WEEK 6 END OF WEEK FORMATIVE Flashcards
(25 cards)
Which of the following is not a subtype of endometrial carcinoma? A - Endometrioid B - Choriocarcinoma C - Serous D - Clear Cell E - Mucinous
B - Choriocarcinoma
What are the different types of endometrial carcinoma?
Type 1 - Endometrioid (and mucinous) endometrial carcinoma Type 2 - Serous (and clear cell) carcinoma
Which of the following does not apply to a uterine leiomyoma? A - benign tumour of smooth muscle B - often multiple C - may present with menorrhagia D - growth is oestgoen dependent E - uncommon neoplasm
E - uncommon neoplasm
A leiomyoma, also known as fibroids, is a benign smooth muscle tumor What is a maligannt smooth muscle tumour known as?
This would be a leiomyosarcoma
Which of the following statements regarding endometriosis is true? OPTIONS: A Ovarian endometriosis is rare B The disease is more common among multiparous women C Defined as endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity D Rarely symptomatic E The risk is increased for women using oral contraceptives
A - ovarian endometriosis is rare
What are risk factors for endometriosis?
Nullparity Low BMI Early menarche/late menopause Multiparity and combined oral contraceptive have a negative association with endometriosis ie they decrease the risk of the disease occurring
Which of the following is not a germ cell neoplasm? OPTIONS: A Dysgerminoma B Teratoma C Granulosa cell tumour D Embryonal carcinoma E Yolk sac tumour
C - Granulosa cell tumour - this is a sex cord / stromal tumour
What do granulosa cell tumours produce? How may they present?
These tumours can produce oestrogens May cause precocious puberty if in a young female or Post-menopasual bleeding
What is the most common malignant primitive germ cell tumour? What electrolyte is this tumour associated with an increase in? What age group does this tumour occur in?
Dysgerminoma Associated with an increase in calcium and occurs almost exclusively in children and young adults -average age 22
Which of the following statements do not apply to an ovarian teratoma? OPTIONS: A Often contains adipose tissue B Always benign C Can include well developed teeth D May be bilateral E Can present acutely with torsion
B - always benign Mature teratomas include dermoid cysts and are generally benign. Immature teratomas may be cancerous
Which of the following muscles covers the majority of the pelvic side wall? OPTIONS: A coccygeus B levator ani C obturator internus D pirifomis E puborectalis
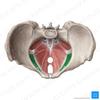
B - obturator internus The obturator internus covers the obturator membrane - can see the obturator internus laterally here Piriformis covers the posterior pelvic wall

What makes up the levator ani?
Levator ani - puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus
Lymph from the gonads drains to which of the following lymph node groups? OPTIONS: A Deep inguinal B External iliac C Inferior mesenteric D Lumbar (caval/aortic) E Superficial inguinal
D - Lumbar (caval/aortic)
What is the major advantage of MRI over CT scan for imaging the pelvis in females of reproductive age? OPTIONS: A Rapid image acquisition time B Suitable for patients with claustrophobia and pacemaker C No ionising radiation D Provides good tissue resolution on lungs, abdomen and pelvis for accurate cancer staging E Readily available as a ‘bed-side’ imaging test
C - No ionising radiation The CT is quicker for acquisition than MRI MRI cant have any metal for the scan CT provides good lung, abdo and pelvic resolution
MRI scan is far better than CT scan in depicting the local disease extent in staging of cervical cancer. Which of these features cannot be assessed on MRI of pelvis performed for staging cervical cancer? OPTIONS: A Parametrial invasion B Tumour infiltration into rectum and bladder C Extension of cancer into uterus and vagina D Distant metastases to lungs and mediastinum E Metastatic involvement of pelvic lymph nodes
D - distant metastases to lungs and mediastinum
Factors that increase the risk of developing breast cancer include all of the following except: OPTIONS: A Early menarche B Late menopause C Nulliparity D First or second trimester miscarriage E Age >30 years at time of first pregnancy
It is the increased exposure to oestogen that increases the risk of breast cancer D - first or second trimester miscarriage doesnt increase the risk of developing breast cancer
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/picture2jpgpngjpg-161D1EA2FFA5D74AD17.png

D - 25 year old with a 2cm ER negative tumour with clear surgical margins (whole breast radiotherapy) and boost
Which of the following statements regarding the menopause is FALSE? A The menopause is retrospective diagnosis which can only be made following 1 year of amenorrhoea B FSH levels should be routinely checked in all women, with a single level over 30IU/l being diagnostic of menopause C The ovaries contain a finite number of oocytes which decrease steadily until they become deplete at the time of menopause D The average age of menopause in the UK is 51 years E Peri-menopausal symptoms can begin a number of years prior to the last menstrual period
B - FSH levels should be routinely checked in all women, with a single level over 30IU/l being diagnostic of menopause
Which of the following statements regarding Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is TRUE? A Oestrogen only HRT should be given routinely to women with a uterus B The risk of breast cancer with HRT is not affected by age or duration of use C Continuous combined HRT is suitable for use in peri-menopausal women prior to their last menstrual period D The Mirena IUS can be used for up to 5 years to provide endometrial protection in conjunction with oestrogen-only HRT E All vaginal bleeding within 6 months of starting HRT should be investigated
D - the Mirena IUS can be used for up to 5 years to provide enometrial protection in conjunction with oestrogen only HRT Oestrogen only HRT can only be given to women who have had a hysterectomy Sequential combined HRT should be used in perimenopasual women
The risk of malignancy index (RMI) for calculating the likelihood of ovarian cancer is calculated according to the following OPTIONS: A CEA level x ultrasound score x menopausal score B CA125 level x ultrasound score x eGFR C CA125 level x ultrasound score x age of patient D CA125 level x ultrasound score x menopausal score E CA125 level x CT score x menopausal score
D - CA125 score x ultrasound score x menopasual score Refer when RMI >250
An ovarian mucinous cystadenoma is OPTIONS: A A malignant epithelial ovarian tumour B An ovarian germ cell tumour C A benign epithelial ovarian tumour D Likely to have metastasised from elsewhere E Unlikely to present with a pelvic mass
C - a benign epithelial ovarian tumour Cystoadencarcioma - malignant epithelial ovarian tumour (get serous, endometrioid, mucinous, clear cell and Brenner)
A fibroid uterus OPTIONS: A Cannot grow bigger than a 4 month pregnancy ( 20 weeks size, up to the umbilicus) B Is likely to be malignant C Needs to be removed surgically if causing symptoms D Usually causes severe pain and tenderness E May present with urinary urgency, frequency or incontinence
E - May present with urinary urgency, frequency or incontinence Fibroids can cause menorrhgia, and pain (red degeneration of fibroid - due to thrombosis of vessels during pregnancy) Fertility problems also
A large endometriotic ( chocolate) cyst OPTIONS: A Is usually asymptomatic B Is a type of cancer C Can present with a pelvic mass and high CA125 level D Is a type of haematoma E Will not rupture
C - can present with a pelvic mass and high CA125 level
The condition most likely to be associated with a normal CA125 level OPTIONS: A Liver disease associated with ascites B Peritonitis C Endometriosis D Uterine Leiomyoma E Ovarian cancer
D - uterine leiomyoma


