Mental illness Flashcards
mental illness carries the highest disease burden
causes inability to function, affects younger generation more
prevalence
higher in females, symptoms start early and you live with them for a while, difference in ethnicity may be due to access to care and how openly people talk about it

what is considered mental illness?
dysfunction in thinking, emotion, and/or behavior
distrubances distress the person greatly and/or interfere with daily life
categories
anxiety, mood, SCZ and psychotic, dementia, eating, addiction
symptoms of SCZ
positive (adding these symptoms): delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
negative (taking away normal activities): reduced expression of emotion (flat affect), poverty of speech, difficulty in initiating goal-directed behaviors
cognitive: working memory impairment, attention deficit, poor executive function
BUT, no trends to generalize all cases
numbers of SCZ
1% of population, 24 avg age of peak onset, 2.6 mortality odds, 1.4 male vs female, 20 years less of life
dopamine hypothesis
amphetamines- act like dopaine (agonist), overdose causes SCZ like symptoms
dopamine antagonist blocks dopamine receptors- works as a treatment to reduce positive sympotms but has no effect on negative symptoms
I: general hyperdopaminergia
II: frontal hypodopaminergia and striatal hyperdopaminergia
III: D2 receptor related presynaptic dopamine dysregulation that impairs stimuli appraisal, precipiating psychosis symptoms
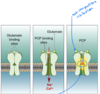
glutamate hypothesis
ketamine and PCP- block glutamate receptors (antagonist)- cause SCZ like symptoms
GABA hypothesis
reduced number of GABAergic neurons

SCZ is heritable

MHC

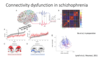
connectivity dysfunction
LISTEN TO LECTURE