Diagnostic cytology Lecture 1 Flashcards
What method of fine needle aspiration is likely to yield the best results?
Non-aspiration method - samples are often better quality than those obtained with aspiration - needed in poorly exfoliating areas
What cell types are best suited to cytology?
Round cells + epithelial cells tend to exfoliate more readily yielding good cellularity
What are the five general categories of cytologic interpretation?
- Non-diagnostic - cannot make an interpretation based on it 2. No cytologic abnormalities - cells are present in normal numbers + no significant criteria of malignancy 3. Inflammation - inflammatory processes classified by type of inflammatory cells in the lesion 4. Hyperplasia/dysplasia - increase in the number of cells in a tissue 5. neoplasia
What is the steps in creating a microscopic description in cytopathology?
- Comment on the background 2. State the predominant cell type and distribution that is seen 3. State predominant cell features 4. State minor cell population + features 5. Non-cellular features 6. Organisms
What is are the features of a suppurative cytopathology slide and what could be a differential?
> 85% neutrophils - non-degenerative neutrophils - resembling those in blood w/condensed + clumped chromatin Ddx: immune-mediated conditions, sterile irritants (bile + urine), bacterial, protozoal or fungal infections
Name the predominant cell type that is shown below:

Non-degenerate neutrophils
Name the features shown in the neutrophils below:

- Pyknosis
- Karyorhexis
- Karolysis
What type of reaction would it be if the cells shown below were the primary cell type?

Histiocytic/macrophagic
What are the implications of observing erythrophagocytosis versus haemosiderophagocytosis in tissue?

Erthrophagocytosis: indicated recent haemorrhage (<24 h)
Haemosiderophagocytosis: haemosiderin represents storage form of iron + originates from phagocytosed RBCs - supports prior haemorrhage (>24h duration)
What type of inflammatory reaction is shown below?

Pyogranulomatous - characterised by mixture of neutrophils+ macrophages - neutrphils typically non-degenerate
What types of cells are seen in lymphocytic or lymphoplasmacytic inflammation?
Mixture of mostly small lymphocytes along with plasma cells
Differentials: antigen/immune stimulation (e.g. tick bite, viral infections or chronic inflammation)
What are the main cytoplasmic criteria of malignancy that are seen?
- Variation in size - anisocytosis
- Variation in cell shape - pleomorphism
- Cytoplasmic colour - basophilia
- Increased nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio
- Variation in nuclear size - anisokaryosis
- Increased mitotic figures
- Chromatin pattern: clumping
- Multi-nucleation
- Abnormal mitosis
- Nuclear moulding
What is shown in the image below?

Abnormal mitosis
What cell type is shown below?

Round cells
What cell type is shown below?

Epithelial cells
What cell type is shown below?

Mesenchymal
Name the neoplasm that is shown below and state three unique characterisitics of this cell type:

Plasmacytoma:
- Round to slightly oval cells
- Distinct cell borders
- Blue cytoplasm + perinuclear clear zones
What type of neoplasm is shown below?
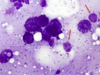
Mast cell tumour (MCT) - Backgorund is filled with granules from ruptured cells
Name the neoplasm that is shown below (include grade):

Mast cell tumour (Grade 1)
Name the tumour that is shown below:

Mast cell tumour (MCT) grade 2
Name the type of neoplasm that is shown in the image below:

Mast cell tumour (Grade 3)
Name the neoplasm that is shown below:

Histiocytoma - sponataneous regression often occurs due to a cytotoxic T-cell immune response
Name the neoplasm that is shown below:

Transmissible venereal tumour (TVT)
Name the neoplasm that is shown below:

Transmissible venereal tumour (TVT)











