Dermatology Lecture 1 Flashcards
What is the normal colour of a dogs skin?
Normal colour of a dogs skin is typically whitish-grey colour
What is erythema?
Erythema = skin that appears to be redder than normal
What is hyperpigmentation?
Skin that is darker than normal - leading to black/coloured skin
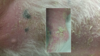
Describe the change that is shown below:

Erythema
Name the change that is shown below:

Erythema
Name the skin condition that is shown below:

Erythema
Name the skin condition that is shown in the image below:

Hyperpigmentation
Name the condition that is shown in the skin below:

Hyperpigmentation
Name the condition that is shown in the image below:

Hyperpigmentation
Name the condition that is shown in the image below:

Hyperpigmentation
Name the condition that is shown in the image below:

Hyperpigmentation
Name the condition that is shown in the image below:

Loss of pigment
Name the condition that is shown in the image below:

Loss of pigment
Name the condition that is shown below:

Loss of pigment
Name the condition that is shown below: (hint combination of three things)

Rash - collection of skin lesions - erythymatous macules, papules and pustules
Name the conditions that are shown below and provide a definition of it:

Erythematous mascule: circular, flat area pf erythematous skin - up to 1 cm in diameter
Name the condition that is shown below and define it:

Papules - small, red, raised, circular solid mass less than 1 cm in diameter
Name the condition that is shown below and proivde a definition of it:

Pustule - red, circular spot containing a central, yellow sac of pus
Name the condition that is shown below and provide a definition of it:

Staphylococcal ring
Name the two ways in which allopecia can arise:

- Alopecia - common presenting sign - spontaneously/or secondary to pruritis
- Spontaneous allopecia - sign of disorder affecting hair follicle - follicular infections and endocrine disorders
Name the condition that is shown below:

Focal alopecia
Name the condition that is shown below:

Regional allopecia
Name the condition that is shown below:

Multifocal allopecia
Name the condition that is shown in the image below:

Symmetric diffuse truncal allopecia