Sleep Flashcards
(17 cards)
define sleep
readily reversible state of reduced responsiveness to, and interaction with, the environment
electroencephalogram (EEG)
EEG waves are generated by synchronous activity (action potnetial firing) of cortical neurons

generation of synchronized brain rythms
interactions of cotrical neurons
pacemaker activity of thalamic neurons

Sleep stages: wake
high frequency (alpha and beta), low amplitude, little synchronization

Sleep stages: stage 1
very light sleep, occasional theta waves

Sleep stages: stage 2
light sleep, sleep spindles, K complex (first signs of synchrony)

Sleep stages: stages 3 and 4
deep sleep, low frequency, delta waves, high amplitude, lots of synchrony

Sleep stages: REM sleep
dreaming, similar EEG to wake

Sleep architecture

flip-flop model of sleep/wake control
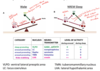
narcolepsy
caused by loss of orexin signaling, inability to stay awake, rapid transition from wake to REM sleep
sleep deprivation
total sleep deprivation or REM depreivation in rats is lethal (most die before 3 weeks)
hyperphagia (increase in food intake) but lost weight
body temperature dysregulation
peripheral abnormalities (fluid in lungs, stomach ulcers, skin lesions)

imporance of sleep quality
human volunteer screened for normal sleep behavior, sleep fragmented for next two nights, increase in sleepiness during those days

memory consolidation
NREM sleep seems to consolidate declaratie memory
REM sleep seems to consolidate procedural memory
(record place cells during sleep- fire in same pattern as they did while in a maze but backwards)

restoration theory of sleep
sleep restores something, but: quiet/restful wake is not a duitable substitute for sleep, and brain is still active during sleep, especially REM
adaptation theory of sleep
evolutionary advantage to sleep (especially animals of prey), but: reduced responsivity to environment is not an advantage, and all animals sleep, including predators
glymphatic hypthesis of sleep
injected tracers (dyes) into a mouse brain while it was either awake or sleeping, much more movement of dyes in sleeping animals, more clearance of toxins during sleep from brain/CSF


