Action Potential Conduction Flashcards
(6 cards)
Na channels open? inactive? closed?
K channels open?
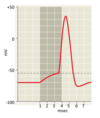

Na channels open? inactive? closed?
K channels open?


Refractory period
absolute: absolutely cannot get another action potential because Na+ channels are inactivated (closed).
relative: can get action potential if have enough depolarization (Na deinactivating)
Axon hillock
place that had to reach threshold for action potnetial to occur. decision is made here
Propagation of action potential
Na channels open and Na rushes into the cell causing depolarization. Na moves to the right in the axon because the Na channels on the left are inactive. More Na channels to the right open. Na channels on the left inactive through ball and chain mechanism. K+ channels open and K rushes out of axon.
Factors affecting rate of propagation
Axon diameter: smaller axon = higher internal resistance = slower rate of propagation.
Membrane resistaace: less leak channels = higher membrane resistance = faster rate of propagation
Myelination: saltatory conduction through nodes of ranvier allow you to not have to generate the action potential as frequently so it can propagate faster


