Yr1 Spotter Qs (including Yr 1 Rogo Qs) Flashcards
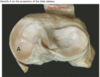
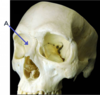
Which congenital heart defect can be identified in this image?
Patent foramen ovale
Atrial septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Ventricular septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot

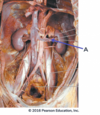
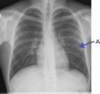
Which congenital heart defect can be identified in this image?
Patent foramen ovale
Atrial septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Ventricular septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot
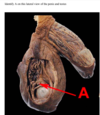
which muscles move the arm into this position? [2]

deltoid
supraspinatous
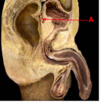
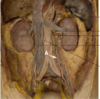
which cranial nerve is affected in this patient?

trigeminal
which segmental level is being assessed here?

S1
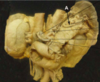
structure E is WHAT? [1]

white ramus
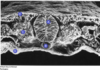
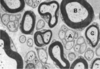
In this cross section of a peripheral nerve, what type of fibre has a morphology as illustrated by C?
- C axon
- A-beta axon
- A-gamma axon
- A-alpha axon
- A-delta axon

In this cross section of a peripheral nerve, what type of fibre has a morphology as illustrated by C?
- C axon
- A-beta axon
- A-gamma axon
- A-alpha axon
* *5. A-delta axon**
Which pathway runs through the region indicated by the asterisk?
- Lateral lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
- Corticospinal tractt
- Spinocerebellar tract

Which pathway runs through the region indicated by the asterisk?
- Lateral lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
* *4. Corticospinal tractt** - Spinocerebellar tract
In order to perform a lumbar puncture, the needle should inserted at position
A
B
C
D
E
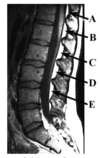
In order to perform a lumbar puncture, the needle should inserted at position
A
B
C
D
E
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow that helps stablise the hip joint
- long head of biceps tendon
- articular capsule
- acetabular labrum
- acetabular ligament
- ligamentum teres

Identify the structure indicated by the arrow that helps stablise the hip joint
- long head of biceps tendon
- articular capsule
- acetabular labrum
- acetabular ligament
* *5. ligamentum teres**
The muscles that produce this movement are innervated by which nerve?
- sciatic
- common peroneal
- femoral
- tibial
- obturator

The muscles that produce this movement are innervated by which nerve?
- sciatic
* *2. common peroneal** - femoral
- tibial
- obturator
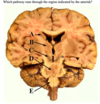
The functions of area B include:
- Control of mastication and facial expression
- Processing discriminative touch sensation from the limbs
- Control of visual and auditory reflexes and conjugate eye movements
- Control of tongue movements, swallowing, coughing and vomiting
- Regulating cortical arousal and sleep wake cycles
The functions of area B include:
- Control of mastication and facial expression
- Processing discriminative touch sensation from the limbs
- Control of visual and auditory reflexes and conjugate eye movements
4. Control of tongue movements, swallowing, coughing and vomiting
5. Regulating cortical arousal and sleep wake cycles

- CT
- MRI
- Myelogram
- Angiogram
- Ventriculogram

- CT
- MRI
3. Myelogram - Angiogram
5. Ventriculogram
what type of tissue is this?
dense irregular fibrocollagenous tissue
2. dense regular fibrocollagenous tissue
3 compact bone
4. cancellous bone
5. hyaline cartilage

what type of tissue is this?
dense irregular fibrocollagenous tissue
2. dense regular fibrocollagenous tissue
3 compact bone
4. cancellous bone
5. hyaline cartilage
The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are located in this section.
A
B
C
D

The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are located in this section.
A
B
C
D
sympathetic action of this would cause pupil dilation
A
B
C
D
E
F

sympathetic action of this would cause pupil dilation
A
B
C
D
E
F
what is A?
- ciliary
ganglion - Edinger
Westphal
nucleus - pretectal
nucleus - sympathetic
ganglion - medial
vestibular
nucleus - oculomotor
nucleus
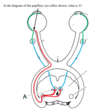
what is A?
- ciliary
ganglion
2. Edinger
Westphal
nucleus
- pretectal
nucleus - sympathetic
ganglion - medial
vestibular
nucleus - oculomotor
nucleus
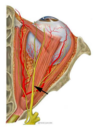
which is the highlighted nerve?
- Optic
- Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal
- Troclear
- Abducens
- Oculomotor

which is the highlighted nerve?
- Optic
2. Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal
3. Troclear - Abducens
- Oculomotor
ID B
- F wave
- Stimulus
artefact - H wave
- M wave

