Musculoskeletal Growth/Injury and Repair - tendon injuries Flashcards
Muscle/Tendon - composite unit
what is the structure of a tendon?
- muscle origin (from bone)
- muscle belly
- musculotendinous junction
- tendon
- ± sesamoid bone - e.g. patella
- ± tendon sheath
•tendinous insertion (into bone - Sharpey’s fibres)

how are cells and fibres arranged in tendons?
longitudinal arrangement of cells (mostly tenocytes) and fibres (collagen type 1 - triple helix)

• fascicles of long narrow spiralling collagen bundles
- COLLAGEN BUNDLES covered by ________,
- FASCICLES covered by ________,
- TENDON covered by _______
endotenon
paratenon
epitenon

what is the tendon sheath?
• tendon sheath - e.g. flexor tendons in distal palm and fingers
- tendons connected to sheath by vincula
- synovial lining + fluid (gliding lubrication and nutrition)
- thickenings which form strong annular pulleys (Trigger fingers occurs at A1 pulley)

what is the function of tendons?
- flexible and very strong in tension
- movement is life; immobility reduces water content & glycosaminoglycan concentration and strength
hwo can injury of tendons occur?
- degeneration
- inflammation
- Enthesiopathy – problems where tendons fix into bone
- traction apophysitis
- avulsion ± bone fragment *
- tear - intrasubstance (rupture) *
- tear - musculotendinous junction
- laceration/ incision
- crush / ischaemia / attrition
- nodules
what is an example of tendon degeneration?
e. g. Achilles tendon
- intrasubstance mucoid degeneration
- may be swollen, painful, tender; may be asymptomatic
- ?precursor to rupture
• (rheumatoid arthritis considered elsewhere)

what is an exmaple of inflammation of a tendon?
•e.g. de Quervain’s stenosing tenovaginitis
- tendons of EPB + APL passing through common tendon sheath at radial aspect of wrist
- swollen, tender, hot, red
- positive Finklestein’s test

what is Enthesiopathy?
Inflammation at insertion to bone
Muscle/Tendon - Usually at muscle origin rather than tendon insertion - e.g. lateral humeral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) - common extensor origin
Ligament - Plantar Fasciitis
repetative injury that doesnt repair

what is traction apophysitis? e.g. Osgood Schlatter’s disease
This is the condition where excessive pull by a large tendon causes damage to the unfused apophysis to which it is attached (inflammation or stress injury to the areas on or around growth plates in children and adolescents)
insertion of patellar tendon into anterior tibial tuberosity
adolescent active boys
Recurrent load
Inflammation
what is Avulsion ± bone fragment?
an avulsion is an injury in which a body structure is torn off by either trauma or surgery
- Failure at insertion
- Load exceeding failure strength while muscle contracting
- Mallet finger
- insertion of extensor tendon into dorsum of base of distal phalanx of finger
- forced flexion of extended finger

what is the Treatment of Avulsion?
•Conservative:
- Limited application
- Retraction tendon
•Operative
- Reattachment tendon - Through bone
- Fixation bone fragment

what is shown here and how is it caused?

Intrasubstance Rupture
- tear - intrasubstance - e.g. Achilles tendon
- Load exceeds failure strength
what is the mechanism of rupture?
pushing off with weight bearing forefoot whilst extending knee joint (53%) e.g. sprint starts or jumping movements
unexpected dorsiflexion of ankle (17%) e.g. slipping into hole
violent dorsiflexion of plantar flexed foot (10%) e.g. fall from height
how do you test for Achilles tendon rupture?
“positive” Simmond’s (squeeze) test (if squeeze calf muscle then your foot will plantarflex and if achilies tendon damaged then it wont)
palpable tender gap
(right is normal and left is not)
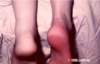
what is a Musculotendinous Junction
Tear?
e.g. medial head of gastrocnemius at musculotendinous junction with Achilles tendon
“plantaris syndrome” (mis-called)
often partial - treated conservatively
occurs with sudden forceful contraction

what is the tremtent of a rupture?
• Conservative:
- Where ends can be opposed (can use ultrasound to see) - Mobilise (partial rupture) e.g. med lig knee, Splint/cast
- Where healing will occur - Not intraarticular
•Operative:
- High risk rerupture
- High Activity
- Ends cannot be opposed
who gets Laceration (incision) and how is it managed?
• e.g. esp. finger flexors (FDS & FDP) - often cutting hands when cutting food
common
males > females
young adults
repair surgically & early - beware old injuries!
“technically challenging”!


