Week 7 - Week 7 - I.T.S Breast - Benign disease (fibroadenoma), Postnatal problem, Breast cancer (Pagets & cancer in pregnancy) Flashcards
CASE 1 History : A 35 year old woman with no family history of breast disease comes to your office with a complaint of a left breast mass of one month duration. She has regular periods, and no change in the mass was noted through one menstrual cycle. The mass is located in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. It is smooth, non-tender, very mobile with no skin retraction, no fixation to the chest wall and examination of both axillae is negative. Question 1 What is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
Most likely diagnosis is a fibroadenoma
Question 2: What are risk factors for development of benign breast disease?
No obvious risk factors - nullparity maybe
Question3: What investigations will you perform as a next step? and as for diagnosis?
As history and examination have already been taken
Would perform an ultrasound scan is this patient is younger than 40 years old Breast ultrasound as patient under the age of 40.
- Mammograms are of no benefit as the breast density of young women is too high and will hide small opacities or speculated masses..
Ultrasound guided core biopsy for tissue diagnosis.
Question 4: What is the next step in management for this patient ?
Conservative manageement especially as she has no other symptoms Advice self examination to check if there is an increase in size at all
Question 5: The histology result shows Fibroadenoma of the breast. Can you describe what a fibroadenoma is?
A fibroadenoma is the benign overgrowth of fibrous collagenous mesenchyma tissue from of one breast lobule resulting in the formation of a lump
Question 6: Can you remember advice for self breast examination? Use pictures provided to remind yourself.
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/picture2jpgpngjpg-1627195556922D9450E.png

CASE 2 History: A 40 year old woman comes to emergency maternity triage with history of painful and swollen breasts. She has delivered normally vaginally 5 days ago in Midwifery led unit. There were no complications antenatally or during labour. She feels unwell and says she had rigors for the last 4-5 hours Question 1: Discuss in brief Physiology of lactation in response to suckling
Suckling reflex acts on the higher cerebral centres -it inhibits the release of prolactin inhibitory hormone therefore increasing prolacin which causes milk production in the breast The higher cerebral centres also stimulate production of oxytocin in hypothalamus which is stored in posterior pituitary to be released and this cause contraction of smooth muscles in breast to cause milk ejaculatory reflex
Apart from the higher cerebral centres responding to the babies suckling for milk production and ejection, what else will it respond to?
The higher cerebral centres will respond to the sound of the babies cry

History: A 40 year old woman comes to emergency maternity triage with history of painful and swollen breasts. She has delivered normally vaginally 5 days ago in Midwifery led unit. There were no complications antenatally or during labour. She feels unwell and says she had rigors for the last 4-5 hours Question 2: How will you assess this patient? Question 3: What is the differential diagnosis?
History and examination of the patient
Also will carry out a NEWS score to make sure she has no signs of infection and rule out other causes of infection ie uterine tenderness
- Mastitis, engorgement, abscess, blocked ducts
On examination.
A lot of her left breast is swollen, red & very tender to induration with a possibility of an abscess at the base of the breast.
Q 4: She has following Observations: P- 130/min, BP- 90/50, Temp- 39.9 ̊C. , RR- 20/min.
- With the chart provided (Sepsis 6 bundle) decide the next immediate course of action?

Initiate the sepsis 6 protocol now
- Monitor urine output and give fluids
- Take bloods for culture and give IV antibiotics
- Measure lactate dehydrogenase and give high flow oxygen