ID B
1. F wave
2. Stimulus
artefact
3. H wave
4. M wave

damge to the blue arrow causes:
- Agraphia
- Expressive aphasia
- Loss of musical appreciation
- Alexia
- Conduction aphasia
- Receptive aphasia

damge to the blue arrow causes:
1. Agraphia
- Expressive aphasia
- Loss of musical appreciation
- Alexia
- Conduction aphasia
* *6. Receptive aphasia**
ID H
- Basal ganglion
- Midbrain
- Thalamus
- Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Fornix
- Pons

ID H
- Basal ganglion
- Midbrain
* *3. Thalamus** - Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Fornix
- Pons
what is A?
- extensor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicis longus
- flexor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicic brevis
- extensor pollicis brevis

what is A?
- extensor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicis longus
- flexor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicic brevis
- extensor pollicis brevis
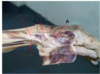
Which spinal curve is exaggerated in this woman?
- lumbar lordosis
- sacral kyphosis
- thoracic kyphosis
- cervical lordosis

Which spinal curve is exaggerated in this woman?
- *1. lumbar lordosis**
2. sacral kyphosis
3. thoracic kyphosis
4. cervical lordosis
what is 10?
- Tibiotalar ligament
- tendon of tibialis anterior
- spring ligament
- Deltoid ligaments of the ankle
- calcaneal tendon
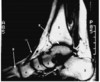
what is 10?
- Tibiotalar ligament
- tendon of tibialis anterior
3. spring ligament - Deltoid ligaments of the ankle
- calcaneal tendon
what is a
- synovial fluid
- nucleus pulposus
- bone
- epiphyseal growth plate
- annulus fibrosus

what is a
- synovial fluid
* *2. nucleus pulposus** - bone
- epiphyseal growth plate
- annulus fibrosus
Identify the structure which prevents adduction of the leg
- A
- G
- B
- D
- F
- C
- E

Identify the structure which prevents adduction of the leg
- A
- G
- B
- D
- F
* *6. C** - E

What muscle group is being tested in this image?
- hip extensors
- knee extensors
- hip adductors
- hip abductors
- knee flexors
- hip flexors

The image below depicts the process of?
Activation of complement
Agglutination
Antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Neutralisation
Opsonisation

The image below depicts the process of?
Activation of complement
Agglutination
Antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Neutralisation
Opsonisation

Antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is the process by which antibodies assist immune cells to identify and destroy infected cells by apoptosis.
What is A?

what is A?
bulobspongiosus
crus of penis
urogenital diaphragm
corpus caveronsum
corpus spongiosum
ischiocavernosus
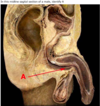
what is A?
bulobspongiosus
crus of penis
urogenital diaphragm
corpus caveronsum
corpus spongiosum
ischiocavernosus
what is the cell indicated?
- mesothelial cell
- syncytiotrophoblast
- mesenchymal cell
- cytotrophoblast
- endothelial cell
- decidual cell

what is the cell indicated?
- mesothelial cell
2. syncytiotrophoblast - mesenchymal cell
- cytotrophoblast
- endothelial cell
6. decidual cell
which cells are indicated by the }
- pellucidal cells
- theca externa cells
- fibroblasts
- theca interna cells
- granulosa cells
- granulosa lutein cells 7. theca l
which cells are indicated by the }
- pellucidal cells
- theca externa cells
- fibroblasts
4. theca interna cells - granulosa cells
6. granulosa lutein cells - theca lutein cells
In the ovary, the first layer of stromal cells that organise around the growing follicle is called the Feedback: theca interna. These theca interna cells help to synthesise estrogens.
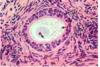
This is an organ of the male reproductive system. The structures cut in cross section here are lined by
acinar glandular epithelium
- germinal epithelium
- simple cuboidal epithelium
- stratified columnar epithelium
- stratified cuboidal epithelium
- pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- stratified squamous epithelium

