Clinical/Comm Skills - Week 5 - Managing Breastfeeding Challenges - Attachment&Position, sore/cracked nipples, engorgement, mastitis, thrush Flashcards
How long should infants be exclusively breastfed?
Infants should be exclusively breast fed up until 6 months of age to achieve optimal growth, development and health and continue up to two years of age or beyond
Why has there been a fall in breastfeeding rates?
This is due to an aggressive marketing of formula feeding Poor hospital practices - not enough breastfeeding information Better infant formulas also now exist
What is the initiative revised in 2012 by WHO and UNICEF to educate mothers on the benefits of breastfeeding?
This would be the Baby Friendly Initiative (revised 2012)
Almost all women can produce enough breastmilkand yet … Insufficient milk” is the commonest reason given for stopping breastfeeding” What are considered the two most important aspects of breast feeding by many?
This would be positioning and attachment

Good attachment is essential for effective pain free breast feeding What can poor attachment lead to?
Poor attachment can lead to: Sore nipples Engorgement Mastitis Unsettled baby as there may be insufficient milk production due to the poor attachment
How should the nipple be placed in the babies mouth?
The nipple should be at the junction between the hard and soft palate of the babys mouth
When the baby attaches to the nipple, should the babies nose or chin be indenting in the mothers breast? Should more areola be visible above the top lip or below the bottom? Should the babies cheeks be pulled in or rounded?
The baby should have a large mouthful of breast with cheeks full and rounded The chin should be indenting into the mothers breast - NOT the nose If areola visible, more should be visible above top lip

Position refers to the mother and baby positioning to ensure good feed and ample opportunity for a good attachment How should the baby be positioned?
The mother should be comfortable and well supported The babies neck should not be flexed - head neck and back in a straight line - babies windpipe/oesophagus fully patent when head is at rest
Poor attachment can lead to: Sore nipples Engorgement Lactating mastitis Lactating thrush And An unsettled baby - not a good milk supply and therefore failure to thrive How can poor attachment cause these?
Poor attachment can causes sore nipples and also cracks The sore nipples can lead to milk not being removed efficiently which can lead to engorgement and the stasis of mouth - (the stasis of mouth along with cracks provides an opportunity for bacteria to enter the breast causing mastitis) The breast-milk not being adequately removed leads to an insufficient milk supply to the baby - baby is frustrated and baby fails to gain weight and breast-milk production declines
Sore and craked nipples Causes: Poor positioning and incorrect attachment Mechanical pumping, Tearing the nipple/ areola junction Detaching the baby or pump from the breast incorrectly. What are the signs and symptoms of sore and cracked nipples?
Signs and symptoms Sore nipples May have engorgement Worse at start of feeding Red, blistered nipples Baby may vomit blood
Can see the cracked nipple due to poor attachement What are the causes of engorgement?

Delay for the first feed Poor positioning and attachment Restricted feeding Ineffective emptying Supplementing
What are the signs and symptoms of engorgement?
The breasts look shiny due to the oedema and can be painful Milk does not flow as well due to the increased pressure Breasts may be red and the mother may feverish
Engorgement occurs when normal breast fullness develops into oedema, increased lymphatic, blood supply and milk flattening nipple leading to attachment difficulties. What can engorgement frequently lead to?
Engorgement can frequently lead to an insufficient milk supply and the opportunity to have breast infections Severely engorged breasts
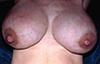
Poor management of engorgement leads to mastitis and a rise in Feedback Inhibitor of Lactation and suppression of lactation. What can be done to manage engorgement?
Express prior to feed to release the pressure in the breast Hand expressing is less painful and traumatic and warm baths or compressors are soothing and help with the expression Ensure good attachment and fully emptying one breast before moving to another Antibiotics are not helpful in engorgement and can lead to Candida infections
The causes of mastitis * plugged milk duct * breast infection * Poor positioning and attachment * Infrequent feeds * Consistent breast pressure (bra, clothing) * Dummies Supplementation * Trauma What are the signs and symptoms of mastitis?: how to differ between a blocked duct and breast infection?
Signs and symptoms Blocked duct - tender spot, redness, sore lump without fever Breast infection - tender spot, redness, sore lump wit fever Also may have nausea and vomiting Infective mastitis may have cracks, pus and bleeding
Highlight that there is a difference between a plugged duct and an infection Remember if untreated, likely that a plugged dill become infected Describe the differences?
Plugged duct * Comes on gradually with a sore lump without the mother having a fever * The breast is red but not flaming hot and usually the pain is mild, mother is generally well Infection Comes on suddenly, with breast red hot and swollen, mother has flu-like symptoms and has a fever In both - the pain is localised to the area of infection
What is the most important treatment of mastitis?
Encourage the mother to continue breastfeeding / expressing even if they are not wanting Massage and express if needed and anti-inflammatory medication
What medication for symptoms relief is usually given to the mother?
Symptom relief with NSAIDs - ibuprofen or paracetamol
Tender spot, redness, sore lump without fever – blocked duct A tender spot or lump and a low grade fever – breast infection When are antibiotics considered in mastitis?

If symptoms relief with medication + the expressing before feeds with warm bath or warm compressors fail to improve symptoms or symptoms worsen after 12-24 hours - consider antibiotics
What antibiotics are recommended in mastitis? What is second line? What is usually the causative organism?
Flucloxacillin is recommended for 7-10 days first line Clindamycin is second line if pen allergic Usually staph aureus is the causative organism
A breast abscess is a localised collection of pus which forms in an area of the breast that has no opening for drainage ands so must either be aspirated or surgically drained. It is a serious and painful;l condition that need immediate medical attention. It can be differentiated from mastitis by the more localised inflammation and the presence of a regularly-shaped lump. How is a breast abscess treated?
An abscess is a localised collection of pus which forms in an area of the breast that has no opening for drainage ands so must either be aspirated or surgically drained. The aspiration fluid is then sent for cilture and flucloxacillin is gain (obviously change if a different bacterial cause)
Lactating thrush can affect the mother or baby What are the signs of thrush in the mother?
Intense pain in the nipple or pain that does not change when changing attachment Sudden pain in breast/nipple after a long period of pain free feeding Cracks that will not heal Nipple may be red, flaky, or sensitive to touch
What are the signs of thrush in the baby?
Nappy rash Oral thrush Baby pulling off breast while feeding Baby windy, fretful or difficult to settle
This picture shows a topical candida (thrush) infection of the breast. It can be distinguished from trauma by the lack of cracks and the spread of the inflamed area, as well as by the mother’s account of the pain. What is the treatment for the mother with thrush?

For mother cream For baby oral gel Mother - miconazole 2% cream applied to nipple and areola after each feed for 7 days
What is the treatment for thrush in the baby? What age does the treatment change?
Treatment changes before and after 4 months before 4 months Miconzaole oral gel applied gently to mucosa after feeds After 4 months Nystatin oral suspension after feeds
What is the different treatment of thrush in the mother and baby?
Mother * Miconazole 2% cream applied to nipple and areola after feeds for 7 days Baby Before 4 months * Miconzole oral gel applied gently to oral mucosa after feeds After 4 months * Nystatin oral suspension after feeds


