Anatomy of the Hip and Knee - Clinical Flashcards
the hip is a diarthrodial joint, what does this mean?
A diarthrodial joint is one in which the adjoining bone ends are covered with a thin cartilaginous sheet and joined by a joint capsule lined by a synovial membrane, which secretes synovial fluid
the hip is a ______-bearing joint
weight
what type of synovial joint is the hip?
Ball and Socket
the hip is a stable joint enhanced by what?
Enhanced by static and dynamic stabilisers
Static stabilisers– ligaments and shape of the hip
Dynamic stabilisers - muscles
what is the normal angles of the hip?
Neck Shaft ~130deg
Fem Anteversion 15deg
Acet Anteversion 20deg

cover the labels and name the different parts of the pelvis
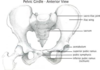
what bones make up the hip?

name the different labels of the surface anatomy

name the ligaments of the hip
Inguinal ligament connects anterior superior iliac spine to pubic tubercle
The iliofemoral ligament is a ligament of the hip joint which extends from the ilium to the femur in front of the joint. It is also referred to as the Y-ligament - most important one

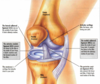
picture showing anatomy of the hip joint
Head of the femur and the acetabulum covered in hyaline cartilage and if damaged it doesn’t repair itself, and if bone exposed you start to get arthritis process

what are the static hip stabilisers?
Bony morphology:
- Congruence
- Anteversion of ball and socket
Labrum
-ve intra-articular pressure
what are the dynamic stabilisers of the hip?
Musculature (never truly NWB-ing)
what are the Hip Flexors, their origin, insertion and invervation?

whats the storngest muscle that flexes the hip?
Psoas muscles is strongest muscles that flexes the hip
what are the Hip extensors, their origin, insertion and invervation?

a

gluteus maximus
b

biceps fomoris
c
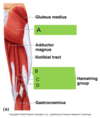
semitendinosus
d
semimembranosus
what muscles make up the hamstring?
biceps femoris
semimembranosus
semitendinosus
what are the Hip abductors, their origin, insertion and invervation?

name a and b
a = gluteus medius
b = gluteus minimus

what are the Hip adductors, their origin, insertion and invervation?

cover the labels and name the hip adductors

what are the Hip Internal Rotators, their origin, insertion and inervation?

what are the Hip external Rotators, their origin, insertion and inervation?

Diagnosing Hip Pathology is done how?
- “C” sign
- Exacerbating Factors
- Worse WB-ing (weight bearing)
- Difficulty tying shoe laces
- Site of pain:
- Trochanteric
- Buttock
- Groin
- Referred

what is shentons line?
If shentons line is disrupted then points to hip pathology

Blood Supply to Femoral Head is done by what?
- Capsule via Medial and Lateral Fem. Circumflex
- Intramedullary
- Ligamentum Teres via acetabular branch of Obturator Artery

how is a extra-capsilar injury managed?
- Always fix
- Blood supply intact

how is a intra-capsular injury managed?
- Blood supply (to femoral head) compromised
- Management based on age of patient, and displacement:
- Undisplaced-Fix
- Displaced and Young – Fix
- Displaced and Old – Replace (either hemiarthroplasty or THR)

what type of joint is the knee and what movements does it do?
• Sophisticated hinge
- Flexion extension primary plane of motion
- But also rotation, varus/valgus, AP translation
is the knee:
- Weightbearing
- diarthrodial
Weightbearing - yes
diarthrodial - yes
is the knee more or less stable than the hip and what does this mean?
- Less stable than hip, more reliant on soft tissue constraints
- Prone to injuries
Bony anatomy of th eknee:
how. many articulating surfaces and what is the ROM?
- 3 Articulating surfaces
- Relatively unconstrained
- Normal ROM -5 – 130deg
Femur, tibia and fibula

what is the patella and its role?
- Largest sesamoid bone in body (Sesamoid bone is a bone placed within a tendon)
- Thickest hyaline cartilage
- 3x body weight through PFJ on stairs, 7x during squats
- Role in increasing extensor lever arm

what is the Knee Alignment?

what are some static some tissue constraints?
Collateral ligaments
ACL/PCL (cruciate ligament)
Capsule
ITB
Meniscii
what are some dynamic tissue constraints?
Quadriceps
Hamstrings
Medial and lateral gastroc.
Popliteus
what is the soft tissue anatomy of the knee
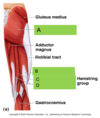
what muscles make up the knee extensors, what is their origin, insertion and inervation?
All are parts/make up the quadriceps

what muscles make up the knee flexors, what is their origin, insertion and inervation?

what muscles make up your hamstrings?
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Biceps femoris
what ar ethe Meniscii?
- Crescent of fibrocartilage
- Avascular centrally
- Medial C-shaped - Less mobile and Firmly attached to tibia
- Lateral “Circular” - More mobile and Unattached at popliteus hiatus
A meniscus is a piece of cartilage found where two bones meet (joint space). Menisci (plural of meniscus) protect and cushion the joint surface and bone ends. In the knee, the crescent-shaped menisci are positioned between the ends of the upper (femur) and lower (tibia) leg bones
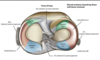
what is the role of meniscii?
- Load Transmission
- Stability - Esp AP translation
- Proprioception
- Shock absorbtion

what are different knee injuries that may occur?
- Meniscal tears
- Ligament injuries
- OCD lesions (osteochondral defects)
- Loose bodies
- Fractures
- Quads/Patellar tendon ruptures

How do ACL injuries occur, how do they present and what investigation is required?
- Knee buckles during pivot
- Unable to play on
- Immediate haemarthrosis (haemorrhage into a joint space )
- Recurrent instability
- X-ray - Haemarthrosis, Segond fracture (a type of avulsion fracture (soft tissue structures pulling off fragments of their bony attachment) from the lateral tibial plateau of the knee, immediately below the articular surface of the tibia)



