Circadian Rythms Flashcards
(11 cards)
two-process model of sleep regulation
process C: circadiam rythm- very regualr, constant pattern
process S: sleep homeostat- irregular, accumulate more and more of a need to sleep throughout the day
TST: total sleep time, SWA: slow wave activity (delta waves)

sleep homeostasis following prolonged wakefulness
increased TST does not equal total sleep lost
deeper NREM sleep: SWA power increases aka slow wave amplitude inreases
measured using fast fourier transorm
types of sleep deprivation (SD)
SD at the beginning of the night targets NREM sleep (NREM sleep recovery prioritized)
SD at the enf of night targets REM sleep (REM sleep recovery prioritized ie REM rebound)
It is possible to selectively deprive REM sleep, but not NREM sleep
circadian rythms
refer to any biological process with cyclical activity lasting ~24 hours
ex. sleep/wake and locomotor activity, body temp, cortisol levels, melatonin release, growth hormone release
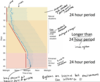
measuring circadian rythms in constant darkness
molecular clock

zeitgeiber
“time giver,” tells us a new day has come or that its night time, outside factors that can shift or reset the molecular clock
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
master clock of the body, all cells have clock but need this to synhronize all of them

intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs)
input to SCN, not important for vision (don’t have photoreceptors or biopolar cells), use melanopsin as photopigment, information about light and circadian timing sent to SCN via retinohypothalamic tract

heritability of SCN function
hamsters: very regular circadian rythms, small size, high number of offspring, behavior is easy to quanitfy (running on wheel)
evidence that SCN rythms are heritable: mutations that affect rythms are passed down to offspring (slight abnormalities run in families), transplantation of a healthy SCN in hamster with mutant SCN shifts rythms


