has occured, how does signal transduction occur?
light passes through the & meets intercalated discs of rods and cones: glutamate is continously released from synaptic endings of rods and cones onto bipolar cells in the dark
this release is supressed by light
bipolar cells then depolarise & release NTs onto ganglion cells
ganglion cells project their axons into the optic nerve and therefore signal this light sensation to the brain

which 3 cells cause seeing stuff x
- *photorceptors** (rods & cones - recive light signal & lose inhibitions) that connect to
- *bipolar cells** that connect to
- *ganglion cels** that send axons to optic nerve
blood supply to eye:
- inner retina is supplied by the X artery?
- photoreceptors are supplied by choriod, a network of capillaries supplied by the X arteries? [1]
blood supply to eye:
- inner retina is supplied by the X artery? [1]
- *central retina artery**
- photoreceptors are supplied by choriod, a network of capillaries supplied by the X arteries? [1]
- *cilary arteries
cope for demands of the photoreceptors for oxygen means the retina has DUAL blood supply**
how is oxygen provided to photoreceptors? [1
what else is transported away in the blood supply to the photoreceptors? [1]
how is oxygen provided to photoreceptors? [1]
oxyen diffuses into photoreceptors from choroid capillaires, through the layer of cells called: pigment epithelium
what else is transported away in the blood supply to the photoreceptors? [1]

**old & worn out membranes is constantly being shed at the distal tip of the rods / cones
epithelial cells phagocytose the worn-out ends of the photoreceptors and transfer the debris in the capillaries of the choroid**


which of the following is the lacrimal artery?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is the lacrimal artery?
A
B
C
D
which of the following is the ciliary arteries?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is the ciliary arteries?
A
B
C
D
which of the following is the central retinal artery?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is the central retinal artery?
A
B
C
D
which of the following is the opthalmalic artery?
A
B
C
D

which of the following is the opthalmalic artery?
A
B
C
D
which CN causes the secretion of lacrimal gland?
optic nerve
trigeminal nerve
oculomotor nerve
facial nerve
vagus nerve
which CN causes the secretion of lacrimal gland?
optic nerve
trigeminal nerve
oculomotor nerve
facial nerve
vagus nerve
where do tears enter [1] & exit [1] the eye?
where do tears
enter [1]:
excretory ducts of lacrimal gland
& exit [1]
lacrimal punctum -> drains into lacrimal punctum
the eye?

parasympathetic efferents to the lacrimal glands synpase at the X ganglion? [1]
pterygopalatine ganglion
where is aq. humour made? [1]
where does the aqueous humour of the eye drain into? [1]
what creates intraocular pressure? [1]
where is aq. humour made? [1]
ciliary body (posterior chamber)
where does the aqueous humour of the eye drain into? [1]
canal of Schlemm
what creates intraocular pressure? [1]
caused by the difference in production / draining of aw humour
what is glaucoma? [1]
what raises risk factor of glaucoma? [lots]
what is glaucoma? [1]
drainage of fluid into canal of schlemm is blocked: raises pressure and damges the retina
what raises risk factor of glaucoma? [lots]
over 40
family history
African, hispanic, asian
far / near sighted
eye injury
diabetes
what are the two subtypes of glaucoma?
how doe drug treatments for glaucoma work?
how do u treat? [5]
open angle glaucoma / type 1: slowly progressive condition. trabecular meshwork becomes gradually blocked. normal angle betweeen cornea and iris
primary angle close glaucoma: occurs when angle between cornea & iris is reduced. flow cannot go into canal of schlemm = rapid increase in pressure. sudden pain and visio n loss

what is cataracts caused by?
light catalyses the formation of free radicals -> damages the lens (esp. cuz light is focussed within here)
if levels of antioxidants is reduced in the aq. humour: lens becomes opaque: cataract


where are most photoreceptors found in the eye? [1]
* which bit of blood circulation can you see in eye using opthalmoscope? [1] *
where are most photoreceptors found in the eye? [1]
fovea
* which bit of blood circulation can you see in eye using opthalmoscope? [1] *
inner circulation


