Anatomy of Lower Leg, Ankle and Foot Flashcards
what are the different muscle compartments?
3 compartment – anterior, lateral and posterior
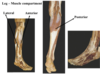
what nevres supply eatch of the muscle compartments?
Each compartment has its own nerve
The sciatic nerve divides into 2 main branches
Deep fibular = anterior compartment
Sup fibular = lateral compartment
Tibial nerve = posterior compartment

ankle joint:
- Most frequently _______ major joint in the body
- Critical in _______ bearing & _______
injured
weight
walking
what type of joint is the ankle joint?
- Hinge type of synovial
- Uniaxial - (having or relating to a single axis) as it is a hinge synovial joint like the knee
where is the ankle joint?
Between the distal part of tibia,fibula & upper part of talus

name all the labels

a - fibula
b - tibia
c - talus
d - lateral malleolus
e - medial malleolus
Metacarpal in hand and _________ in foot
metatarsal
what is the malleolar mortise?
Malleolar mortise formed by lateral and medial malleolus and the lower part of the transverse tibia ligament
- Malleolar mortise with pulley- shaped trochlea of talus
- Malleolar grip is strongest during dorsiflexion

when is the ankle joint unstable?
• Joint is unstable during plantar flexion
Most ankle injuries happen during unstable plantar flexor positions
describe the fibrous capsule and ligaments of the ankle
- Capsule is thin in front & behind
- Supported on each side by strong collateral ligaments
- Medial or deltoid ligament & Lateral ligament

what is the Medial or deltoid ligament like and what is its role?
- Large, strong triangular band
- Three slips from medial malleolus to talus, calcaneus & navicular
- Stabilizes the joint during eversion
one of the strongest ligaments of the ankle

what is the Lateral ligament like?
- Has three slips (2 slips going to the talus)
- Weaker than medial ligament
- Commonly involved in ankle injuries

what are the 2 main acitons of the ankle joint
dorsiflexion and plantarflexion
what muscles are involved in dorsiflexion?
Tibialis anterior
Extensor digitorum longus
Extensor hallucis longus (Hallucis for the big toe and pollicis for the thumb)
Peroneus

what muscles are resopnsible for dorsiflexion?
- Gastronemius
- soleus
- Assisted by plantaris,
- Tibialis posterior
- Flexor hallucis longus
- Flexor digitorum longus

what are different injuries of the ankle that may occur and what causes them?
- Ankle sprains – Inversion injury
- Pott fracture –dislocation of ankle (normally during eversion)
- Footballer’s ankle - repeated strain on the anterior capsule
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (tibial nerve compression – Deep to flexor retinacula)

what is shown here

Plantar Aponeurosis
what is shown by both the arrows?

left - Lateral plantar nerve and artery
right - Medial plantar nerve and artery
what is green and what is purple?

what is the function and structure of the foot?
- Support the body in standing & progression
- Lever it forwards in walking, running & jumping
- Skeleton is divided in to tarsus, metatarsus & phalanges
In big toe only proximal and distal phalanges
In other toes you have proximal, middle and distal
7 tarsal bones (similar to the 8 carpel bones)

what movements occur at the foot?
Inversion & Eversion
Movements occur at subtalar & transeverse tarsal joint
Uniaxial synovial joint

what is responsible for inversion and eversion of the foot
Invertors:-Tibialis anterior & posterior
Evertors :- Fibularis lonus & brevis
what are the arches of the foot and their function?
- Bony arches
- Flexible & deform with each ground contact
- Acts as shock absorbers
- Distribute weight over the foot
- Act as springboards during walking,running & jumping

whata re the different arches of the foot?
- Longitudinal arch –Medial & lateral parts
- Medial longitudinal arch is higher and more important than lateral
- Transverse arch –run from side to side
- All parts act as a unit in spreading the weight

Integrity of the arches is maintained by what?
- Shape of the united bones
- Plantar aponeurosis
- Long & short plantar ligaments
- Spring ligament (calcaneonavicular)
- Intrinsic muscles of foot

what are some clinical problems with the feet and their cause?
- Flat feet – common in children before the age of 3 (due to subcutaneous fat)
- Flat feet are common in old people
- Acquired flatfeet (fallen arches) due to dysfunction of tibialis posterior (arch support)
- High arched foot -congenital



