Visual Retinal Processing Flashcards
(10 cards)
receptive field
the region of a sensory surface that, when stimulated, changes the membrane potential of a neuron (the neuron doesn’t have to be physically close to the sensory surface) peripheral cells have a lot of convergence so their receptive fields are larger than cells in the fovea
bipolar cells
do not fire action potentials, two types: OFF- depolarize in response to dark, express AMPA receptors, synapse onto OFF ganglion cells. ON- depolarize in response to light, express metabatropic glutamate receptors (mGluR) that closes a cation channel, synapse onto ON ganglion cells



biopolar cells’ receptive fields
center-surround: always have oppostie responses to the same stimuli
center: direct input from photoreceptors to bipolar cells
surround: indirect input to biploar cells from photoreceptors via horizontal cell

horizontal cells
inhibit photoreceptors in the center of receptive field

depolarization for OFF bipolar cells

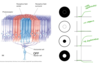
depolarization for ON bipolar cells


retinal ganglion cells
have action potentials, center-surround receptive fields

OFF retinal ganglion cell response to edges

color- opponent ganglion cells
red-green
blue-yellow


