Obstetrics - UWorld Flashcards
(26 cards)
What is the Definition of Oligohydramnios?
Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) < 5 cm

What is the Definition of Polyhydramnios?
Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) ≥ 24 cm

What are (5) Causes of Oligohydramnios?
- Preeclampsia
- Abruptio Placentae
- Uteroplacental Insufficiency
- Renal Anomalies
- NSAIDs

What are (5) Causes of Polyhydramnios?
- Esophageal Atresia / Duodenal Atresia
- Anencephaly
- Multiple Gestation
- Congenital Infection
- Diabetes Mellitus

What are (3) Complications associated with Oligohydramnios?
- Meconium Aspiration
- Preterm Delivery
- Umbilical Cord Compression

What are (4) Complications associated with Polyhydramnios?
- Fetal Malposition
- Umbilical Cord Collapse
- Preterm Labor
- Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes ( PPROM )

How is Polyhydramnios Diagnosed?
Ultrasound to evaluate a Fundal Height that is LARGER than expected for Gestational Age.

What is (1) Maternal Complication associated with Polyhydramnios?
Respiratory Distress Syndrome from impaired Diaphragm movement.

What are (3) Adverse Fetal Outcomes associated with Polyhydramnios?
- Preterm Delivery
- Macrosomia
- Neonatal Mortality

What is the Clinical Presentation for Pregnancy-induced Skin Changes?
Focal Pruritus (NO rash)
What is the Clinical Presentation for Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy?
Generalized Pruritis with Hand & Foot involvement (NO rash)

What is the Etiology of Pregnancy-induced Skin Changes?
Pregnancy Hormone Changes
What is the Etiology of Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy?
Intrahepatic Cholestasis

What are (2) potential Lab Findings in a patient with Pregnancy-induced Skin Changes?
- None
- +/- Mild Transaminitis
What are (2) potential Lab Findings in a patient with Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy?
- Increased Bile Acids
- Transaminitis

Are there Obstetric Risks associated with Pregnancy-induced Skin Changes? If so, what are they?
None (no obstetric risks)
Are there Obstetric Risks associated with Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy? If so, what are they?
Intrauterine Fetal Demise

What is the Obstetrical Management for Pregnancy-induced Skin Changes?
Expectancy
What is the Obstetrical Management for Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy?
Delivery at 37 weeks

What are (3) Treatments for Pregnancy-induced Skin Changes?
- Oatmeal Baths
- Ultraviolet (UV) Light
- Antihistamines
What are (2) Medicinal Treatments for Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy?
- Ursodeoxycholic Acid
- Antihistamines

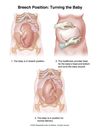
What are (3) Types of Anomalies associated with a Persistent Breech Presentation?
- Uterine anomalies (eg, Leiomyoma, Bicornuate Uterus)
- Placental anomalies (eg, Placenta Previa)
- Fetal anomalies

Many Preterm Fetuses are in Breech Presentation; however, most Spontaneously Convert to Cephalic Presentation when?
At Term (37+ weeks)

If a Preterm Fetus in Breech Presentation does NOT Spontaneously Convert to Cephalic Presentation by Term, what Maneuver should be attempted?
External Cephalic Version (ECV)