This is an organ of the male reproductive system. The structures cut in cross section here are lined by
acinar glandular epithelium
2. germinal epithelium
3. simple cuboidal epithelium
4. stratified columnar epithelium
5. stratified cuboidal epithelium
6. pseudostratified columnar epithelium
7. stratified squamous epithelium
This is a diagram of the mature placenta and associated maternal structures. What is indicated by A?
- chorion
- amnion
- stratum basalis of the endometrium
- decidua capsularis
- myometrium
- decidua basalis
This is a diagram of the mature placenta and associated maternal structures. What is indicated by A?
- chorion
- amnion
- stratum basalis of the endometrium
- decidua capsularis
- myometrium
* *6. decidua basalis
The decidua basalis is the maternal part of the placenta derived from the endometrial tissue where the embryo implanted.**
Which cranial nerve innervates the structures that form in the arrowed pharyngeal arch?
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, recurrent laryngeal branch)
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, superior laryngeal branch)
- cranial nerve VII (facial)
- cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal)
- cranial nerve V (maxillary branch)
- cranial nerve V (mandibu

Which cranial nerve innervates the structures that form in the arrowed pharyngeal arch?
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, recurrent laryngeal branch)
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, superior laryngeal branch)
- cranial nerve VII (facial)
- cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal)
- cranial nerve V (maxillary branch)
* *6. cranial nerve V (mandibur branch)**
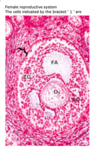
Identify the type of ovarian follicle.
- primordial 2. secondary (antral) 3. Graafian 4. primary 5. atretic 6. growing
Identify the type of ovarian follicle.
1. primordial 2. secondary (antral) 3. Graafian 4. primary 5. atretic **6. growing
A growing follicle has several layers of granulosa cells associated with the large central oocyte.**
This is a cross section through a female pelvis. A is the ischium, B is the pubic body and c is obturator internus. Identify d.
A iliococcygeus
B. coccygeus
C. puborectalis
D. deep transverse perineal muscle
E. internal anal sphincter

This is a cross section through a female pelvis. A is the ischium, B is the pubic body and c is obturator internus. Identify d.
A iliococcygeus
B. coccygeus
C. puborectalis
D. deep transverse perineal muscle
E. internal anal sphincter
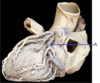
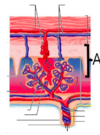
What is the name of the fetal shunt shown in the diagram?
- umbilical vein
- foramen ovale
- ductus venosus
- ductus ateriosus
- ligamentum teres
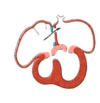
What is the name of the fetal shunt shown in the diagram?
- umbilical vein
2. foramen ovale - ductus venosus
- ductus ateriosus
5. ligamentum teres
The peripheral blood cell that is most involved in the defence against viral pathogens is indicated by which letter?
A
B
C
D
E
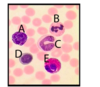
The peripheral blood cell that is most involved in the defence against viral pathogens is indicated by which letter?
A
B
C
D
E
This patient was diagnosed with autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. The cells indicated by the arrows are
- nucleated erythrocytes 2. neutrophils 3. sickle cells 4. reticulocytes 5. spherocytes 6. target cells 7. lymphocytes
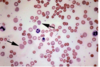
This patient was diagnosed with autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. The cells indicated by the arrows are
- nucleated erythrocytes 2. neutrophils 3. sickle cells 4. reticulocytes 5. spherocytes 6. target cells 7. lymphocytes
A characteristic of haemolytic anaemia is the increased production of red blood cells to compensate for increased destruction. As a result, increased numbers of immature erythrocytes are seen on a blood film. Reticulocytes are such immature red blood cells. They still possess mRNA and so stain slightly bluish and are larger than mature erythrocytes. Also they do not have the mature cell’s bi-concave form yet so don’t have a pale centre.
what is nerve supply to the pleura indicated?
- phrenic nerve
- vagus nerve and greater splanchnic nerve fibres
- pulmonary plexus
- intercostal nerves
- internal thoracic nerve

what is nerve supply to the pleura indicated?
- phrenic nerve
- vagus nerve and greater splanchnic nerve fibres
3. pulmonary plexus - intercostal nerves
5. internal thoracic nerve
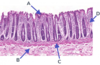
the image of the bronchus from an asthma patient, the arrow indicates
- dense fibrocollagenous tissue
- hyaline cartilage
- basement membrane thickening
- hyperplasia of mucous glands
- bronchus associated lymphoid tissue
- elastic cartilage
- hypertrophied smooth muscle

the image of the bronchus from an asthma patient, the arrow indicates
- dense fibrocollagenous tissue
- hyaline cartilage
- basement membrane thickening
- hyperplasia of mucous glands
- bronchus associated lymphoid tissue
- elastic cartilage
* *7. hypertrophied smooth muscle**
this a pohotmicrogrpah taken of the small intestine, the arrow indicates
- basement membrane
- muscularis mucosae
- lamina propria
- submucosa
- epithelium

this a pohotmicrogrpah taken of the small intestine, the arrow indicates
- basement membrane
- muscularis mucosae
3. lamina propria - submucosa
5. epithelium
Identify the organ of the alimentary system shown in the high power magnification photomicrograph of part of its mucosa.
- stomach 2. large intestine 3. small intestine 4. oesophagus

