Action potential Flashcards
(13 cards)
current clamp
measures the membrane potential (difference in charge across the membrane; volts), controlling the amount of current that we are injecting into the cell and see how that affects voltage
voltage clamp
measures net current flow across a membrane (rate of charge flow; amperes), keep neuron at fixed voltage to see how current responds
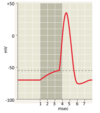
depolarization
a change in the membrane potential from the value at rest to a less negative value, excitatory
hyperpolarization
a change in the membrane potential from the value at rest to a more negative value, inhibitory
The action potential graph (current clamp)

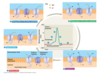
voltage gated channels
open in response to voltag; as we depolarize inside of membrane becomes positive. positive charges in channel want to move away. conformational change in the channel so the positive areas move outwards. channels opens
Properties of voltage gated channels
Na opens quickly, inactivates quickly through ball and chain, deinactivates with slight delay at resting membrane potential; K opens with a delay, does not have inactivation, and closes with a slight delay at resting membrane potential
the action potential
Hodgkin and Huxley
studied the action potential using the squid giant axon, manipulated ion concentration to see what happens to the action potential
Voltage clamp


Voltage clamp: Elimintation of K+


Voltage clamp: elimination of Na+


Toxins that block voltage gated channels
TTX blocks Na, TEA blocks K


