Children’s Orthopaedics - Complex needs - CP, Talipes,Scoliosis Flashcards
what is complex needs?
“A child with multiple and complex disabilities has at least two different types of severe or profound impairment such that no one professional, agency or discipline has a monopoly in the assessment and management.”
how is someone deifnied as having complex exceptional needs?
learning and mental functions
communication
motor skills
self care
hearing
vision
A child or young person (< 19) is defined as having CEN if :
severe impairment in at least 4 categories together with enteral/parenteral feeding
OR
severe impairment in at least 2 categories and ventilation/CPAP
AND
impairments are sustained for more than 6 months and ongoing
what are some complex needs examples with orthopaedic involvement?
(Principles for looking after a complex needs child is similar for all them)
Cerebral Palsy (probably most common)
Spina Bifida
Muscular Dystrophy
Arthrogryposis
Neurofibromatosis (genetic tissue, benign tumours that cause neurological dysfunction)
Syndromes – Downs, Turners….
it is a Multidisciplinary effort looking after someone with complex needs but who is involved?
Wheelchair services
Orthotics
Occupational Therapy
Social work
Physiotherapy
Education support
Community paediatrics
Orthopaedics
Other specialties - Ophthalmology, Audiology, psychology
Cerebral Palsy - An example of a spectrum of needs
what is it?
“A permanent and non-progressive motor disorder due to brain damage before birth or during the first 2 years of life.”
The (brain) lesion is static but the clinical picture is not
Account for 7% of children with ‘complex needs’
Cerebral palsy is the name for a group of lifelong conditions that affect movement and co-ordination. It’s caused by a problem with the brain that develops before, during or soon after birth
what is the incident of CP?
Incidence 2 per 1000 live births
CP epidemiology - what are the different type of causes?
prenatal
perinatal
postnatal
Probably several aspects are causative
Perinatal probably most common cause
CP epidemiology - what are the prenatal causes?
placental insufficiency, toxaemia, smoking, alcohol, drugs, infection such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, CMV and herpes type II (TORCH)
CP epidemiology - what are the perinatal causes?
prematurity (most common), anoxic injuries, infections, kernicterus, Haemolytic disease of new born
CP epidemiology - what are the postnatal causes?
infection (CMV, rubella), head trauma
what are the 2 different types of classification for CP?
physiologic and anatomical
No one classification
what are the different physiologica classifications of CP?
Spastic (pyramidal system, motor cortex) -stiffness
Athetoid (extrapyramidal system, basal ganglia) - movement and cordination problems
Ataxia (cerebellum and brainstem)
Mixed (combination of spasticity and athetosis)
what are the different anatomical classificaitons of CP?
Monoplegia (one limb involved)
Hemiplegia (one side of the body)
Diplegia (lower limbs)
Quadriplegia or total body involvement
what is the CP Classification GMFCS? (Gross Motor Function Classification System)
LEVEL I - Walks without Limitations
LEVEL II - Walks with Limitations
LEVEL III - Walks Using a Hand-Held Mobility Device
LEVEL IV - Self-Mobility with Limitations
May Use Powered Mobility
LEVEL V - Transported in a Manual Wheelchair
What are the issues in CP?
Spasticity
Lack of voluntary limb control
Weakness
Poor co-ordination
Impaired senses (Hearing, Vision, Taste, Touch etc)
What happens as a result in CP?
1. Dynamic contractures
Increased muscle tone and hyper-reflexia
No fixed deformity of joints
Deformity can be overcome
2. Fixed muscle contractures
Persistent spasticity and contracture
Shortened muscle tendon units
Deformity cannot be overcome
3. joint subluxation/dislocation
Secondary bone changes/joint degeneration
what areas are Orthopaedic Priorities in CP?
Spine
Hip
Feet
Torsional problems
Upper limb function
(top 3 first and most important)
what functions are Orthopaedic Priorities in CP?
Maintain Sitting balance,
Improve/maintain Standing posture
Optimise Gait
Gait analysis (in CP) An assessment and monitoring tool
How do you do it?
What are the prerequisites?
…by observation
…by video
…by 3D instrumented analysis
+/- EMG, energy expenditure
Compliant patient, Independent ambulator, >5yoa
what are the 2 different phases of gait?
2 main pahses:
stance
swing

what are some hip problems in CP?
Hips are normal at birth
Hip displacement in 1/3 by maturity
Likelihood of displacement proportionate to GMFCS
Dislocated hips are often painful
Dislocated hips upset sitting posture
Early surgical intervention leads to better long term outcome
The higher the GMFCS =The _______ the risk of hip dislocation
higher

wha is the non-surgicsl treatment of CP?
Posture management - Physiotherapy, Seating
Spasticity management:
- Generalised - Baclofen Oral, Diazepam
- Localised - Botulinum toxin, Baclofen intra-thecal pump)
what are some (surgical) interventions used to manage deformity?
- Soft tissue release:
Adductors
Hamstrings
- Bony realignment:
Varus Derotation Osteotomy
Pelvic Osteotomy
what is the surgical decision on wheather to operate on soeone or not?
Balanced risk discussion
‘Pro’
- Reduced risk dislocation
- Reduced risk pain
- Better seating
‘Con’
- Not all would have gone on to dislocate
- BIG surgery
onto Club Feet also known as what?
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus

how common is club foot and who does it occur in?
Most common congenital deformity
- 1 to 2 in 1000 live births (variable)
- 3 Male : 1 Female (different from DDH which is more common in females)
- 50% bilateral
- Risk for 2nd child 1 in 35
what is the aetiologyof club foot?
Multifactorial
Pressure theories - Oligohydramnios, Abnormal fetal position, Unstretched uterus
Placental insufficiency
Constriction bands
Toxin
Temperature
Infective pathogen (enterovirus)
Drugs
Chromosomal abnormality
Sex-linked
Single dominant
Single recessive
Polygenic
EM radiation
how is a prenatal diagnosis of club foot made?
Often can be diagnosed using pre-natal ultrasound prior to birth
Parents can be counselled before delivery on treatment and the likely outcome
60% of cases may be identified by ultra-sound
50% may have defects in other systems
No relationship to ‘stiffness’ of feet

what are the Traditional Treatment Options?
Strapping - Positional talipes only
Serial casting
Dennis Browne Boots
Surgery:
- Postero-medial release
- Ilizarov frame

than anatomy of club foot - what different things occur?
Cavus - high arch foot
Adductus (midfoot) - mid foot is adducted on the hind foot
Varus (hindfoot) - heal tilted towards midline
Equinus (hindfoot) - toes pointing down
This is the sequence of correction

pictures showing treatment progression
avergae of 5 casts
Applied at weekly intervals above knee
Fix cavus first then adductus then varus then equinus

how is correction of equinus done?
Percutaneous tenotomy (the surgical cutting of a tendon, especially as a remedy for club foot) of Achilles tendon
Tight achillies tendon and foot cant be dorsiflexion
May be divided using small knife under sedation
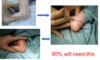
what are trhe outcomes of club foot?
95% of club feet successfully treated
45 year results show that feet are mobile, pain free and plantigrade (90 degrees to the tibia so walking possible)
Results reproduced at major centres around the world
Level 1 RCT (random control trial) evidence
Majority of recurrences due to failure of compliance with splints

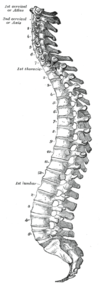
onto scoliosis - What is the normal sagittal spine shape?
Cervical Lordosis
Thoracic Kyphosis
Lumbar Lordosis
Sacral Kyphosis
what is the epdemiology and cause of scoliosis?
Any deviation in coronal plane is a scoliosis
Clinical significance >10 degree deviation (Up to 10 degrees of deviation is normal and is called a scoliotic tilt)
Structural vs non-structural:
non-structural = due to extrinsic cause – a leg length discrepancy (commonest non-structurl cause), a hip problem etc. Resolves when causal factor is addressed
structural scoliosis = abnormal rotation of the vertebrae and is an intrinsic spinal problem. It has a propensity to progress
in scoliosis, first need to decide if structural or non-structural and this is done through __________
examination
in scoliosis, what is the % risk of progression with magnitude and age at presentation
Cobb angle is a radiological measurement made to assess the severity of the curve
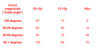
in scoliosis what things indicate a high risk of progession?
Premenarchal (before period)
< 12yoa at presentation
Size of curve at presentation
what ar ethe different classifications by aetiologyof scoliosis?
Congenital (Abnormalities of formation vertebra)
Idiopathic (largest group)
Neuromuscular
Others post traumatic, degenerative, infective, syndromic etc
what is the Classification of Idiopathic scoliosis?
By age at presentation:
Infantile (<3y)
Juvenile (3-10y)
Adolescent (>10y) (probably biggest group and most common in girls)
ho is scoliosis classified by region of spine primarily affected?

what is done on examination of scoliosis?
Inspect posterior torso. Structural scoliosis will look worse when bent forward into flexion
Abnormal neurology or pain should be noted (Pain not normally a feature of scoliosis)
Risk factors for progression:
How is Investigation of scoliosis done?
AP Erect Whole spine +/- Lateral (Tilting films to assess flexibility)
MRI:
Cord abnormalities - Tethering, syrinx (fluid filled cavity), diastematomyelia (bar of bone placed sagittally and transfixes the spinal cord)
Vertebral anomalies - failures of formation and segmentation
Tumours
Early diagnosis …matters because…..
outcomes less favourable from severe curves:
- Cardiorespiratory compromise
- Pain from rib/pelvic abutment
- Seating issues
- Surgical challenge
Neuromuscular causes (esp Cerebral Palsy & Muscular Dystrophy) are at high risk of progression
what is the non-surgical management of scoliosis?
Bracing
Older types Poorly tolerated
Needs to be worn 23/24 hours to work
Delays progression of curve
Custom made
Usually used to delay surgery while spine growing
Particularly idiopathic group - Most common in teenage girls

what is the surgical management of scoliosis?
Complex and extensive
Surgical approaches - Anterior, Posterior, Both
Wake up test (Traditional)
Intra-operative spinal cord monitoring

what are some surgical complications in scoliosis?
Nerve root damage
Cord traction injury
Vascular injury
Degenerative changes later (back ache)
Problems of growth
- Growing rods
- Changing rods
- Crankshaft phenomenon (spine in younger child has been instrumented posteriorly but continues to grow anteriorly and this can cause twisting of the spine as the child grows older



