Male Reproductive System Flashcards
4 components of the male reproductive system
1) testes
2) duct systems
3) accessory glands
4) penis
4 portions of the duct system
1) ductuli efferentes
2) epididymis
3) ductus deferens
4) ejaculatory ducts.
Function of male reproductive system
1) produce spermatoza and seminal flui
2) endocrine function: testosterone produced inside the testes by laydik cells.
the ductus deferens runs from the __- to the ___.
scrotum to the urethra
Testes are surrounded by a ___ ___ ___ connective tissue capsule called ___ ___
DENSE IRREGULAR FIBROUS connective tissue known as the TUNICA ALBUGINEA.
most capsules in the body are made of what type of CT?
dense irregular fibrous ct.
the tunica albuginea gives rise to CT ___ that divide the testis into about 250 lobuels
SEPTA
function of testes
testes are paired glands with both exocrine (spermatozoa) and endocrine (testosterone) functions in laydik cells.
testes contain ___ ___ which is where sperm cells are produced.
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
Label the image

seminiferous tubule

outline the procession of sperm from the seminiferous tubules
seminferous tubules –> straight tubules –> rete testes –> ducte efferentes –_>epididymis –> vas deferens
the _____ houses the rete testis, which an indentation in the testes where straight tubules run into
the mediastinum
label

Testes slide

each lobule of the testest made of dense irregular fibrous connective tissue contains 1-4 ___ ____. Each tubule is a loop attached by a ____ tubule to the ___ ___, a maze of channels embedded in the medianedatstinum. From the __ ___, sperm moves to the ___
each lobule of the testest made of dense irregular fibrous connective tissue contains 1-4 seminiferous tubules. Each tubule is a loo attached by a STRAIGHT tubule to the RETE TESTIS, a maze of channels embedded in the medianedatstinum. From the RETE TESTES, sperm moves to the EPIDIDYMIS
Each lobule contains 1-4 coiled ___ __, and ___ connective tissue.
seminiferous tubules, and loose connective tissue aka INTERSTITIAL CT
the seminiferous tubules are sites of ____
spermatogenesis
3 cells that make up the seminiferous tubules and function
1) sertoli cells: structural support
2) myoid cells: modified mucus cells
3) spermatogenic cells: makes germinal epithelium which develops into mature sperm cells
which type of epithelium gives rise to mature sperm cells
germinal epithelium
Capsules are made of ____, where as interstitial tissues are made of ____
capsules are often made of dense irregular fibrous connective tissues, whereas interstitial tissues are made of areolar.
____ tissue lies in between seminiferous tubules. Which types of cells and fibers are present in this tissue?
intersitial tissues are between seminiferous tubules. contain:
1) interstitial cells aka LAYDIC cells.
2) fat droplets
3) areolar connective tissue (collagenous and elastic fibers)
surrounding each seminigerous tubules are ___ cells, which contract to help move sperm out of the tubule into the straight tubule
MYOID CELLS.
are spermatogonia diploid or haploid. which types are in a seminiferous tubule?
they are DIPLOID, located near the basement membrane.
type A: on the edges.
type B; a bit less on the edges, has an OBVIOUS nucleus and nucleolus.
Primary spermatocytes undergo _____ and are located_
primary spermatocytes undergo MEOSIS and are located closer to the lumen of the tubule.
label

M- myoid cells
IC= interstitial cells
SC= sertoli cells
SG= spermatogonia
label cell types

observe seminiferous tubule cell types in lab manual

sertoli cells are joined by ___ ___ and are intimately associated with spermatogonia cells. What is the function?
joined by junctional complexes. Functions:
1) protection and nourishment of spermatogenic cells
2) phagocytosis.
spaces between seminiferous tubules are ___ connective tissue. Contains:
loose connective tissue (areolar). contains:
1) lymphatic and blood vessels
2) nerves
3) interstitial cells of leydig which produces testosterone
straight tubules are aka ___ ___
tubuli recti
T/F tubuli recti (straight tubules) contain germinal epithelium
false. but they do have sertoli support cells.
seminiferous tubules are lined with ___ epithelium, whereas rete testes are lined with ___ ___ epithelium and are located within the mediastinum of the testical
seminiferous tubules are lined with GERMINAL epithelium, whereas rete testes are lined with SIMPLE CUBOIDAL epithelium
label

S= seminiferous tubule
T= tubuli recti
R= rete testes (lined with simple cuboidal epithelium)
the rete testes becomes the ___ ___, which opens into the epididymis.
DUCTULI EFFERENTES
2 types of epithelium found in the ductuli efferentes
1) simple columnar ciliated – moves sperm along ducts
2) simple cuboidal non ciliated– might have microvilli for water absorption.
Supported by a thin muscle layer.
Looks a little scalloped because there are patches of cuboidal interspersed with taller columnar cells.
What are these two structures?

