Physical exams Flashcards
How could you begin a cardio exam?
Present yourself, General inspection (P)
Chaperone, comfort, pain? (CCP)
Remember the cat can jive
Radial pulse
Temp
Cap test
Clubbing
JVP + Hepatojugular reflex
Heaves and thrill dance
Murmurs dance
summarise = abulatory monitoring, resp exam, BP, pulse oximeter, spygmamommeter, (POS)
What to do when taking a history?
NAME, AGE, Present
What?
When?
Why?
How?
SOCRATES
BUFTASS - Blood, unintentional weight, fever, temp changes, appetite, sweating, secretions
Past conditions
Drugs - allergies
Family related
Social - work
Systems - visual changes, headache, mood, sleep, eating, waterworks, bowel movements, chest pain, breathing, movement, sensation
What should you ask in a urinary history?
Frequency
Output
Urgency
Nocturia
Dribbling
Dysuria
Blood
(at)
LUTS
Appearance
Smell
Temperature
Jendrassik’s manoeurve
Ask the patient to grit their teeth or clench their hands whilst testing reflexes.
How do you examine the thyroid?
WIPE
Permission - expose chest
Questions - lump, duration, travel
General inspection
PANTS - pulse, acropachy, nails, temperature, swearing
HOLES - hair loss, opthalmoplegia, lid retraction, exopthalmos,
TONGUE - can they stick it out. Swallow with water.
Lump - feel
Lymph nodes
Thyroid bruit listen
Stand and get out of chair with arms - proximal myopathy (hyperthyroidism)
Check shins for pre-tibial myxedma (hyperthyroidism)
Finish and thank
Further tests T4/ TSH
In what condition do you get pre-tibial myxoedma?
Hyperthyroidism
How can you assess tremor in thyroid disease?
Lay paper on hands
If the person sticks tongue out and there is movement what can that suggest?
Thyroglossal cyst
What are the stages of a vascular exam?
Introduce
General exam
Arms
Pulses
Carotids
Abdomen
Legs
Special test
What are the stages of cannulation?
Name and date of birth
WIPE
Allergies
Gather equipment: dressing, swabs, pre filled saline, gloves, needle, tourniquet
Saline flush kit
Inspect vein
Tourniquet
Sharp scratch and secure from below
Withdraw introducer
Advance cannula
Remove tourniquet
Bandage
Flush
Label
What are the tests for a diabetic foot exam?
Inspect
Toes
Redness/ rashes
Ulcers
Skin change
Texture
Erythema
Dorsum and plantar surfaces checked
Pulse
Capillary refill
Temperature
Reflexes
Special tests - monofilament, vibration, soft touch, proprioception
Walk and Foot wear
Thanks
To complete:
BM.
neurovascular assessment
advise on foot care
What are some changes seen in venous insufficiency?
Hemosiderin
Ulcers
Reverse bottle signs
Swelling
Trophic changes
What are the signs of aortic regurgitation?
De Musset Sign
Mullers sign
Corrigans collapsing pulse
Quinke sign

What are the signs of aortic stenonis?
- Slow rising carotid pulse
- Narrow pulse pressure
- Heaving, non-displaced apex beat (can be displaced if there is left ventricular hypertrophy)
- Ejection systolic murmur
- Heard best at the second intercostal space on the right
- Can be described as “harsh”
- Transmitted well to the carotids
- Soft S2 heart sound
- Ejection click may be heard in some cases (early systolic)
What is the signs of mitral stenosis?
