Mini Symposium: Introduction, Spinal Injuries and Cases Flashcards
(50 cards)
what are the different areas of the spine?

what are the vertebra like in different regions?
basic block of the bony
- 3 main types of vertebrae
- similar
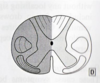
- viewed from above
1. vertebral body – WB surface
2. spinal formamen – conating the cord and later the spinal nerve roots
3. posterior elements, lamina superior and inferior articular procsess
4. Pedicles
5. spinous prcess and trasverese prcoess- allow muscle attachments
Spinal canal in the lumbar is smaller so there is less space for the cord
Laminar long and thin in the cervical region and small and thick in the lumbar region
The transverse processes in lumbar are nearly horizontal but in thoracic area they are oblique and in the cervical region they don’t have them
All vertebra have spinous process, bifid in the cervical region
Facet joints – synovial joints linking the vertebra in the posterior elements, coronal plane in the thoracic region to allow lateral tilting, in lumbar region they are more in sagittal plane which allows forwards flexion and extension
Foramen for the vertebral artery in the cervical region

each individual vertebrae _________ with the level below and above
articulates

thoracic spine is a rigid structure much less flex/ext. but allows _______
rotation

what is the shape of the spine?
7 cervical segments, t12 thoracic 5 lumbar , 5 sacral and variable coccygeal
charcetertistic s shape in sagital plane
cervical and lumbar lordosis balanced by t spine kyphosis
In the coronal plane

what are the muscles around the spine?
Abdominal muscles also act on spine

Nerve emerges at the _________ foramen at each level and if it is compressed it can cause pain that distribution of the spinal nerve
intervertebral

what is a dermatome?
A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by a single spinal nerve
what is a myotome?
A myotome is the group of muscles that a single spinal nerve innervates
how are the dermatomes of the arms different form the legs?

In trunk horizontal distribution but in lower limb more vertical distribution

what are the myotoms of the upper limbs?
C5 - Shoulder abduction (deltoid)
C 6 - Elbow flexion/ Wrist extensors (biceps)
C 7 - Elbow extensors (triceps)
C 8 - Long finger flexors (FDS/FDP)
T 1 - Finger abduction (interossei)
what are the myotomes of the lower limbs?
L2 - Hip flexion (iliopsoas)
L3,4 - Knee extension (quadriceps)
L4 - Ankle dorsiflexion (tib ant)
L5 - Big toe extension (EHL)
S1 - Ankle plantar flexion (gastroc)
spinal inuries
what are different spinal injuries
fracutres (left)
spincal cord injuries - SCI (right)
(C5 translated on C6 on the left picture)

how many people with fractures/dislocation will also have SCI?
- 15% of people with a fracture/dislocation will have SCI
- Majority of people with SCI will have an accompanying column injury
how many spinal cord injuries occur and in who?
- 1000 SCI / year in the UK
- 50 000 people in the UK living with paralysis
- Male > Female
- Peak 20-29yrs
what is the most common causes of SCI?

what symptoms and signs would be seen in a complete SCI?
no motor or sensory function distal to lesion
no anal squeeze
no sacral sensation
ASIA Grade A (most severe group)
no chance of recovery
what symptoms and signs would be seen in a incomplete SCI?
Some function is present below site of injury
More favorable prognosis overall
can you determie acutley if it is complete or incomplete?
NOT ABLE TO DETERMINE ACUTELY AS PATIENT MAY BE IN SPINAL SHOCK
what are the different ASIA Classification?

in ASIA Classification, is grade A or E worse?
A
what are the different patterns of injury that may be seen?
- Tetraplegia/Quadriplegia (above innervation of arms)
- Paraplegia (injury level below innervation of arms)
- Central Cord Syndrome
- Anterior Cord Syndrome
- Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Depends on where injury caused
Bottom 3 are incomplete injury
what is tetraplegia?
- AKA Quadriplegia
- Partial or total loss of use of all four limbs and the trunk
- Loss of motor/sensory function in cervical segments of the spinal cord