Joints and Synovial Fluid and Cartilage Flashcards
what are the different types of joints?
- Fibrous - lots of collagen fibres, densely packed
- Cartilaginous - not that mobile but more mobile than fibrous
- Synovial - the most mobile ones – often these are the joints found in limbs

what are examples of fibrous joints?
not much movement

what are the 2 types of Cartilaginous joints and what makes them up?
- Primary c. joint: only hyaline cartilage
- Secondary c. joint: hyaline & fibrocartilage
what is a Synchondrosis?
Primary cartilaginous joint
only hyaline cartilage
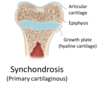
what is a Symphysis?
Secondary cartilaginous joint
hyaline and fibrocartilage

what are common features of a synovial joint?
Fibrous capsule around the synovial joint
Lined on inside with synovial membrane – in green
Articular cartilage on bone surface
In joint space you have synovial fluid

what may some synovial joints contain?
Articular discs
Ligaments - can be in or out the joint capsule
Bursae - fluid filled pillows, variable around joints
name this synovial joint

Plane
name this synovial joint

Hinge
name this synovial joint

Pivot
name this synovial joint

Condylar (ellipsoid)
name this synovial joint

Saddle
name this synovial joint

Ball and socket
what are factors that play a role in joint stability?
- Shape of articulating surfaces
- Capsule & ligaments
- Muscles
e.g. Shoulder is a shallow socket so very mobile but also unstable so can dislocate easily

what cartilage is present in synovial joints?
Knee joint diagram, ooking from superior - lateral right and medial on left
Darker blue is articular cartilage – hyaline cartilage
Meniscus made of fibrocartilage
Wavy fibres in fibrocartilage is collagen, also get some collagen in the hyaline cartilage but cant see them in this photo
Fibrocartilage is stronger due to densely packed collagen

what are the different layers of Articular cartilage (Hyaline cartilage)?
- Superficial/tangential layer: flattened chondrocytes that produce collagen and glycoproteins (e.g. lubricin)
- Transitional layer: round chondrocytes that produce proteoglycans such as aggrecan (really good at binding to water which is important to cartilage)
- Change in collagen orientation from superficial to deep layers
- >75% water (water = incompressible) - Water changes as you age. Water protects tissue from extreme compression and damage
Articular surface at top where the synovial fluid is
Chondrocytes round at bottom and flat at top – cartilage cells (they produce collage fibres, produce molecules that are important of healthy function of the cartilage called lubricin)
Thick black lines indicate the different collagen fibres
At top you find fibres parallel to the superficial surface, Oblique in the middle, Then vertical ones to the bone at the bottom. Makes sense to have the different fibre orientation. Collagen fibres good at resisting tensile strength

‘Who is who’ of important molecules
When carbs (glycans) meet proteins …
what are Glycoproteins (e.g. lubricin)?
proteins to which oligosaccharide chains are attached, i.e. more a protein than a carbohydrate!
‘Who is who’ of important molecules
When carbs (glycans) meet proteins …
what are Proteoglycans (e.g. aggrecan)?
proteins that are heavily glycosylated (= a protein core to which one or more GAGs attach), i.e. tend to be more carb than protein!
‘Who is who’ of important molecules
When carbs (glycans) meet proteins …
what are Glycosaminoglycans or GAGs (e.g. hyaluronic acid)?
long unbranched polysaccharides, which are highly polar and thus attract water
Articular cartilage - what is its thickness and forces?
average: 2-3 mm
interphalangeal joint: 1 mm (Small joints that are not load bearing are thinner than average)
patella: 5-6 mm (small bone but thick cartilage, forces acting on patella is high)
whata re the 3 main features of Cartilage?
- Avascular
- Aneural
- Alymphatic
Transport of nutrients to cartilage?
Removal of waste products?
how is it done?
Synovial fluid produced by synovial membrane (synovium)
tasks are done by the synovial fluid that surrounds the articular cartilage
what is the Synovium?
The synovium, also called the synovial membrane, is the soft tissue. The synovium lines the entire inner surface of the joint, except where the joint is lined with cartilage
- Synoviocytes producing the fluid
- Rich capillary network
- No epithelial lining
→ Direct exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide & metabolites between blood & synovial fluid

what are the different types of Synoviocytes?
type A
type B

what are the features of type A synoviocytes?
- Look like macrophages
- Remove debris
- Contribute to synovial fluid production
what are the features of type B synoviocytes?
Fibroblast like
Main producer of synovial fluid
what are the features of Synovial fluid?
- Viscous fluid
- Hyaluronic acid & lubricin
- Fluid component (from blood plasma)
- Small volumes (knee joint: ̴0.5 ml )
- Rapid turnover ( ̴2 hours)
what are the functions of synovial fluid?
- Nutrition of cartilage (articular c., menisci/discs)
- Removal of waste products
- Lubrication = less friction = less wear
what are the different mechanisms of lubrication?
- Boundary - Glycoproteins such as lubricin bind to receptors on articular surfaces to form a thin film
- Hydrodynamic (like aquaplaning)
- Surfaces kept apart by liquid pressure
- Viscosity changes with load and velocity of movement
• Weeping - Fluid that is present in the cartilage is squeezed out into the synovial cavity to increase fluid volume
what is the coefficient of friction?
Result of these mechanisms working together
Coefficient of friction – quantify the amount of friction between 2 surfaces
Lower coefficient of friction is lower the friction

what are Bursae?
- Synovial membrane
- Fluid-filled
- Reduce friction
- Bursitis (inflammation, painful, not do their job properly)

what happens to your joints as you age?
• Viscosity of synovial fluid increases
- Slower joint movements
- Reduced lubrication
• Water content of cartilage decreases - Reduced shock absorption
→ Less protection of articular surfaces & increased risk of damage
What happens in Osteoarthritis?
Common in elderly
In effected joints – uncontrolled bone growth around the margins of the joint
Bony spurs growing around the margin of the joint
See the same in knee or hips joints affected by this
It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time



