How to Describe a Fracture Flashcards
(31 cards)
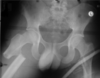
Identification of X ray - what is needed?
- Right person
- Right time
- Right part
- Right views – are they adequate enough to diagnose what you are trying to diagnose
how is identification of a x-ray done?
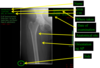
what do you look at in an x-ray?
Cortical outline
Cancellous architecture (make up of bone), also look at pedicles
Soft Tissue (triangles)
Joints (sacroiliac joints and hip joints
Alignment (this patient has scoliosis)
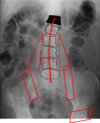
what things are important to look at in a joint?
Joint Space
Cortical outline (shape)
Subchondral bone (bone under cartilage)
Cyst
Osteophytes
Alignment
what things are used to describe a fracture?
- Mechanism & energy of injury
- Skin & soft tissues
- Site
- Shape
- Comminution
- Deformity
- Associated injuries
when describing a fracture, what are radiological features and what are clinical features?
radiological:
- Site
- Shape
- Comminution
- Deformity
clinical:
- Mechanism & energy of injury
- Skin & soft tissues
- Associated injuries
what are the Rules of 2 for Trauma Radiographs?
- 2 views, at 90° to each other (often AP & lateral, but others possible, sometimes obliques)
- 2 joints (above and below)
- 2 bones (if appropriate – e.g. radius and ulna, tibia and fibula)
- 2 occasions (e.g. for scaphoid # which may not show up on initial X-ray, but may be evident 7-14 days later)
when describing a fracutre, how is the site described?
SIDE (RIGHT / LEFT ! – clear & consistently correct)
LIMB
BONE(S)
REGION
ARTICULAR INVOLVEMENT:
- Intra-articular
- +/- Dislocation / Subluxation
- Ligamentous avulsion
- Epiphyseal (in children if epiphyseal injury)
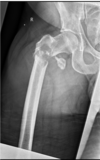
whata re the different sites a fracture can occur? (on a femur)

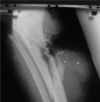
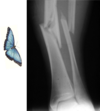
what is shown here?

Left is AP of the elbow, right elbow
Inner side of right elbow in right picture
Olecranon fracture
what are the different shapes (configuration)of a fracture?
TRANSVERSE (usually due to direct trauma/blow)
OBLIQUE (usually due to a bending moment of force)
SPIRAL (always due to a rotational force)
COMPLEX (combination of forces, often causing comminution +++)
what shape of fracture is shown here?
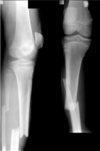
TRANSVERSE (usually due to direct trauma/blow)
AP
Straight
Child due to growth plate
tibia
what shape of fracture is shown here?

OBLIQUE (usually due to a bending moment of force with slight rotation)
Slightly squint
what shape of fracture is shown here?
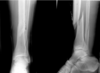
SPIRAL (always due to a rotational force)
Rotates its way up
Spiral fracture
One part of tibia overlapping another
what shape of fracture is shown here?

COMPLEX (combination of forces, often causing comminution +++)
A lot of bits
Maybe 8 different bits of bone
High velocity injuries normally
what is Comminution?
the action of reducing a material, especially a mineral ore, to minute particles or fragments
A comminuted fracture is a break or splinter of the bone into more than two fragments. Since considerable force and energy is required to fragment bone, fractures of this degree occur after high-impact trauma such as in vehicular accidents
is Comminution shown here?

no none
what type of comminution is shown here?
BUTTERFLY
3 bits
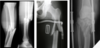
do you get different degrees of comminution?
COMMINUTED +, ++, or +++
Tibia on left, comminuted fracture of the mid shaft tibia and fibula with an associated undisplaced fracture running up into the proximal third
Different degrees of comminution
what type of comminution is shown here?
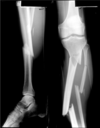
Segmental
3 pieces
Long section in the middle
Left tibia and fibula
Have a particular pattern of healing and one end can fail to heal
what is a deformity?
Definition = movement of distal fragment with respect to supposedly stationary proximal fragment
i.e. Describe what has happened distal to the fracture
what are the different types of deformity? (4 types)
DISPLACEMENT (% diameter of bone)
ANGULATION (degrees)
ROTATION (degrees)
AXIAL DEFORMITY (cm)
a form of deformity is deplacement, how is it assesed?
Has it moved Anterior / posterior / medial / lateral
What percentage of the bone has moved?
Lateral and anterior posterior x-ray
1 you can see fracture of femur at junction of the middle and distal third
1 – undisplaced
2 – lateral displacement of distal femur and no anterior or posterior movement, 50% lateral displacement
3 – on lateral x-ray there is posterior displacement, 80 or 90%
4 – movement posteriorly and medially
When movement in 2 directions then less contact area between bones so longer healing time

another type of displacement is angulation (degrees), how is it assessed?
Anterior / posterior / varus / valgus
n.b. possible composite displacement / angulation – e.g. posteromedial
1 – valgus angulation
2 – moved forward
When angulation the joint forces are important as they are abnormal