Anatomy of the Hip and Knee Flashcards
how would you describe the hip joint?
Strong, Stable, multiaxial, ball and socket type of synovial joint
what make sup the ball of the hip joint?
Ball – Femoral head

What is the socket called?
Socket – Acetabulum (very deep but in shoulder it is shallow)

Head of the femur articulates with the cup-like what?
acetabulum of the hip bone
Depth of the acetabulum increased by what?
Depth of the acetabulum increased by the fibrocartilaginous acetabular labrum and the transverse acetabular ligament

The head is covered with articular cartilage, except for the pit or fovea for what?
the ligament of the head of femur

the Joint Capsule has 3 main ligaments, what are they?
Iliofemoral ligament – Y shaped, prevents hyperextension of hip joint
Pubofemoral ligament- Prevents overabduction of hip joint
Ischiofemoral ligament – From ischial part of the acetabular rim to the neck of the femur

what ligament prevents hyperextension of hip joint?
Iliofemoral ligament
what ligament Prevents overabduction of hip joint?
Pubofemoral ligament
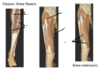
hip movements - what is the chief flexor of the hip joint?
•Iliopsoas (Chief flexor of the hip joint) (psoas major merges with iliacus to form a common tendon and inserts into the lesser trochanter)
what are some other flexors of the hip joint?
- Sartorius
- Tensor fasciae latae
- Rectus femoris
- Pectineus
- Adductor longus, brevis and magnus (anterior part)
- Gracillis
a

Iliacus
b

Psoas major
c

Pectineus
d

Sartorius
e

Adductor muscles
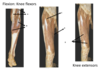
what are the hip extensors?
- Gluteus maximus
- Hamstrings : 1)Semitendinosus,
2) Semimembranosus
3) Biceps femoris – Long head
•Adductor magnus - posterior part
(Extensors of the hip joint and they are the flexors of the knee joint, act on both joints)
name a and b

a - Gluteus maximus
b - Hamstrings
what are the hip adductors?
(Most of these are part of the hip adductor compartment - medial side of thigh)
- Pectineus
- Adductor longus
- Adductor brevis
- Adductor magnus
- Obturator externus
- Gracillis
name a, b and c

a - Pectineus
b - Adductor longus
c - Gracillis
what are the Hip Abductors & Medial Rotators (internal)?
- Gluteus medius
- Gluteus minimus
- Tensor fasciae latae

what are the laterla rotators of the hip?
- Obturator internus & externus
- Piriformis
- Gluteus maximus
- Gemelli
- Quadratus femoris

Gluteus medius and minimus are _______ rotators but the gluteus maxius is a ________ rotator
internal
lateral
what is the Blood and Nerve supply of the hip joint?
- Medial and lateral circumflex arteries – Branches of profunda femoris artery
- Artery to head of femur – branch of the obturator artery supplies medial compartment)
- Nerve supply: Femoral, obturator and superior gluteal nerve