R= rete testis. note the cuboidal cells with no germinal epithelium.
E= ducutles efferentes. note the cuboidal and columnar cells.
label

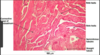
function of epididymis
1) site of sperm storage
2) absorption of water by stereocilia.
what type of epithelium lines the epididymis
pseudostratified columnar epithelium with STEREOCILIA.
function of the PCC epithelium in the epididymis
contains stereociliar that;
1) absorbs water
2) digests residual bodies produced during spermatogenesis.
the epididymis contains ___ ___ that can helpmove sperm towards the ___ ___
smooth muscle that moves sperm towards the ductus deferens (vas deferens)
the epididymis is encapsulated by the ___ ___.
tunica vaginalis. between teh duct of the epididymis and the capsule is connective tissue.
label
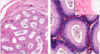
epididymis.
TV= tunica vaginalis capsule
V= blood vessles
DE- ducts of epididymis
arrow: pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
S= sperm bodies
the ductus deferens is also known as the
vas deferens
purpose of vas deferens
conducts spermatozoe from epididymis to urethra.
what type of epithelium lines the vas deferens. what modifications are there?
pseudostratified columnar epithelium with some sparse stereocilia
the epithelium and lamina propria contain ___ ___ which are folded to allow for expansion of the vas deferens (ductus deferens) during ejaculation
elastic fibers
the ductus deferens is covered by ____
adventitia
the ductus deferens forms the ____ after passing over the urinary bladder
ampulla
how many layers of smooht muscle are tehre in the ductus deferens?
3 layers: long, circ, long.
outline the layers of the vas deferens cross section
1) mucosa layer (with elastic lamina propria)
2) inner long SM
3) circular SM
4) outer longSM
5) adventitia.
label
vas deferens
M= mucosa layer
E= epithelium (part of mucosa layer) (pseudostratified squamous epithelium)
LP= lamina propria (Part of mucosa layer)
L-SM= longitudinal smooth muscle
C-SM= circular smooth muscle
A= adventitia
This is most likely a picture of:

vas deferens
3 primary accessory glands of male reproductive system
1) seminal vesicles 2) bulbourethral glands 3) prostate gland (bilobed)
The ejaculatory duct joins the opening of the __ ___ to the urethra. What epithelium is it lined with? Does it have muscle?
ejaculatory duct connects the seminal vesicles to the urethra
lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium. NO MUSCLE
What do seminal vesicles secrete? What type of epithelium?
secretes fructoes, fibrinogen and prostaglandins. contains a mixture of SIMPLE and pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
The seminal vesicles have ___ fibers in the lamina propria and ___ layers of smooth muscle. Do seminal vesicles have a submucosa?
the seminal vesicles have ELASTIC fibesr in the lamina propria and 2 layers of smooth muscle. they DO NOT HAVE A SUBMUCOSA and the lamina propria blens in with the lining and smooth muscle.
T/F the seminal vesicles is surrounded by adventitia
false. glands do not have serosa or adventitia.
what is this?

seminal vesicles: A) low power resolution shows the primary, secondary and tertiary folds.
SM= smooth muscle
LP= lamina propria with elastic fibers
note the simple and and PCC epithlium at high resolution
What kind of structure are the glands in the prostate? What kind of epithelium lines the prostate?
tubuloalveolar glands. lined with simple columnar and PCCC epithelium.
T/F Seminal vesicles have a filler in between the ducts
false. seminal vessicles DO NOT have a CT stroma, but the prostate does have a FIBROMUSCULAR STROMA FILLER
the prostate produces ____ fluid. purpose
prostatic fluid: nutralizes acidic environment of vagina.
an older individual may have ___, which are made of ___ and ___.
CONCRETIONS made of calcified GLYCOPROTEINS and GAGs (glycosaminoglycans)
Label

this is a prostate. note the large amount of stroma made of connective tissue (FIBROMUSCULAR STROMA).
S= stroma
G= tubuloalveolar gland
CA= concretions
LP= lamina propria
E= PCCC epithelium
M= smooth muscle

purpose of the bulbourethral glands? What type of epithelium is it lined with?
produces mucus to lubricate the urethra just before ejaculation. lined with columnar epithlium
the prostate is found
at the root of the penis
the penis has ___ bundles of erectile tissue called:
Where is the urethra in the penis?
the penis has 3 bundles of erectile tissue:
2x corpora cavernosa
1x corpus spongiosum
the urethra lies WITHIN THE corpus spongiosum
each bundle of erectile tissue in the penis is surrounded by the ___ ___ and filled with blood sinuses
surrounded by TUNICA ALBUGINEA
What is this?

Penis.
3 bundles of erectile tissues
CC= corpora cavernosa
CS= corpus spongiosum
U= urethra
Ta= tunica albugenia
s= skin.
What is this? where is this located?

this is the urethra which is found in the corpus spongiosum of the penis
the most primitive cell of the gemrinal cell line
spermatogonia.
spermatogonia divide by mitosis to produce ____ and ___ spermatogonia, and eventually primary ____
type a and b spermatogonia, and eventually primary speratocytes.
primary spermatocytes undergo ____ to produce ___ secondary spermatocytes
undergo MEIOSIS 1 to produe HAPLOID SECONDARY SPERMATOCYTES
secondary spermatocytes undergo ____ to produce____
MEIOSIS 2 to produce SPERMATIDS
Label

A= type A spermatogonia
B= type B spermatogonia
PS= primary spermatocyte
Sz= spermatozoa
Sd= secondary spermatocyte
TP= tunica propria which houses myoid cells for contraction
difference between spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis
spermatogenesis andspermiogenesis is that spermatogenesis is the formation of sperm cells whereas spermiogenesis is the maturation of the spermatids into sperm cells.
spermatids undergo ___ to become spermatozoa
spermiogenesis
spermiogenesis involves the development of an ____ and ____, and phagocytosis of the residual body by ____ cells.
development of an ACROSOME AND FLAGELLA, and phagocytosis of excess cytoplasms by SERTOLI CELLS.


