Anatomy of the Shoulder and Elbow Flashcards
Upper limb more mobile than lower limb due to what?
the pectoral girdle
Pelvic bones give almost zero movement
Push shoulder forward = ???
Push backwards = ???
protraction
retraction
what are the arteries of the arm?

Axilla region, pyramidal shape, on lateral chest wall
How the neurovascular supply enters the upper limb
do they go above or below the clavicle?
below
what are the end nerves of the brachial plexus?
Median, ulnar, radial, axillary, musculocutaneous nerve at end

what do the end nerves of the brachial plexus supply?
Axillary is supplying the shoulder
Musculo-cutaneous is supply flexor compartment of arm
Radial nerve is all extensor muscles nearly
Ulnar – few of the medial muscle in the forearm and the small muscle in the hand
Median – flexor of the forearms
The shoulder girdle consists of what?
the scapula, clavicle and associated musculature
The muscles which move the scapula, and therefore the entire upper limb, take their attachment from the _____
trunk
what are the dorsal muscles?
Trapezius can move the scapula in many different directions by contracting different fibres
Levator scapulae and rhomboid help with elevation
Latissimus dorsi is a huge muscle and eventually attaches on humerus and pulls it down and also pulls on latissimus dorsi

what is the Serratus anterior, its innervation and its function?
Serratus anterior is a protractor
Long thoracic nerve vulnerable in breast surgery and cant hold the scapula. Get a winged scapula as it moves away. Classical clinical sign of injury to long thoracic nerve
a muscle that originates on the surface of the 1st to 8th ribs at the side of the chest and inserts along the entire anterior length of the medial border of the scapula. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax

what is the Ventral musculature?
Actually attaching onto the humerus
Can move all of the pectoral girdle

what is the Glenohumeral rhythm?
Scapulohumeral rhythm (also referred to as glenohumeral rhythm) is the kinematic interaction between the scapula and the humerus

what is the function of the deltoid?
Deltoid produces the contour of the shoulder, and is involved in almost all movements of the arm at the gleno-humeral joint, but chiefly abduction
Fibres running different directions
Attaches at the deltoid tubercle on the humerus
Bring arm out to the side that abduction and back to side is adduction
Anterior fibres pull arm forward which is flexion and posterior deltoid will extent the shoulder backwards
Lateral deltoid abducts

what nerve innervated the deltoid?
Supplied by the axillary nerve - commonly injured in shoulder dislocation
what are the Short scapular muscles: Posterior group?
Supraspinatus fossa and infraspinatus fossa have their muscles in it
Teres major and minor very similar in function
Stabilize the head of the scapula, important for just holding this joint together
Teres major is actually attaching on the anterior side of the humerus, as it is anteriorly attached it pulls the other way, so teres major doesn’t stabilize the shoulder joint due to where it is attached as it does not cross the joint whereas the other 3 do as they pull the humerus into the scapula and prevent it dislocating
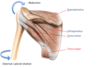
what are the Short scapular muscles: Anterior group?
Normally rib cadge in front - Deep surface of the scapula
Subscapularis crosses the glenohumeral joint and attaches onto the humerus and pulls the humerus in and prevents shoulder dislocation
Provides a location movement on the humerus
The blue blob is where the teres major is attaching
Both attach anteriorly on the humerus so both medial rotators

Key flexors and extensors of the elbow joint - what is the extensor muscle?
One large multi-headed muscle spans the posterior surface of the humerus - Triceps brachii extends the arm and forearm
got 3 heads
Right picture showing the lateral head is cut to show the radial nerve, deep to muscle on the surface of the bone. When you have a midhuemral fracture the sharp edges of bone can damage the radial bone and effects supply to the lower side of the triceps
2 separate parts can be seen, one more medial and one more lateral
Lateral head and the long head
The third head is deep and going down to the bone so not very apparent

what joints does the triceps cross?
Tricpes extends at both the shoulder at the glenohumeral joint and the forearm at the elbow joint
Spans both joints so is a key extensor

where does the triceps attach?
Elbow is the ulnar bone and called the olecranon process of the ulnar bone
Attaches onto that olecranon process

what is the antagonist msucle to the triceps?
Biceps brachii is triceps antagonist, but it does not attach to the humerus, rather attaching from the scapula to the radius
what are the attachemnts and functions of the bicep?
Its attachment on the radius allows flexion and supination of the forearm
Arrow showing long head of the triceps brachii
Supra and infra glenoid tubercle
Good for moving the tubercle in different directions - Allows us to flex and extend
2 heads – long and shorts
Deltoid sits over the top - Long head often covered and looks short, long head attaches at top blue arrow over the top of the humerus
Biceps also crosses 2 joints - Flexor of both
Radius is the bone that is mobile in the forearm
Biceps don’t work when wrist facing down (pronated)
Brachialis is under the bicep and attaches to the ulnar and doesnt matter what position as the ulnar doesn’t move

what is the function of the brachialis and the brachioradialis?
Biceps taken away
All muscles in this region supplied by the musculocutaneous nerve – supplies forearm flexors
Strong in mid position – thumb upwards – holding anything with a handle

what movements are associated with the forearm?
- In the forearm, the ulna is involved in flexion and extension at the elbow joint
- The radius also carries out these movements, but in addition is able to move around the ulna, by articulating at the superior and inferior radioulnar joints
Radius is moving around the ulnar, Ulnar moves very slightly

We have already seen that Biceps brachii is a powerful supinator
Its antagonists are what?
Its antagonists are Pronator teres and Pronator quadratus



