Audition-Signal Encoding Flashcards
(11 cards)
Three frequency groups
low: 15-500 Hz, middle: 500-5000 Hz, high: 5-200 kHz
path of auditory information
spiral ganglion– (auditory nerve) –> ventral cochlear nucleus-> superior olive– (lateral lemniscus) –> inferior colliculus -> thalamus -> auditory cortex

tonotopy
location of vibration on basilar membrane depends on tone. certain tones then project onto certain sprial ganglion and certion portions of the cortex (like labeled line coding)

how are sounds generally coded for across the basilar membrane?

coding for low frequencies
APs are locked in with the sound wave; the frequency of the sound wave = frequency of sprial ganglion firing
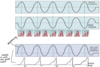
coding for middle frequencies
labeled line and phase locking: high rate of sound waves, APs in a single neuron cannot keep up bc of refractory period, phase locking across a population, by looking at many across a population we can see the frequency of the sound wave

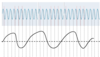
coding for high frequencies
not precise, too many to keep up with, random, labeled line
intensity/ loudness: depolarization and auditory nerve
louder = higher amplitude = more movement of membrane = more depolarization (but not more hyperpolarization)
higher amplitude = more thresholds are reached = more auditory nerve cells actiavted

intensity/ loudness: number of nerves activated across tonotopic map
louder sounds have higher amplitudes so more cells around the main tone must move, causes more activation
location: horizontal plane
low: intraoral time delay or phase shift (difference in time between first and second ear hearing it)
middle: intensity differences
high: can’t tell

location: vertical plane
sound bounces off pinna/ reflects in different directions causing delays


