Dermatology Lecture 5 Flashcards
(11 cards)
What are the two main causes of alopecia?
Alopecia can be differentiated into two main categories: - excessive hair loss (mostly inflammatory) - inadequate production of hair
How can a trichogram be used to differentiate between the cause of allopecia?
Is animal is pruritic - the tips of the hair will probably be broken off - if the hair is falling out for any other reason the tips of hair will be tapered (normal)
Describe how a diagnosis of inflammatory alopica (folliculitis) can be made:
- Look for the presence of inflammation and/or primary lesions such as papules or pustules, scale and crust, epidermal collaretes
- Pattern of hair loss - patchy, focal-to-mutlifocal (“moth eaten”) alopecia
- Pattern of hair loss - long haired animals - increased shedding + dull hair coat
Briefly explain how furunculosis will appear:
- When furunculosis develops - entire follicular wall is destroyed - erythematous nodule in dermis - associated with hair loss
Name the conditon that is shown below:

Furunculosis
Name the lesion that is shown below:
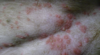
Bacterial folliculitis
What is deep bacterial folliculitis and what is a potential sequaelae to it?
- Inflammation of entire hair follicle w/or without furunculosis
- Deep follicular inflammation leads rupture of hair follicle + granulomatous foreign body response
Name the lesion that is shown below:
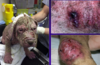
Bacterial folliculitis
What is dermatophysis?
Dermatophysis - superficial infection of hair, skin + nails - results in alopecia, scale, crust and erythema
What is the cause of dermatophytosis?
Direct transmission of fungal spores to the host
What is follicular dystrophy and when is it likely to be apparent?
- Follicular dysplasia - abnormal hair shafts and/or hair follicle malformation - altered hair quality and alopecia
- Clinical signs are likely to be present during the anagen phase