Identify the organ of the alimentary system shown in the high power magnification photomicrograph of part of its mucosa.
1. stomach 2. large intestine 3. small intestine 4. oesophagus
what is A?
- conjoint tendon
- internal oblique muscle
- inguinal ligament
- spermatic cord
- superficial inguinal ring
- rectus sheath

what is A?
1. conjoint tendon
2. internal oblique muscle
3. inguinal ligament
4. spermatic cord
5. superficial inguinal ring
6. rectus sheath
sheath of connective tissue formed from the lower part of the common aponeurosis of the abdominal internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle, joining the muscle to the pelvis
what is A
- left gastric artery
- splenic artery
- left renal artery
- inferior phrenic artery
- pancreatic artery

what is A
- left gastric artery
2. splenic artery - left renal artery
- inferior phrenic artery
5. pancreatic artery
what type of hernia is shown here?
Indirect inguinal hernia
- Direct inguinal hernia
- Femoral hernia
- Incisional hernia
- Congenital inguinal hernia

what type of hernia is shown here?
- Indirect inguinal hernia
2. Direct inguinal hernia - Femoral hernia
- Incisional hernia
5. Congenital inguinal hernia
ID the structure identified
- cochlear
- vestibule
- incus
- semicircular canals
- stapes
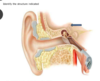
ID the structure identified
1. cochlear
- vestibule
- incus
* *4. semicircular canals** - stapes
what is structure C?
- Anterior Commisure
- Fornix
- Corpus callosum
- Posterior commisure
- Internal capsule

what is structure C?
1. Anterior Commisure
- Fornix
- Corpus callosum
- Posterior commisure
* *5. Internal capsule**
Identify the cranial nerve indicated on this diagram of the dorsal aspect of the brain stem
- trochlear
- abducens
- oculomotor
- trigeminal
- facial
- opthalmic
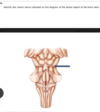
Identify the cranial nerve indicated on this diagram of the dorsal aspect of the brain stem
1. trochlear
- *2. abducens**
3. oculomotor
4. trigeminal
5. facial
6. opthalmic
What is the function of the nerve indicated?
- motor to the muscles of facial
expression - motor to most of the
extraoccular muscles of the
eye - sensory for hearing and
balance - sensory to the pharynx and
the posterior 1/3 of the tongue - sensory nerve of the face and
motor to muscles of
mastication

What is the function of the nerve indicated?
1. motor to the muscles of facial
expression
2. motor to most of the
extraoccular muscles of the
eye
3. sensory for hearing and
balance
4. sensory to the pharynx and
the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
5. sensory nerve of the face and
motor to muscles of
mastication
In the diagram of the pupillary eye reflex shown, what is A?
- oculomotor nucleus
- sympathetic ganglion
- pretectal nucleus
- Edinger Westphal nucleus
- medial vestibular nucleus
- ciliary ganglion
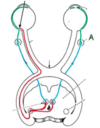
In the diagram of the pupillary eye reflex shown, what is A?
- oculomotor nucleus
- sympathetic ganglion
- pretectal nucleus
- Edinger Westphal nucleus
- medial vestibular nucleus
* *6. ciliary ganglion**
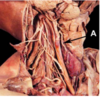
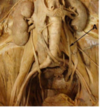
In this anterior dissection of the neck region, identify D
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Sympathetic trunk
- Accessory nerve
- Vagus nerve

In this anterior dissection of the neck region, identify D
1. Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
* *3. Sympathetic trunk** - Accessory nerve
- Vagus nerve
A lesion in the optic tracts will result in which visual field defect
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G

A lesion in the optic tracts will result in which visual field defect
- A
- B
- C
* *4. D** - E
- F
- G
What is A
- Caudate nucleus
- Putamen
- Hypothalamus
- Globus pallidus
- Thalamus
What is A
1. Caudate nucleus
- Putamen
- Hypothalamus
- Globus pallidus
* *5. Thalamus**