Lecture 28 - Liver 3 Flashcards
What are the three parts of the portal triad and what is the name for the structure in the middle of the hepatic lobule (hexagon)?
3 parts of portal triad: bile duct, hepatic artery, portal vein Middle structure: central vein
What are the three zones of the hepatic lobule from outside to in?
periportal > mid zonal > centrilobular
What is the name of the structure where bile enters the duodenum?
common bile duct
What is the consequence of disturbances to bilirubin excretion and secretion?
Know as cholestasis - complications include icterus and jaundice and hyperbilirubinaemia
What are the consequences of inadequate conversion of ammonia to urea?
Increased ammonia, decreased urea, hepatic encephalopathy
What are the consequences of defects in protein synthesis?
Hypoalbuminaemia and decreased clotting factors (coagulopathy)
What are the consequences of abnormal carbohydrate and fat metabolism?
Hypoglycemia. May see decreases cholesterol and hepatic lipidosis
What is a consequence of acquired portosystemic shunting?
Hepatic encephalopathy
What is a consequence of portal hypertension?
Ascites
What is a consequence of abnormal metabolism of chlorophyll?
Secondary (type III) photosensitisation (herbivores)
What is a consequence of Kupffer cell activity?
Increased bacteria entering the circulation
What is the functional reserve of the liver?
70-75%
What is the main cause of pre-hepatic hyperbilirubinaemia and provide an examples of a bacterial and parasitic agent causing this?
IMHA = immune mediated haemolytic anaemia Bacteria: Rickettsia Parasitic: Babesia
What is an example of a specific post-hepatic condition that could cause jaundice?
Bile duct obstruction - pancreatitis or choleliths
What is an example of viral agent that could cause random focal hepatocellular necrosis?
Herpes
What is an example of a protozoa that could cause could cause random focal hepatocellular necrosis?
T.gondii
Provide an example two bacteria that could cause random focal hepatocellular necrosis?
Salmonella (S.dublin in cattle) Clostridium piliforme
Name the condition that is shown below:

Zonal hepatocellular degeneration/necrosis
Name the type of zonal pattern that is shown below, comment on its frequency what processes are you considering and why?
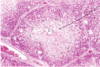
Common - Centrilobular degeneration/necrosis - should be considering hypoxic or toxic insult - least oxygenated blood (hence most suspectible to hypoxia) and contains the greatest concentration of mixed function oxidases
Name the type of zonal pattern that is shown below:

Paracentral degeneration/necrosis
Name the type of zonal pattern that is shown below and provide a potential aetiology:

Midzonal degeneration/necrosis - rarest caused by some toxicities e.g. aflatoxicosis
Name the type of zonal necrosis that is shown below and what is a characteristic of a toxin that would cause this?

Periportal degeneration/necrosis - caused by direct exposure toxins that do not require metabolisation with MFO’s
What type of zonal necrosis is shown in the image below?

Bridging degeneration/necrosis









