Week 5 - C - Healthy Term Infant/Normal Newborn Care - APGAR, Vaccination, Guthrie Test, Neonatal Examination Flashcards
(48 cards)
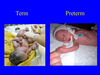
When is a baby said to be term?
A baby is said to be term from 37+0 weeks until 40+6weeks of gestation This is the NHS guidelines on what a term pregnancy is, if any other of the flashcards state differently, then this is the correct one
What is the normal weight for a newborn baby? (in both kilograms and in pounds/ounces) WHat is foetal macrosomia?
Normal weight - 2.5kg (5 pounds 8 ounces) to 4kg (8 pounds 13 ounces) Greater than 4kg is foetal macrsomia Less than 2.5kg weight is a low birth weight .A baby diagnosed with fetal macrosomia has a birth weight of more than 8 pounds, 13 ounces (4,000 grams), regardless of his or her gestational age.
What is large and small for gestational age?
Large for gestational age - when the baby weighs greater than the 90th centile for their gestational age Small for gestational age - when the baby weighs less than the 10th centile for their gestational age
What is the approximate fat gain per day in the last 4 weeks of pregnancy leading to the baby being term?
What are the two different types of fat that accumulate in the baby?
Approximately 7grams of fat are gained per day in the 4 weeks leading up to a term pregnancy
- White fat - this mainly has calories for the baby
- Brown fat - accumulates between scapulae and internal organs - mitcohondria packed and burns energy to produce heat for the neonate
Pre-term has a lot less fat
In the labour environment, the uterine contractions cause the baby to become slightly hypoxic with each contraction How does the foetus attempt to overcome this?
Foetal haemoglobin releases oxygen much more readily than adult and therefore this is used to try and combat the hypoxia with each uterine contraction
When the foetus is born there are some perinatal adaptions in the foetus What do these include?
Due to the first breath/cry, there is alveolar expansion in the lungs with a decreased pulmonary vascular resistance to allow more blood to go to the lungs The decrease in the resistance causes the pressure in the right atrium to become less than that of the left atrium and therefore the foreman ovale closes Circulating prostoglandins decrease and ductus arteriosus closes also There is an increased partial pressure of oxygen in the blood after birth also
What is the scoring system used as an objective measure of perinatal adaption at birth?
This is the APGAR scoring system
What does APGAR stand for and how is it correctly scored? ie what does each letter in Apgar stand for (colour, heartbeat, reflex irritability, muscle tone, respiratory effort)
The total score is out of 10 with 0,1 or 2 given for each of the 5 componenents
- A - appearance (colour)
- P - pulse (heartbeat)
- G - grimace (reflex irritability)
- A - activity (muscle tone)
- R - respiration (respiratory effort)
What is a normal apgar score in a newborn baby?
A normal apgar score is a score of >/= 8
Describe 0,1 and 2 scoring for all the different regions of the Apgar scoring system Appearance (colour) Pulse (heartrate) Grimace (reflex irritability) Activity (muscle tone) Respiration (respiratory effort) What is acrocyanosis?
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/picture2jpg-1616FFEDF5D01B44C64.png

When is the apgar score carried out? Score of 0 means the thing you are assessing is absent score of 1 means it is kind of present State the max score of 2 for each section?
The apgar score is carried out at one minute, 5 minutes and 10 minutes after birth Appearance - no blue discolouration - baby is pink all over Pulse - pulse greater than 100bpm Grimace - baby has a strong cry/coughs well when stimulated Activty - full muscle action/flexion Respiration - strong cry, good breathing
What is the apgar score usually in infants who are non-responsive, limp and pale and in need of immediate life saving efforts?
The apgar score in these infants is usually 0-3
What is advised to keep the baby warm? When is feeding advised to start? What is the milk that the baby feeds on known as in the first 3/4 days?
Skin to skin contact is important to ensure the baby does not become hypothermic It is also advised to attempt feeding straight away with the baby - normal term infant will be able to use its own glucose and ketones for fuel as blood sugar The colostrum - rich in antiboides and proteins for the baby
What is the difference between foremilk and hindmilk? This is the normal breastmilk that the mother produces after a few days post-natal
Foremilk - high in sugar, water and proteins Hindmilk - high in fat and calories - important for the baby to fully drain milk from one breast before moving on to the other in order to access the full range of milk
Attahcment is crucial for the babies emotional development and therefore should be given skin to skin contact with the mother instantly What are the reasons for babies being relatively vitamin K deficient? What are the vast majorites of babies given at birth to combat this?
Reasons for baby being relatively vitamin K deficient - vitK crosses the placenta poorly, levels of vitK in the breast milk are poor and the gut flora has not been fully produced yet - intestinal flora usually produces vitamin K Therefore vast majority of babies are given 1mg vitK IM at birth
What are the vaccinations given to the mother during pregnancy?
Maternal pertussis vaccine and the influenza vaccine (whooping cough and flu vaccine)
What is the vaccination schedule for children? (4, 2, 3, 4, 2) Which vaccine is given to girls at age 12-13 years?
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/picture2jpg-1617022D2B84A65353D.png

What is the newborn screening test carried out at 5 days known as? What is the mnemonic i have to remember the tests?
This is Guthrie’s test Sometimes Chris Cares Poorly, Meanwhile Mhairi Is Greatly Happy
State what are the 9 things tested for in Guthrie’s test?
- Sickle cell disease - autosomal recessive
- Cystic Fibrosis - autosomal recessive
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
- Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD)
- Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
- Isovaleric acidaemia (IVA)
- Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA1)
- Homocystinuria (pyridoxine unresponsive) (HCU)
Top to toe examination is carried out by midwifery staff immediately following delivery Formal neonatal examination is a required part of health care When does the top to toe examination of the newborn generally take place?\
Generally takes place within 72 hours of birth of the newborn but usually by 24 hours
The neonatal examination is a systematic head to toe examination What are 4 main important parts in the head to toe examination of the newborn?
Red reflex of the newborn - congenital cataracts Examine the mouth carefully Examine the femoral pulse - coarctation of the aorta Hip - looking for developmental dysplasia of the hip
What is examined on the head of the head to examination?
Feel the fontanelles - anterior and posterior - identify whteher sunken or bulging Assess facial features -symmetry and eye positions The measure the occipital head circumference Check for any ventous/foreceps marks
When looking at the head, the head can present with different bulges if there is a build up of blood in different layers of the What are the layers of the scalp before discussing which layers two common swelling arise between? Which layer of the scalp is very vascular?
Skin Connective tissue Aponeurosis - epicranial aponeurosis Loose areolar connective tissue Periosteum The connective tissue layer of the scalp is very vascualr
What does the epicranial apnoeruosis exist between?
The epicranial aponeurosis is the aponoeurosis between the fronatalis and the occipitalis













