Neurogenesis and axon guidance Flashcards
(11 cards)
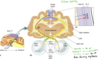
developing telencephalon
ventricular zone: contains radial glia which migrate radially to form excitatory neurons in the cortex
medial ganglionnic eminance: contains stem sells which migrate laterally to form inhibitory neurons

migration of radial glia in ventricular zone
as they divide, cell bodies move up and down
cells may divide vertically or horizontally as the ventricular surface

division of radial glia cells
transcription factor profile determies cell identity
vertical division creates identical daughter cells (more stem cells)
horizontal division creates differentiated cells

radial glia form
cortical neruons and astrocytes
construction of cortex
“inside out”

growth cones
tip of growing axon, have many finger like, actin rich projections called filopodia that explore the environment and have receptors that respond to guidance cues

axon guidance cues
expressed in EC space
chemoattractants: molecules that attract a growing axon, netrin (its receptor is DDC)
chemorepellants: molecules that repel growing axon, slit (its receptor is robo)
receptors determine direction of axon growth
intermediate targets
aka choice points, most have multiple cue types
midline of spinal cord
an intermediate target for motor axons,

axon growth in the absence of robo or DDC
no robo: motor axons circle the midline
no DDC: axons would remain ipsilateral, mirror movement disorder

retinal ganglion cell axons
dorsal- contralateral
temporal- ipsilateral



