Mini Symposium - Fractures 1 (Basics, healing and complications) - Dislocations Flashcards
(15 cards)
what is the difference between a dislocation and subluxation?
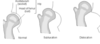
- Dislocation = complete joint disruption
- Subluxation = partial dislocation – not fully out of joint
A = fully contact
B = partial contact
C = no contact

how is the diagnosis made? and what is the management?
Clinical and Radiological diagnosis - history of trauma, Can be hard to tell between dislocation and fracture so use radiological imaging
Associated injuries, soft tissue, musculoskeletal, multi-system
Have nerves that may be injured around it – need to test before to make sure reduction manovers havnt caused nerve damage
Associated injuries - #’s, neurovascular damage- assessment pre post
Emergency treatment
Surgery
Sequelae
Recurrent instability (e.g. shoulder) or stiffness
what are common dislocaitons?

what is the management plan?
Clinical examination and X-ray
N.b. ligament and capsule damage
Associated injuries - #’s, neurovascular damage
(warn of) Recurrent instability (e.g. shoulder) or stiffness
what is shown here?

Squaring off of shoulder
Humeral head dislocated and humeral head lying anterior to the glenoid
what is shown here?
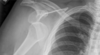
Glenoid superior and humeral head inferior
AP x-ray of right shoulder
No obvious fracture around humeral head
what is hsown here?

Attempt to reduce the shoulder
Many different manoveures
what is shown here?

Posterior dislocation
More uncommon but often missed
Often in people who are electrocuted, grand mal fits, hypoglycaemic fits
Humeral head dislocated posteriorly
Not much seen when looking at patient
When you try external rotate arm you cant do that as humeral head is behind glenoid and it would bang against it and couldn’t continue to rotate
Head looks like a light bulb sign so called light bulb sign
Need 2 views
what is shown here?
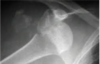
Inferior dislocation
top left is the greater tuberosity that has broken off humeral head when dislocated
what nerves can be dmaged in elbow dislocation?

Olecranon humeral dislocation
Some nerves can be damaged in ulnar dislocation, particularly the ulnar nerve
Watch again!!
what is shown here?

Olecranon prominent posteriorly
Bit of bone came off
what is shown here?

Reduce using manoeuvre
Will pull round the angle and lock into place
what is shown here? and how has it happend?

Hips tends to be a dislocation caused by falls from height or RTA but also in total joint replacement
Hip pushed out of the back and goes posteriorly and the leg shortens
Femur lies internally rotated and adducted
Look subluxed but its not, the head is behind
If fracture then need more careful treatment and would be open reduction as could pull head off the femur
what is shown here and how does it occur?

Direct injury to the knee
Knee extended when examining patient
Dislocated posteriorly and takes outs both cruciates and part of the medial and lateral ligaments and is grossly unstable and if reduce it it wont stay in joint as wont have the soft tissue restraints
Early surgery done to reconstrict the ligaments
Tibia posteriorly
Very severe
Early treatment as vessels are compressed or maybe torn so vascular compromised to the limbs so reduce the leg and see if the vascularity recovers and if not they may need vascular surgery
May have angiogram prior to reduction
what is shown here and its process?
Dislocate laterally most common
Externally rotated
Prominent medial malleolus
Skin over medial malleolus is significantly stretched and if this is left for any length of time, the skin will necrosis and have a large defect over medial malleolus
Medial ligament ruptured
Can get secondary infections and secondary problems
Subtalar dislocation are often very stiff afterwards and take a while to get going and may get secondary osteoarthritis


