HD EOYS9 Flashcards
What pathology causes this slide from testis [1]
Explain your answer [1]

The seminiferous tubules contain Sertoli cells, but none of the characteristic cells of spermatogenesis. Abundant Leydig cells remain in the interstitium.
What is the name for this surgery? [1]

Orchiectomy
What is the name for this surgery? [1]

Orchidopexy
What is the name for this surgery? [1]

Orchidopexy
Which hormone has the following role:
inhibits the synthesis and release of the follicle-stimulating hormone in the pituitary gland and reduces the hypothalamic LH - releasing hormone content [1]
Inhibin
Which of the following type of Nonseminomatous Testicular Tumors causes high hCG
Choriocarcinoma
Teratoma
Yolk Sac Tumor
Embryonal Carcinoma
Which of the following type of Nonseminomatous Testicular Tumors causes high hCG
Choriocarcinoma
Teratoma
Yolk Sac Tumor
Embryonal Carcinoma
A 16-year-old patient presents with increasing testicular pain of 1-month duration. On exam, a left testicular mass is identified. A radical orchiectomy was performed, and the testicular mass was found to have a stroma that was infiltrated with numerous lymphocytes along with extensive hemorrhage and necrosis. Light microscopy reveals a diffuse sheet-like pattern of cells. Which of the following diagnoses is the most likely given this description?
A. Seminoma
B. Embryonal carcinoma
C. Leydig cell tumor
D. Choriocarcinoma
A. Seminoma
Seminoma is the most common pure germ cell tumor and is predominantly found in white populations.
Which two markers are rasied in non-seminoma cancers? [2]
AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) and/or beta-hCG are elevated in 80-85%
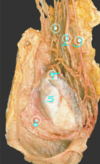
Label A-C

A: Semineferous tubules
B: Tunica albuginea
C: Epididymis



Describe the process of spermatogenesis [5]
Spermatogenesis:
* Division of spermatognia into more spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes via meiosis
* Spermatogonia remain in the basal compartment
* Primary spermatocytes migrate away from the basement membrane and cross in the adjuminal comparment towards the lumen of the ST
* Primary spermatocytes then enter meiosis (prolonged prophase) - which faciliates the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes
* First division creates secondary spermatocytes with 23 pairs of chromosomes
* Secondary spermatocytes divide into haploid spermatids

Name the two stages of spermatogenesis [2]
Spermatogenesis (Spermatogenesis is the process by which an undifferentiated spermatogonium develops into a spermatid)
Spermiogenesis (Spermiogenesis is the process by which a spermatid matures into a spermatozoan)
What is the final product of spermatogenesis? [1]
Haploid spermatid
Describe the role of sertoli cells:
- Structurally [1]
- Which molecules does it produce? [2]
- synthesize androgen-binding protein: keeps testosterone levels high in the ST
- Structural and chemical support to the developing spermatogonia, spermatocytes and spermatids: forms barrier stopping sperm
- produce inhibin: controls amount of FSH produced
Why is there no testosterone produced in prepuberty testis? [1]
No FSH produced so no testosterone produced
Where in the testis do sperm become mobile? [1]
Epididymis
Describe the structure of the ducuts / vas deferens
- Muscular wall comprised of: Inner longitudinal, middle circular, and outer longitudinal
- Pseudostratified cells bearing stereocilia

Seminal vesicles are glandular sacs that produce a secretion that composes 80% of the seminal fluid. Name three productst that are in the secretion produced by the seminal vesicles
Contains fructose, fibrinogen, and prostaglandins (energy for sperm; keeps seminal fluid liquid)
The prostate produces a secretory product containing what? [2]
Citric acid and proteolytic enzymes that prevent coagulation of semen and break down female mucus
In which condition would you see atrophic testis? [1]
Atrophic testes occur in cryptorchidism, when testis fail to descend into the scrotum

Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate: which part of the prostate does it occur in? [1]
Transitional zone has proliferation and hypertrophy

Adenocarcinoma prostate:
Occurs in which zone of the prostate? [1]
How does is it present histopathologically/ [1]
peripheral zone w/ adenocarnioma
Note the malignant glands are generally smaller than benign glands
Benign: L; Malignant: R

Treatment of testicular torsion? [3]
Treatment
* Detorsion
* Orchidopexy (surgical procedure that moves an undescended testicle into the scrotum). Plus contralateral side check
* Orchiectomy (a surgical procedure to remove one or both testicles) 42% during surgical evaluation
What are the two types of testicular cancer & where do they originate? [2]
Which is more common? [1]
Which is more likely to metastasise? [1]
Seminomas:
* Originate in germinal epithelium of seminiferous tubules (germ cells)
* More common
Non-seminmomas
* Yolk sac, embryonal cell, choriocarcinoma and teratomas
* More likely to metastasise