Clinical chemistry Flashcards
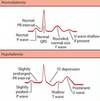
What 4 ECG changes are seen with hyperkalemia?
Tall tented T waves
Large QRS
No P waves
Sine waves

What ECG changes are seen with hypokalemia?
What are some differences between azotemia and renal AKI?
Pre-renal has low urine sodium vs renal <15 vs >40
Prerenal has urea >>creatinine
Better fluid response

Causes of renal AKI?
iSCHAEMIA
When does a GP manage CKD?
STAGE 1 - 3A
How does a specialist measure CKD?
Treat CKD?
ACR and eGFR
Stage 3b-5
IV
Less K+ DIET
Erythropoietin
Alfacaldol
Phospjhate binders

What is the main cause of hypernatremia?
Low fluid or fluid depletion
How is sodium conc calculated?
ECF Na+/ ECF water
What should always be asked of eldrely?
Are they drinking water? (dementia)
What are two causes of hyponatremia?
- Reduced sodium due to excess of water
- Reduced sodium
What is the most common cause of hyponatremia?
Bendroflumethiaze diuretics
What is the difference between SIADH and excessive drinking?

What causes hyponatremia?
Increase intake of fluid
or reduced sodium
What causes hypernatremia?
Low water intake
(elderly hyper)
What calcium drives mechanisms?
Free calcium
What can affect calcium?
Albumin conc –> more albumin reduces free calcium
ph
Low ph –> more calcium (acidity
What causes hypocalcemia?
Hypoparathyroidism
Acute pancreatitis
Magnesium (co-factor)
(EDTA)
What hydroxylation happens in kidneys
1 hydroxylation
What is pseudohypoparathyroidism?



