Embryology Flashcards
(23 cards)
Early Stages - when does growth of the limbs begin? and what is it due to?
- Begins near the end of 4th week
- Activation of mesenchymal cells in the somatic lateral mesoderm - embryonic connective tissue, undifferentiated
- Homeobox genes regulate patterning - regulate development of the limbs as needs to be precise
what do the upper and lower limbs grow from and when does this occur?
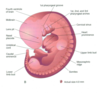
Around cervical and lumbar region you can see upper and lower limb bud
- Day 24 – Upper limb bud appear
- 1 to 2 days later – Lower limb bud appear
Proximo-distal patterning - HOX genes - what is their function?
Regionally expressed in limbs and determine which skeletal element formed HOX gene expression results from a combination of the expression of SHH, FGF’s and WNT-7a
HOXd 9-13 genes expression in upper limb
Remove HOXa 11 and HOXd 11 and the radius and ulna do not form

Limb buds:
- Limb buds elongate by the proliferation of ___________
- Upper limb buds develop opposite the caudal _______ segments
- Lower limb buds form opposite the _____ and _____ segments
mesenchyme
cervical
lumbar
sacral
what is found at the apex of each limb bud?
•At the apex of each bud the ectoderm thickens to form an apical ectodermal ridge (AER)
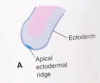
what is the Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER)?
- AER restricted to end of limb bud
- Multilayered epithelial structure
- Exerts an inductive influence on the limb mesenchyme
- The mesenchyme adjacent to the AER consits of undifferentiated, rapidly proliferating cells
- whereas mesenchymal cells proximal to it differentiate into blood vessels and cartilage bone models

Describe the development of hand & foot plates
- The distal ends of the limb buds flatten into paddle-like hand plates and flipper-like foot plates
- By the end of 6th week, mesenchymal tissue in hand plates has condensed to form digital rays
- During the 7th week digital rays are formed in the foot plates

what happens to the skin inbetween the fingers and toes?
Programmed cell death (apoptosis) is responsible for the tissue breakdown in the interdigital regions – mediated by bone morphogenetic proteins

Describe what happens in the final stages of limb development
- Cartilaginous precursors of the limb bones develop by chondrification within the mesoderm in the 6th week
- Primary centres of ossification appear in weeks 8 to 12 in response to growth factors
- Endochondrial ossification for all limb bones except the clavicle (membranous)
Membranous – mesenchymal tissue converts directly to bone
Endochondral – mesenchymal tissue turns into cartilage and is infiltrated by developing blood vessels then turns into bone

what limb rotation occurs?
- Upper limbs and lower limbs rotate
- Upper limbs rotate 90o laterally so that extensors are on the lateral and posterior surfaces (and the thumb is lateral)
- Lower limbs rotate 90o medially so that the extensors are on the anterior surface (and the big toe is medial)

how does the development of the dermatomal patterns of the limbs occur?
During the 5th week, peripheral nerves grow from the developing limb plexus (brachial and lumbosacral) into the mesenchyme of the limbs
Originally the nerves in a vertical arrangements

Birth Defects of Limbs
Often associated with other defects – hereditary or teratogen
what does amelia and meromelia mean?
Total absence (amelia), partial absence (meromelia)
Birth Defects of Limbs
Often associated with other defects – hereditary or teratogen
what does phocomelia mean?
Some long bone absence (phocomelia)
Birth Defects of Limbs
Often associated with other defects – hereditary or teratogen
what does micromelia mean?
All parts present but small (micromelia)
what is this due to?
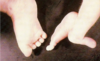
Lobster claw foot can be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait
Critical period of limb development is when?
24-36 days after fertilization
what is Polydactyly?
- Presence of more than 5 digits on the hands or feet
- Extra digit is incompletely formed and lacks muscular development
- May be inherited or teratogen induced
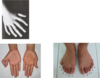
what is Syndactyly?
- Common birth defect of the hand or foot
- Cutaneous Syndactyly (simple webbing between the digits) is a common limb defect
- More frequent in the foot than in the hand
- Osseous Syndactyly (fusion of bones) occurs when notches between the digital rays fail to develop
2 types – cutaneous and osseous. Cutaneous is simple webbing but osseous is to do with joining/fussing of bones
what is Thalidomide and its effects?
- 1957-1962 used as a sleeping tablet and anti-nauseant
- Absence or deformity of long bones (intestinal atresia and cardiac anomalies)
- ‘Sensitive’ period 4-8wks
- Acts by disrupting cell adhesion and angiogenesis
- Now used to help cancer, leprosy and AIDS patients

what is Congenital Clubfoot?
- Also known as TALIPES EQUINOVARUS (Club foot)
- Relatively common birth defect
- Sole of the foot is turned medially and the foot is inverted
- Cause: 1) Multifactorial (genetic and environmental factors)
- 2) ? Abnormal positioning or restricted movement of the fetus’s lower limb in the utero – Evidence is inconclusive
How does Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip occur?
Abnormal development of acetabulum:
- 15% of infants with congenital dislocation of the hip
- Common after breech(buttocks) deliveries -? Breech posture during late part of pregnency (abnormal development of acetabulum and head of femur
Generalized joint laxity:
- Multifactorial
- Associated with congenital dislocation of hip

Case study 1:
A neonate presented with clubfeet. The duty doctor explained to a group of medical students that this is a common birth defect.
- What is the most common type of club foot?
- How common is it?
- Describe the feet of infants born with this birth defect
Case study 2:
A baby was born with syndactyly (webbing between her fingers). The plastic surgeon examined the baby and assured the parents that this minor defect can be easily corrected surgically
- Is syndactly common?
- Does it occur more often in the hands than in the feet?
- What is the developmental basis of syndactyly?


