Pre-Practical Lecture – Upper Limb Flashcards
(41 cards)
whata re the different parts of the upper limbs?
- Axilla
- Brachial plexus
- Arterial supply, Venous and Lymphatic drainage
- Pectoral girdle - the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side
- Shoulder joint and Rotator cuff
- ARM – anterior and posterior
- Cubital fossa
- Forearm – Anterior and Posterior
- wrist joint and hand
What bones make up the upper limbs?
Clavicle top middle
Scapula on the left
Humorous second form the left
8 carpel bones
Metacarpal phalanges, only proximal and distal in thumb but also got middle in rest of fingers

hwat is found in the axilla?
- Axillary artery & branches
- Axillary vein & tributaries
- Cords & branches of brachial plexus
- Axillary lymph nodes

what clinical problems may occur at the axilla?
- Compression of axillary artery
- Injury to axillary vein
- Enlargement of axillary lymph nodes

the brachial plexus is the network of nerve sof the uppe rlimbs
what makes it up?
Superior, middle and inferior trunk
Goes in-between the anterior and middle scalene
Can do an interscalene block
Need to be aware of hitting arteries and nerves

what are the Main branches of brachial plexus?
Axillary nerve: C5 and C6
Long thoracic : C5,C6 and C7
Thoracodorsal: C6,C7 and C8
Subscapular: C5 and C6

what is the clinical relevance of the brachial plexus?
Clinical:
- Brachial plexus injuries: 1) Upper trunk (C5 & C6) or Lower trunk (C8 &T1)
- Brachial plexus block

Vascular input to the upper limb:
what are the arteries?
Subclavian – left is direct branch of arch of aorta and right is branch of the brachiocephalic trunk
Deep and superficial palmar arteries

Vascular input to the upper limb:
what are the veins?
Cephalic and basilic vein in the forearms
Cephalic vein in-between deltoid and pectoralis major

clinical: what ar ethe different pulse points?

Lymphatic drainage of the upper limb –Axillary lymph nodes
Can get enlargement if infection

Bones and joints of the pectoral girdle
AC joint – Synovial plane
SC joint – Synovial saddle
GH joint – Synovial ball and socket

what are the movements of the scapula?
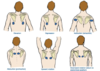
what are the Muscles of pectoral girdle?
Also have a infraspinatus (left arrow)
Scapula no joints, held by muscles
Scapula can easily move around the chest wall
Rhomboid major in middle picture
The anterior muscles include the subclavius, pectoralis minor, and serratus anterior. The posterior muscles include the trapezius, rhomboid major, and rhomboid minor

what is involved in elevation of the scapula?

what is involved in depression of the scapula?

what is involved in protraction and retration of the scapula?

what is involved in rotation elevating the glenoid cavity of the scapula?

what is involved in rotation depressing the glenoid cavity of the scapula?

what makes up the shoulder joint?
Large head and shallow glenoid cavity
Articular surface covered by hyaline cartilage
Lip of the glenoid cavity is called the labrum – fibrocartilage
Synovial joint

what are the ligamens involved in the shoulder joint?
Ligament strength joint on the superior and anterior aspect – coracohumeral (superior) and glenohumeral (anterior)
One of the weakest part of the shoulder joint in the inferior aspect
Coracoaecromial ligament also called arch – prevents upwards displacement of the humorous head – extrinsic ligament, good support for the shoulder joint
Bicep has 2 heads – long head is intracapsular

what are the bursae in the shoulder?
Bursae are synovial pouches
Can get between a muscle and a bone
Protective structure
Extension of the joint cavity or isolated
Subacromial bursae – protects the tendon of the
Subscapular is an extension of the joint cavity
These 2 are important ones
a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous synovial fluid. It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint

what are the msucles of the rotator cuff?
4 muscles
All originate from the scapula
3 attach to the greater tubercle – TIC
Stabilises and supports the shoulder joint
Supraspinatus initiates abduction

what are the msucles of the anterior arm?
Biceps- Flex shoulder and elbow, Supinates forearm
Brachialis – Flexes elbow
Coracobrachialis – flex and adduct Shoulder joint
Nerve: Musculocutaneous C5, C6 and C7
Musculocutaneous – supplies all 3 muscles of the anterior compartment, becomes cutaneous/sensory in the forearm




