- Mitral facies (malar flush) - cutaneous vasodilation due to carbon dioxide retention
- Low volume pulse
- Atrial fibrillation
- Elevated JVP (prominent ‘a’ wave due to raised right atrial pressure, or absent ‘a’ wave in AF)
- Tapping, non-displaced apex beat (palpable S1)
- R ventricular heave (suggestive of pulmonary hypertension)
- Inspiratory crepitations (pulmonary oedema) and other signs of right heart failure
Stages of the resp exam
Respiratory exam
- Check name and DOB
- Wash hands, introduce, position, exposure
- Inspection:, prescriptions, look (respiratory rate, accessory muscles and deformity and scars), equipment, aids, diet
- Hands: tremor, asterixis, tar staining, clubbing, sarcopenia, temperature, cap test
- Pulse: pulsus paradoxus
- Eyes: horner’s syndrome, anaemia,
- Face: pleuritic face CO2 rentention
- Mouth: tongue for cyanosis, candida infection
- JVP inspection (cor pulmonale), tracheal deviation, cricosternal distance for hyperexpanded chest
- Lymph nodes
- Scars Chest deformities (pectus excavatum or carinatum), apex beat, expansion (SAE)
- Percuss, ausculate (bell in apices and diaphragm everywhere else), tactile fremitis (PAT)
- Check for oedema legs, DVT, warm legs sacrum
- Finish exam – cardiovascular exam, PEFR, ABG, chest x ray
Stages of cardiac exam
Cardiovascular exam:
- Introduction and checking patient name and DOB
- Wash hands, introduce ‘my name is Sam, I am a third year medical student/ ‘this exam will entail me having a look and listen of your chest, but also assess other parts of your body and have a look at hands, legs), position, expose
- Comfort, chaperone, pain
- General inspection: Prescription (heart medicines/ GTN spray), look (Marfainoid, asymmetry, pacemakers, deformity, scars ), equipment, aids, scars, everything else e.g. diet nil by mouth
- Hands: Janeway lesions, splinter haemmorhages, oslers nodes, koilonychia, clubbing, cap test, quike’s sign (aortic regurg), temp,
- Pulse: slow rising (aortic stenosis), collapsing (aortic regurgitation), pulsus alternans (left ventricular impairment), brachial pulse, corrigan’s pulse, BP cuff
- Radio-radial delay or radiofemoral delay for coarcation or dissection, collapsing pulse
- Face: Demusset sign (AR), mitral facies/ stenosis. Eyes anaemia, xanthelasma, corneal arcus. Mouth for glossitis, angular chelitis, high arch palate
- JVP + hepatojugular
- Carotid assessment
- Heaves and thrills
- Apex beat
- Listen with pulse
- Accentuate leaning forward, carotids, or to left, EXPIRATION
- Check legs for oedema and sacrum
- Bibasal crackles checking
How is the peripheral arterial exam performed?
- ID
- WIPE - down to underwear, supine, the blood supply to your body
- comfort, pain, chaperone
- general inspection - GUS HASS - gangrene, ulcers, skin color, hair loss, amputation, scars, sores
- Temperature
- Capillary refill, skin changes
- Arms
- Pulses,
- Carotids
- Abdominal aorta
- Legs
- Special tests
- ABPI and conclude
What are the parts of the knee exam?
Front, side and back - bulk, erythema, cysts, scars and swellings (BECS)
Walk, walk, walk
Antalgic or trendelenburg
Together and apat
Feel 5 - at rest, bent, sweep, tap, temp
movemen - Raise, extend, flex
SLAPS - special tests, lachmanns, anterior drawer, posterior drawer, stress tests
How is the peripheral vascular exam performed/ venous supply?
- ID
- WIPE
- CCP
- Inspection - haemosiderin, ulcers, reverse bottle, lipodermatosclerosis, dermatitis
- Temperature,
- Pitting oedema
- Varicose vein insepction, long sapgenous tenderness and short sapgenous
- Sphena varix at saphenovarix junction
- Tap test - commence on ounykse
- Trendelenvyrg test
- Drainage
- Perches test
- ABPI
What are the 6 s of a thyroid exam?
- Stugmata - Inspection
- Shakes
- Sight
- Swellings
- Sounds - bruit and percussion
-
What is trendelenberg gait?
Hip drop caused by weak adbductor muscles (gluteals)

What does this show?
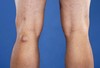
Baker’s cysts
Breast exam
Chaperone




