Spinal Cord Flashcards
Paralysis following spinal cord injury

Where does the spinal cord begin
What is it continuous with at its origin
Begins at foramen magnum
Continuous with medulla
Diameter and length of the spinal cord
Diameter = 1-1.5cm
Length = 45cm
Hence occupies upper 2/3rd of vertebral canal of vertebral column
Where does the spinal cord terminate in
- Adults
- Children
Why does the spinal cord terminate before the vertebral column
- L1-L2 in adults
- Near L3 in young child
Rate of growth of bone (vertebral column) tissue is faster than the rate of growth of nerve tissue
Hence lumbar cistern below termination point
How the 3 meningeal layers transfer to spinal cord

What anchors the spinal cord in its position
Denticulate ligament
A continuation of pia mater
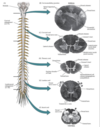
Name and indentify where there are enlargements in the spinal cord
- Cervical enlargement - origin to brachial plexus (C3-T2)
- Lumbar enlargement - origin to lumbosacral plexus (L1-S3)
Name the most inferior structure of the spinal cord
Spinal cord tapers off into CONUS MEDULLARIS

What is the cauda equina
Extension of bundle of nerve roots beyond the cord

What is the filum terminale
A prolongation of pia mater
Descends from conus medullaris to attach to coccyx (anchor)

Dissections of conus medullaris, cauda equina, meningeal layers and filum terminale

What opening do nerves pass through
Intervertebral foramina

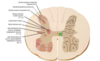
Transverse section of spinal cord

How to distinguish the dorsal (sensory) root from the ventral (motor) root
Sensory ganglia - swelling
* Dorsal root ganglion

Dorsal/posterior roots are _______
Sensory
Ventral/anterior roots are ________
Motor
How is each root attached to the cord
By a series of rootlets
What does the spinal nerve branch into
Anterior/ventral ramus
Posterior/dorsal ramus
Series of smaller branches

Transverse process of spinal cord & spinal nerve branches

What is the dermatomal map
Each spinal nerve carries sensory information for a part of the body surface
Sensation lost in 1 dermatome only when approx 3 adjacent roots have been injured, hence there is a compensatory effect

What do afferent nerve fibres do
Bring information to the spinal cord which then travels up to the brain

What do efferent nerve fibres do
send information from the spinal cord out along nerves

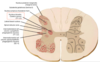
Transverse section of spinal cord
Note - grey matter is at the centre, white matter at the surface edge

What lines the central canal
Ependymal cells