Unit 5 - Cerebellum (anatomy & physio lectures) Flashcards
(72 cards)
How much of the mass of the brain does it comprise
Proportion of the brain’s neurons in the cerebellum
10% mass of brain
50% of its neurons
Functions of cerebellum
- Maintenance of equilibrium (vestibular input // the vestibulocerebellum)
- Adjusting the postural muscles of the body (spinal output - spinocerebellum)
- Programming and fine tuning movements (cortical input - cerebrocerebellum)
vestibulocerebellum function
Maintenance of equilibrium
Spinocerebellum Function
Adjusting the postural muscles of the body
What can be seen on the superior surface of the cerebellum

Cerebrocerebellum function
Programming and fine tuning of movements
Name the dural folds related to the cerebellum
Falx cerebelli
Tentorium cerebelli
Name the 3 lobes of cerebellum
Anterior
Posterior
Flocculonodular
What lobes can be seen on the superior surface of the cerebellum
Anterior & posterior
What fissure separates the anterior lobe from the posterior/middle lobe
V-shaped primary fissure
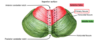
What fissure separates the middle/posterior lobe from the flocculo-nodular lobe
Posterolateral fissure

What fissure does not mark the boundary between any lobes
Horizontal fissure

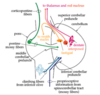
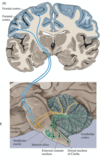
What structure is the roof of the 4th ventricle
Superior medullary velum
Name the structure found IN the 4th ventricle
Choroid plexus
(Surface can also be called the arbor vitae

What are intracerebellar nuclei
Masses of grey matter embedded in white matter of cerebellum on each side of the midline
Name the 3 intracerebellar nuclei
Fastigial (medial)
Dentate (lateral)
Interposed (= emboliform + globose)

Name the 2 nuclei that compose the interposed nucleus
Emboliform + globose
Describe the structure of the dentate nucleus
Crumpled bag shape with opening facing medially

Where do the white matter fibres of the dentate nucleus exit
Superior cerebellar peduncle
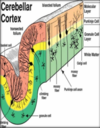
Name the 3 layers in the cerebellar cortex
Grey matter
White matter
Collection of nerve cells inside, from deep cerebellar nuclei

Distinguish between the outer, middle and inner layer of the cerebellar cortex
Outer - molecular layer (ML)
Middle - purkinje cell layer (P) - 1 cell thick
Inner - granular layer (GL)
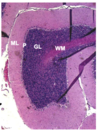
What neurons & cells are present in the outer molecular layer
2 types of NEURONS:
Outer stellate cell
Inner basket cell
Also glial cells *

Describe the contents of the middle purkinje cell layer
Large Golgi type I neurons
Flask shaped
Arranged in a SINGLE layer
Dendrites branch profusely in molecular layer
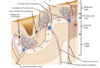
Describe the synaptic relationship between the middle purkinje cell layer and the molecular layer
Branches of purkinje axons synapse with dendrites of basket cells and stellate cells in molecular layer