The 2016 consensus definitions recommend that the SOFA criteria should replace the previously recommended SIRS criteria. Furthermore, the ‘quick’ (q)SOFA criteria are recommended for use outside of the ICU setting to promptly identify patients with suspected infection who are likely to have a poor outcome. What is the difference between the SOFA criteria and the SIRS criteria?
If >/=2 SIRS plus infection likely - think SEPSIS
- Altered mental status, resp rate >20, Temp 38, Known/suspected neutropenia, heart rate >90, WBC 12
If the SOFA has at least 2 of the three scores, poor prognosis -
- Resp rate >/= 22, Altered mental status, Systolic BP =100
Question 5: What will you advice the patient regarding breast feeding and preventative measures?
Start breast feeding as soon as possible Breast feed as often as possible and massage the breasts if sore If unable to feed then express milk into a bottle
Question 6: What are the advantages of breast feeding?
There are health benefits for both mother and child
- Baby
- * Less GI infections and ear infections
- * Higher IQ
- * Less chance of obesity and hence type 2diabetes
- * Less atopic infections
- Mother
- * Lowers risk of ovarian and breast cancer
- * Helps form strong bond and saves money on formula
CASE 3 History: A 55 year old lady presents with a left retracted nipple and discoloration around it. She has noticed a small lump underneath the areola causing disfiguration of the breast areola. She also claims that she has noticed an itchy rash. She is otherwise fit and well. She has not experienced weight loss. She is hoping for some reassurance. Question : How will you investigate this patient?
Investigate with mammogram and tissue guided diagnosis with core biopsy Possibly cancer staging may be required also
Histology shows Paget’s disease of the breast. Question 3: How will you explain the diagnosis to the patient?

This is a high grade ductal carcinoma in situ that has invaded the nipple - ie the cancer cells started off in her lactiferous ducts and have spread to the nipple region of the breast - often causes eczematous like changes and can cause nipple retraction
We will have to consider carrying out surgery and some radiotherapy to treat the non-invasive cancer
In Paget’s disease of the breast, on histology the cells are often stained using a special stain which look for what?
The cells are often stained for low molecular weight glandular cytokeratins
Cytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue
This is seen in Pagets disease of the nipple on core biopsy
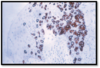
Question 4: What is the next step in management of the patient ?
It is treated just as ductal carcinoma in situ is Surgery - excision of the whole complex (be it mastectomy or wide local excision) and follow up the WLE with adjuvant radiotherapy
CASE 4 History: A 36 year old lady, 24 weeks pregnant, presents with a breast lump. On examination she has a distinct lump in her right breast. There is also some discoloration of the skin and puckering over the lump. Recently she has also noticed intermittent blood-stained nipple discharge. Question 1: From the diagram remind and discuss the lymphatic drainage of the breast.
The majority of lymph drainage from the breast goes to the axillary lymph nodes - 75% and most of the rest goes to the parasternal lymph nodes It is the anterior axillary nodes (lateral and inferior to pec minor) which drains the breasts and these drain to the central axillary nodes (posterior to pec minor) and this drains into the apical axillary nodes (superior and medial to pec minor)
You have done a biopsy and it shows Ductal Carcinoma in situ of the Breast Question 2: What are the ethical challenges that face the woman?
* Continuation of pregnancy * Termination * Potential progression of her disease * Her ability to look after her child during treatment * The effects of treatment on the child
Referral to breast specialist team. Any imaging or further tests should be conducted inconjunction with the multidisciplinary team. When is it safe to carry out breast: Surgery? Radiotherapy? Chemotherapy?
Surgery - this is safe to carry out in all trimesters
- Can opt for mastectomy or breast conserving surgery, although if mastectomy, breast reconstruction is usually delayed due to prolonged analgesia
Radiotherapy is contraindicated until delivery unless it is life saving or to preserve organ function (e.g. spinal cord compression)
Chemotherapy - contraindicated in first trimester but is safe from second trimester
When is it safe to provide hormonal treatment?
Tamoxifen and trastuzumab are contraindicated in pregnancy and should not be used. Women should not breast feed if on tamoxifen or trastuzamab and should not breastfeed whilst having chemotherapy
How long should woman allow after the last dose of chemo before breastfeeding?
Woman should allow 14 days before breastfeeding after last chemo dose
When is recurrence of breast cancer most common in women and therefore how long should woman wait after treatment before trying to conceive again?
Recurrence is most common in the 2-3 years after breast cancer and it is advised woman wait at least this long before trying to conceive again
How long before trying to conceive should the woman stop taking tamoxifen?
;conception during tamoxifen therapy should be avoided because of potential teratogenicity, and a ‘washout period’ of 2–3 months is advised.


